S1) CVS Anatomy Flashcards
State the structure and function of the pericardium
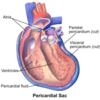
- Structure: a fibroserous sac
- Function: encloses the heart and roots of the great vessels
Identify the 2 layers of the pericardium
- Outer fibrous layer
- Inner serosal layer
Identify and describe the 2 components of the inner serosal layer in ther pericardium
- Visceral pericardium adheres to the external wall of the heart
- Parietal pericardium lines the outer fibrous layer and formed when the visceral pericardium reflects back on itself

What is the pericardial cavity and what does it do?
- The pericardial cavity is the space between the visceral and parietal layers in the pericardium
- It consists of pericardial fluid which reduces friction

Describe the anatomical position of the pericardium
The pericardium is attached to the sternum and mediastinal portions of the right and left pleura
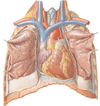
Identify the blood vessels which emanate from the pericardium superiorly and inferiorly
- Superiorly: aorta, pulmonary artery, superior vena cava
- Inferiorly: inferior vena cava

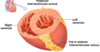
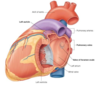
Describe the structures forming the different surfaces of the heart:
- Apex
- Base/Posterior surface
- Anterior surface
- Inferior surface
- Apex - formed by the tip of the left ventricle
- Posterior surface - formed by the atria (mainly the left)
- Anterior surface - formed by the right atrium and ventricle
- Inferior surface - formed by both ventricles (mainly the left)
Identify 2 functions of the heart valves
- Direct blood flow in a forward direction
- Prevent backward leakage
Identify the four major valves in the normal heart
- Atrioventricular valves:
I. Tricuspid valve
II. Mitral valve
- Semilunar valves:
I. Aortic valve
II. Pulmonary valve

What is the endocardium?
The endocardium is the single layer of endothelial cells that lines the surface of the heart valves and interior surface of the chambers

Identify 5 components of subendocardial tissue
- Fibroblasts
- Elastic and collagenous fibres
- Veins
- Nerves
- Branches of the conducting system
What is the myocardium?
The myocardium is the thickest layer of the heart and consists of bundles of cardiac muscle cells

What is the epicardium?
The epicardium is the outermost layer of the heart and is identical to, and just another term for, the visceral pericardium
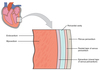
What is external to the myocardium?
External to the myocardium is a layer of connective tissue and adipose tissue through which pass the larger blood vessels and nerves that supply the heart muscle
Identify the 3 vascular structures which open into the right atrium
- Superior vena cava
- Inferior venae cava
- Coronary sinus

Describe the purpose of the vascular structures which open up into the right atrium
- Venae cavae return deoxygenated blood from the systemic veins
- Coronary sinus return deoxygenated blood from the cardiac veins
What is found on the floor of the right atrium?
Tricuspid valve – opens into the right ventricle
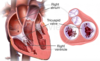
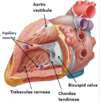
How does the right ventricle get its sponge-like appearance?
The right ventricle is covered by a number of irregular bridges (trabeculae carneae)

How does the right ventricle help to prevent the tricuspid valve opening during systole?
- The right ventricle contains three papillary muscles, which project into the chamber via their heart tendons (chordae tendineae)
- They attach to the edges of the tricuspid valve leaflets & contract to prevent the back-flow of blood
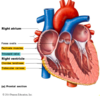
What is found at the apex of the right ventricular outflow tract?
Pulmonary valve – leads to the pulmonary artery

Which vascular structures open into the left atrium?
Four pulmonary veins
What is found in the inferior wall of the left atrium?
Mitral valve – opens into the left ventricle