S1) Anatomy of the Respiratory System Flashcards
How does the respiratory system develop?
- Develops as a ‘diverticulum’ from the pharynx on the anterior side of the primitive gut tube.
- This elongates, bifurcates and branches to form the respiratory system

Identify 5 functions of the nasal cavity
- Induce turbulent flow (nasal conchae)
- Warm and moisten inspired air
- Recover water from expired air
- Speech production (phonation)
- Olfaction

Briefly describe the purpose of the paranasal sinuses
Complement the function of the nasal cavity

What are the three divisions of the pharynx?
- Nasopharynx
- Oropharynx
- Laryngopharynx

Explain the relationship between the pharynx and larynx
The pharynx and larynx work together to ensure that food and air enter the oesophagus and trachea respectively

How does the larynx protect the airway during swallowing?
The epiglottis is a flap made of elastic cartilage attached to the entrance of the larynx which projects obliquely upwards to prevent the aspiration of food/liquids during swallowing

Identify the 6 structures in the conducting zone of the respiratory system
- Trachea
- Primary (main) bronchi
- Secondary (lobar) bronchi
- Tertiary (segmental) bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Terminal bronchioles

Identify the 3 structures in the respiratory zone of the respiratory system
- Respiratory bronchiole
- Alveolar duct
- Alveolus

Identify 2 functions of the cartilage in the trachea
- Keeps airway open (patency)
- Enables movement during breathing
Why is the tracheal cartilage C-shaped?
The cartilage opens at the esophagus and is replaced by connective tissue and muscle allowing the bolus to press against the trachea and be swallowed easily

Which parts of the body do the superior and inferior thoracic aperture communicate with respectively?
- Superior thoracic aperture communicates with the neck
- Inferior thoracic aperture communicates with the abdomen

Which specific nerves innervate the diaphragm?
Left and right phrenic nerves

Which segment of the nervous system innervates the diaphragm?
The diaphragm is a somatically innervated skeletal muscle (voluntary control)
How do we ventilate the lungs?
- Increase the volume of the thoracic cavity
- Reducing the alveolar pressure
What are the three layers of intercostal muscles connecting the ribs together?
- External intercostal muscle
- Internal intercostal muscle
- Innermost intercostal muscle

What is the primary function of the external intercostals?
Assist inhalation
Internal intercostals are antagonists to external intercostals.
Thus, state their function
Assists exhalation (especially forced exhalation)
What is the location of the main neurovascular bundle for the intercostals?
Below the rib, hence entry during pleural aspiration or insertion of chest drain is always made above the rib
Which three structures pass through the diaphragm?
- Vena Cava
- Oesophagus
- Aorta

At what vertebral levels do the three structures pass through the diaphragm?
- Vena cava (T8)
- Aortic hiatus (T12)
- Oesophagus (T10)
Levels correspond to the number of letters in each structure

What are the components of the intercostal neurovascular bundle?
- Intercostal nerve
- Intercostal vein
- Intercostal artery

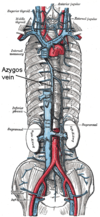
What is the azygos vein and what does it do?
The azygos vein is a vein running up the side of the thoracic vertebral column draining itself towards the superior vena cava.
What are the articulating points of the rib cage?
- The ribs articulate with the vertebral column posteriorly
- The ribs terminate anteriorly as cartilage (costal cartilage)

The typical rib consists of three components.
Identify them
- Head
- Neck
- Body






















