Roman Republic Flashcards

Temple of Portunus
Rome
150 BCE
Close to cattle martket, Tiber River (commercial implications)
Made from stone - didn’t have marble
Columns = limestone covered in plaster
Columns built into wall for decorative purpose (half, or engaged)
Hybrid: Greek/Etruscan temple

Porticus Aemilia
Rome
193-174 BCE
Warehouse - system for food delivery
New building style - series of barrel vault or arch
Used scaffolding, poured concrete
Revolutionizes how things are built
150 feet length

Sanctuary of Fortuna Primigenia
Palestrina
80 BCE
Goddess of luck, predicted people’s future, popular with sailors/travelling merchants
Higher up = holier - communicate with gods
Tourist attraction - terraces where people can buy goods

Altar of Domitius Ahenobarbus
Reliefs of Wedding procession of Neptune and Amphitrite, and Census and sacrifice to Mars
100 BCE
Hellenistic style - shows action
Sides 1-3: honors sea gods, Neptune, triton, sea horse w/ cupid
Side 4: very different, shows history not mythology
Census, sacrifice to Mars (war god)

Versistic portraits of Roman men
1st c BCE
Veris = truth
shows real people (w/ wrinkles, no hair, etc)
origin of portraiture: honors life of accomplishments, realistic, always old men, praised endurance, dignity, wisdom

Aulus Metellus
90 BCE
Bronze statue
High Roman official, speaks Etruscan
Found near Perusia (Etruscan City)
Shows him giving speech - called Orator
Not as sophisticated as Greek statues

Victorius General from Tivoli
75-50 BCE
Roman general - clothed, nudity not heroic
Head = individual, has Roman qualities
Body = hero, exceptional
characteristic of the end of republic
Arch, Barrel Vault & Concrete
Concrete = Roman invention 3rd c BCE
Lime, water, sand, rubble/aggragate
Build mold, line it, pour concrete
Walls no longer have to be straight
Use scaffolding to build barrel vaults or arches
Revolutionizes how things are built
Italic, Plebeian or Popular Tradition
Plebian style refers to lower class, used to describe simple, clear message in art
Class distinctions aren’t accurate (commissioned by high officials)
Terms refer to a style where meanings are inherent = portraiture
Verism
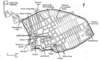
City stated out with square, not well planned
Then made grid streets
Ruts worn into cobblestones show most streets were one-way
Building around forum don’t line up
Forum built ad hoc = one building at a time
Each building is a gift - wealthy expected to contribute to infrastructure

Basilica
Pompeii
150 BCE
Trials, political assembly, auctions, open business space
Platform for speaker
Columns inside organize space and support roof, made of brick, stuccoed to look fluted
Columns also built into wall (1/2)

Amphitheater
Pompeii
80 BCE
Far from center or square, holds more people than city
Used city walls to help support it
Two city magistrates built for Spectacula (spectacles)
First permanent place for gladitorial combat/animal fights

Brawl in Pompeii Amphitheater
Fresco painting
79-60 BCE
Sports rivalry + drinking = riots, many injured/killed
Rome punished Pompeii by closing games 10 years

Stabian Baths
80-70 BCE
First bath to have running, heated water
Hot, warm, cold rooms + swimming pool, hot room
Women had hairdressers, massages, private baths
Nave and aisles
Central aisle in Church or Basilica, rectangular
Aisles run parallel on each side of nave
Clerestory
Series of windows in the upper nave, choir and transepts of a large church
Hypocausts
a hollow space under the floor of an ancient Roman building, into which hot air was sent for heating a room or bath

Roman Atrium House
Public display

House of Sallust
100 BCE
First or Masonry style
Covered concrete, carved into it and painted to look like fancy cut stone/marble

House of the Griffins
Rome
80-40 BCE
Second style (illusionistic)
Walls divided into 3 sections
Painted 3D columns, cast shadows - project from wall

Villa at Oplontis
40 BCE
Second style
Make flat wall 3D with columns, door with stairs
Shows courtyard scene to make space grand
Floors sometimes illusionistic “unswept floor” mosaic

Odyssey Landscapes
Rome
50-40 BCE
Second style - unusual
Focus is landscape and scenes from the Odyssey
Shows atmospheric perspective

Villa of Mysteries
40 BCE
Second style - unusual
Read painted room clockwise
Almost life-like figures, real and mythological
Followers of Dionysus - shown reclining into woman’s lap, could be mother or woman he saved
God of rebirth - maybe shown predicting future






