R.K.Al-Dadah Flashcards
What are the relative merits of gas turbines and stream turbines?

What is combinded heat and power?
Schemes which combine electrical generation with heat for space heating and / or specific industrial processes are referred to as Combined Heat and Power (CHP) .

What are the advantages of CHP?
- Efficient use of fuel resources by recovering about two thirds of the wasted heat.
- Improved national energy efficiency and the preservation of non-renewable energy resources.
- Reduction in environmental pollution - more efficient conversion of less fuel.
- Local generation of electricity and the reduction of the cost of transportation of electricity.
- Investment in industry - investing in city based CHP schemes increases jobs availability in the city and the country on overall.
What is the heat to power ratio?
The ratio of heat energy to electrical energy produced.
What is the back pressure arrangement for the steam turbine CHP system?
For the back-pressure type, the condenser pressure is controlled according to the heat / power ratio. The higher the heat demand, the higher the condenser pressure required to supply the heat needed. But this will be on the account of the power generated.
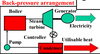
What is the ideal heat to power ratio of the back pressure CHP system?
9:1
What is a prime mover?
Prime mover” is a technical term of art in science and engineering meaning any machine (or component of a machine) that converts energy from a source energy into mechanical energy (shaft power)
How does the pass out arrangment work for CHP steam turbine systems?
For passout type arrangement, the heat is supplied by a proportion of steam bled out of the turbine at intermediate stage through the expansion process

What is the ideal heat to power ratio of the passout arrangment of a CHP steam turbine system?
3:1
What is the ideal heat to power ratio for a gas turbine CHP system?
3:1
What is the ideal heat to power ratio for a large diesel engine?
1:1
What is the ideal heat to power ratio of a small IC engine CHP system?
2:1
What is a tri generation system?

How does absorption cooling work?

How should wind turbines be spaced?

What is a vertical axis wind turbine?

What is the velocity distribution of air as it goes through a wind turbine?
Velocity of air at outlet from the slipstream is smaller than velocity at inlet, but velocities immediately upstream and immediately downstream of the turbine rotor are the same.
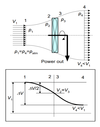
What is the pressure distribution of air as it goes through a wind turbine?

What is Betzs law?
• As the wind turbine extracts energy from the air flow, the air is slowed down, which causes it to spread out and diverts it around the wind turbine to some extent. Albert Betz, a German physicist, determined in 1919 (see Betz’ law) that a wind turbine can extract at most 59% of the energy that would otherwise flow through the turbine’s cross section. The Betz limit applies regardless of the design of the turbine
What is the interferance factor?
a=(v1-v2)/v1
What is the maximum power in the air that goes through a wind turbine?
Pmax=0.5*mflow rate*V2
Pmax=0.5*ρ*A*V3
How do you find the energy extracted by a wind turbine?
Pextracted=KEin-KEout
=0.5*mflow rate*V12-0.5*mflow rate*V42
=ρA2V2*0.5*(V12-V42)
What is the efficiency of a wind turbine in terms of the interferance factor?
η=4a(1-a)2
What interferance factor gives the greatest wind turbine efficiency?
1/3
What are some of the advantages of nuclear power?
- Nuclear power costs about the same as coal, so it’s not expensive to make.
- Does not produce smoke or carbon dioxide
- Produces huge amounts of energy from small amounts of fuel.
- Produces small amounts of waste.
- Nuclear power is reliable.
What can cause a nucleus to be unstable?
Having too many or too few neutrons and having too much energy.
what are the units of the decay constant?
s^-1
what is the decay constant a measure of?
The probability that an individual nucleus will decay in one second.
What is the half life?
The average time it takes for the number of undecayed atoms is halve.
What is mass defect?
The difference between the total mass of a particle and the sum of the masses of the constituent parts.
The mass gets lossed as energy emitted when they bond.
What is the binding energy?
The energy needed to separate all of the nucleons in a nucleus.
How large is the Mev?
1.6 X 10^-13 joules.
Why does nuclear fusion release energy?
Combining small nuclei increases the binding energy per nucleon meaning energy is released.










