Rheumatoid Arthritis Drugs Flashcards
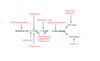
Pathway of autoimmune disease (immunology)
Macrophage/Dendritic Cell takes up self-protein –> presents to Tcell –> Tcell recognizes self protein –> presents to B cells to make autoantibodies –> destroy self cells

Types of Drugs for Arthritis
NSAIDs
Nonbiological Disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
Biological DMARDs
Nonbiological DMARDs
- Methotrexate
- Hydroxychloroquine
- Leflunomide
- Sulfasalazine
- Gold
- Azathioprine
- Cyclosporine
Methotrexate works as _____________
(mechanism)
•Works as an anti-folate
–Blocks dihydrofolate reductase
- Step necessary to activate folic acid (folate) to participate in 1 carbon donor actions
- Results in inhibition of both pyrimidine and purine synthesis
- Most notably prevents conversion of uridine to thymidine
Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) mechanism
- Prevents acidification of macrophage cytosol
- Probably major site of action is on Toll-like receptor 9 on the dendritic (antigen presenting) cell (suppressing it)
Antimalarial
Leflunomide (Arava)
•Inhibits pyrimidine synthesis
–Blocks ororate pathway
–Primarily affects T cells and potentially B cells
Sulfasalazine (azulfidine)
•Metabolized in colon to active substances
–Sulfapyridine, a free radical scavenger
–5 amino-salicylic acid, a cyclooxygenase antagonists
•Not absorbed well from gut but effectively prevents progression of arthritis
Tends to be more toxic
Gold
- Suppresses phagocytosis by macrophages
- Also can suppress development of T cells
- Not a clear mechanism
- Least tolerated of all DMARD’s because of side effects
Azathioprine (Imuran)
•Purine analog used to block DNA synthesis
–Primary mechanism of action appears to be on T cell
Cyclosporine (Sandimmune)
- Immunosuppressant used to control transplant rejection
- Inhibitor of calcineurin
- Major site of action in arthritis is T cell
Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitors
- Etanercept (enbrel), Inflixumab (remicade) and Adalimumab (humira) (also golimumab & certolizumab)
- These are immunosupressants, so they increase infection risk
Injected
Interlukin 1 receptor antagonist
Anakinra (kineret)
Infrequently used
CD 20 binder
Rituximab (Rituxan) inds CD20 on B cell
Suppresses B cell activity –> reduce antibodies
Immunosuppressant
CD 80 Binding agent
•Abatacept (Orencia) binds to CD80 on T cell preventing its activation
folate metabolism inhibitor (T & B cell)
Methotrexate
•inhibits macrophages, maybe TLR9 in dendritic cells
Hydroxychloroquine
Pyrimidine synthesis inhibitor in T cells
Leflunomide
•- Inhibits COX & scavenges free radicals (antigen presenting cells & T cells)
Sulfasalazine
•reduces macrophage phagocytosis and affects antigen presenting cells & T cells
Gold
•Blocks DNA synthesis, primary site of action T cell
Azathioprine
•Calcineurin inhibitor to inhibit T cell activation
Cyclosporine
•Block TNF action
Etanercept, Inflixumab
•Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist
Anakinra
•Blocks T cell activation by antigen presenting cell (CD 80)
Abatacept
Blocks B cell activation (CD20)
Rituxumab
Where everything works? (Draw picture)