Rheum Flashcards
two specific circumstances where methotrexate is commonly used
RA, its usualyl a first line drug
SLE when there is significant arthritis
Systemic lupus erythematosus description
an inflammatory autoimmune disease typically affecting women caused by antinuclear antibodies that leads to trapped antigen complexes in blood vessels
SLE therapy
NSAID
depends on symptms
NSAIDs for joint pain
hydroxychloroquine for joint pain, rash, fatigue
steroids for arthritis, serositis, major organ involvement
methotrextate for arthritis
leflunomide arthritis, rash, major organ involvement
angiogram findings with polyarteriris
multiple anuerysms with tapered narrow and skip areas
diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis
Elevated ESR
normochromic, normocytic anemia
hyperuricemia with significant skin involvement
normal rheumatoid factor
pencil cup deformitity at the PIP on xray
SLE therapy
steroids
steroids for arthritis, serositis, major organ involvement
fibrocartiliaginous joints
synarthrosis with limited movement
ankylosing spondylitis clinical presentation
limited ROM in the lumbar spine, hips, shoulder
synovitis in the knees, achilles, plantar fascia
up to 25% will have anterior uveitis
pain and stiffness that lasts for hours and is made better with activity

uveitis
what is this and what causes it

chondrocalcinosis
gout or arthritis
Dx of fibromyalgia
clinical presentation
exclusion of other factors (hypothyroid, hep c, vitamind D deficiency)
PE findgs for psoriatic arthritis
dactlyitis
enthesitis
skin lesions
nail dystrophy/pitting
sacroilitis
why are eye or pulmonary involvement or vasculitis common in RA
b ecause RA is an inflammatory systemic disease
top three treatment for myositis
steroids
methotrexate
azathioprine
management of OA
medication, rest, exercise, diet, surgery, aids
biologics defined for RA
genetically engineered molecules that work on specific targets
splinter hemorrhages
cause
vertical hemorrhages under the nails
can be caused by vasculitis or bacterial endocarditis
GI protective strategies for NSAIDs
cox 2 nsaid
nsaid with PPI
nsaid with misprostol
nsaid with H2 blocker
radiographic findings associated with OA
narrowed joint space, osteophytes, subarticular cysts
proteoglycans
glucosamine and chondriotin
Dx of giant cell arteritis
elevated ESR and CRP
most patients will have normochromic normocytic anemia with thrombocytosis
temporal artery biopsy that shows thickening
patient presents with a gout flare up and they are curently not on allopurinol
should you start it?
what if they are in a flare up and on allopurinol
no, don’t start it during an acute flaire
no, don’t stop it during a flare if you are already on it
Rhabdomyolysis
a syndrome of acute necrosis of skeletal muscle indicated by myoglobinuria and elevated creatine kinase
T/F the risk of CVD in patients with RA is the same as with diabetes
treu
Takayasu’s arteritis clinical presentation
fatigue, fever, weight loos
vascular damage
GI involvement with PSS
esophagitis
distal motor function
small bowel and colon hypomobility with malabsorption and psuedo obstruction

saddlenose deformity
two distinctive features of Lupus rash
usually involves face and hands and gets worse with sun exposure
Osteoarthritis defined
a degenerative disorder of the joints that produces minimal articular inflammation and no systemic symptoms
skin changes assocaited with limited sclerodactyl
early diffuse fingers welling
slow progression
involves hands below wrists and mouth
telangectasias common
subcutaneous calcium present see a the sights of trauma
renal conditions associated with PSS
major cause of death if untreated
more likly to be in patients with friction rubs, rapid progression, no raynauds
requires BP monitoring and poss treatment with ACE inhibitors
what is the age and gender bias of systemic lupus
female to male 8:1
usually between 20-50 but can be any age and usuallly more mild in elderly
pathogenesis of SLE
excessive helper T activity with low suppressor T leading to prolferation of B cellls and autoantibody production
ankylosing spondylitis treatment
exercise and physical activty
NSAIDs
TNF inhibitors
why is acute gout not treated with allopurinol
it can precipitate episodes by blocking urate pathways
only used for chronic gout
four types of spondyloparhtopathies
ankylosing spondylitis
psoriatic arthetis
reactive arthritis
arthritis from IBD
septic arthritis (gonococcal) signs and symptoms
prodromal migratory poly arthraligias
tenosynovitis
purulent monoarthritis
skin lesion
why is rapid treatment of Granulomatosis with polyangiitis important
because one renal involvement starts it progresses quickly
renal involvement owith polyerarteritis
segmental necrotizing glomerulonephritis
osteoarthritits clinical presentation
decreased ROM
crepitus
pain in the morning that goes away in 15 minutes then come back
tends to effect load bearing joints
safety issues associated with TNF vlockers
adminstration reactions
opportunistic infections
malignancy
demyelination
hematologic abnormalities
congestive heart failure
lupus like symptoms
what will hapen to compliment during active lupus
C3 and C4 will be decreased because you have a lot of cell death
therpay for polyarteritis
steroids, cyclophosphamide
calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)(pseudogout) clinical presentation
painful inflammation similar to gout (red, swollen, hot, tender)
differentiate between fibromyalgia and RA
FM has trigger points and an absence of articular pathology
polymyalgia rheumatica clinical presentation
stiffness in the shoulder worse after rest and in the AM
usually bilateral, proximal, and symmetrical
systemic symptoms
most often presents in women
heliotrope rash
typical distribution
a rash indicative of dematomyositis
usually in shawl type pattern over the chest and eyes (places exposed to sunlight)
syndesmophytes
calcification of ligaments see in ankylosing spondylitis
what two features do scleroderma and crest have in common
raynauds phenomena and positive ANA
FANA test
fluorescent ANA
what percent of people with SLE have APA
how many have APA syndrome
30-40%
less
Direct Coombs
hemolytic anema
are narcotics generally effective for managing PFS
no, PFS is neuropathic pain that nacrotics don’t work well on
blood work associated with myositis
elvated CPK, serum aldolase, sgot
key indicator of diffuse proliferative glomerular nephritis
sudden jump in BP
T/F antiphospholipid antibody syndrome may exist without SLE
true, 5% of people have low level APA
differentiate between radiographic finds of gout and RA
they will both have bite out lesions but gout will have less joint narrowing and speculed appearance
key for RA treatment
goal
early and aggresive treatment
put patient in remission
reactive arthritis clinical presentation
urethritis, conjuctivitis, oligoarthritis, mucous ulcers in conjuction with an STI or gastroenteritis
often effects large joints of the lower body
causes of OA
physical stress
abnormal healing after injury
biochemical/genetic factors
normal components of a joint
water
cartillage
bone
muscle
ligaments
nerves
vasculature
osteonecrosis
bone death that can be associated with corticosteroid use and SLE, among other things
five clincal presentation of psoriatic arthritis
- symmetrical polyarthritis like RA with usually fewer joints
- oligoarticular form that leads to significant destruction of joints
- assymetric for that affects the DIP and leads to nail deformities (pitting, onycholysis)
- arthriris mutilans
- spondylitc form with sacroiliitis and spondylosis
treatment of sjogrens
salagen/evogen
tear duct ablation
plaquenil
nsaids
raynauds associated with limited scleroderma
always presents, usually years before skin changes
incolves all the fingers
calcium channel blocker can be effective to control vasospasm
dactylitis
swelling “sausage fingers” that are assocaited with recative arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and psoriatic arthitis
explain cox 2 and cox 1 in respect to NSAIDs
cox 2 is an inducible enzyme that acts on inflammatory sites, inhibition of this will increase the function of NSAIDs
how is gout DX
negatively birefringent needle shaped crystals
differiate between scleritis and conjuctivitis
scleritis wil go all the way to the iris
diagnosis of sjogrens
positive schirmer test
postive rose bengal stain
abnormal salivary gland or lip biopsy
positve RA or ANA or SSA/SSB
levamisole associated purpura
vasculitis caused by tainted cocaine that presents as retiform purpura and cutaneous necrosis over the ears, extremities, and cheeks
three functionsof disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
reduces symptoms and signs of RA
reduce functional disability
retard radiographc progression
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis treatment
initial induction of remission with rituxumab or cyclophosphamide with corticosteroids
maintenance
juxaarticular erosion
a classic xray sign of RA cuased by the synovium wrapping around the adjacent edges of bone
differentiate between crest and scleroderma
sclereoderma is wide spread especially over the trunk and is much less common
Crest is just the face, neck, and distal extremities and is much more common
pulmonary involvement wth PSS
restrictive pulmonary fibrosis
usually bibasilar in the lungs
if there is an inflammatory component it may response to cyclophosphamide
usually indicated by a gigh SCL 70
treatment for acute gout
colchicine
NSADs (indocin)
steroids
nutrition
septic arthritis (gonococcal) Dx
high leukocyte count in the synovial fluid
positive gonorrhea cultures in the urethral, throat, cervix, or rectum
good response to IV antibiotics
Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA) tests for
wegeners, almost 100% specific
neuro conditions associaed with lupus
headaches
sz
coma
psych
symptoms of RA
morning stiffness greater than 1 hour
diffuse fatigue and aching
subcutaneous nodules
eye involvement
pulmonary involvement
vasculitis
knee problems that commonly effect the knee
anserine bursitis
prepatellar bursitis
baker’s cyst
chondromalacia patella
OA
why can ESR be misleading when diagnosing arthritis
what about rheumatoid factor
ESR will go up with age, up to 1/2 their age
rheum factor will also go up
differentiate between pleural effusion caused by RA and heart failure
RA effusion will have more protein
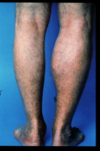
swelling of the synovial sack of the knee
three types of crystal arthritis
gout
pseudogout
hydroxyapatite
why is using colchincine and allopurinol in gout treatment a good idea
colchincine is stopping crystal formation why allopurinal decreases uricemia
age and gender bias of scleroderma
3-4x more common in women, typically onset 30-50
Microscopic polyangitis Dx
ANCA positive
microscopic hematuria
proteinuria
red blood cell casts
segemental necrotizing glomerulonephritis
polymyalgia rheumatica Dx
Clinical presentation without any other explanation
ESR markedly elevated
temporal artery biopsy if suspected GCA
acute bacterial arthritis
Dx
is xray useful
aspriation of synovial fluid with a leukocyte count greater than 2000/mcL, usuallyl over 50,000 mcL
it can help exclude gout due to lack of crystals, but joint aspriation is best
ANA Profile (patterns)
DS DNA
antihistone
anticentromere
anti SCL
SLE (homogeneous, Rim)
drug induced SLE (homogeneous, rim)
Crest
PSS (nucleolar)
primary and secondary indications of sjogren’s syndrome
primary: dry eyes, mouth, common in older women
secondary: associated to another connective tissue disease (lupus, scleroderma, etc)
what is needed before a diagnosis for fibromyalgia can be made
other conditions with suggestive history need to be excluded
most patients with lupus present with what three things
less common signs
fatigue, rash, joint pain
renal, neuro, hematological disorders
diarthroidal joints
synovial joint
Antiphospholipid syndrome DX
venous and arterial occlusions
positive ANA with no features of SLE
repeated SAB
Vectra DA
Ra
gottrons papules
discrete red papules found over the knuckles of people with juvenile dermatomyositis
T/F inflammatory joint disease tend to have stiffness in the morning that quickly goes away
false, that is more typically osteoarthritis
what type of drug is Hydroxychloroquine (plaquenil)
conditions it is used to treat
DMARD
RA, cutaneous and systemic lupus, scleroderma and CREST, sjogrens
What makes TNF blockers a risky treatment for people who have been exposed to TB
what can you do to combat this
what is alternative treatment
usually reactive of latent TB
PPD yearly, CXR area with fungal disease
MTX with isoniazid
heberdens nodes
hard bony swellings of the DIP common in osteoartritis
what is a typical cause of early onset OA
abnormal type II collagen
conditions associated with uveitis
granulamatosus
spondyloarthtitis
behcet disease
why is it useful to add control points when looking for trigger points for PFS
to rule out a significant psychological issue
possible enviromental triggers of scleroderma
vinyl chloride
contaminated tryptophan
trichlorethylene
silicone
epoxy resin
lab monitoring for methotrexate
baseline CBC with platelets, liver enzymes, renal function, CXR
maintenance CBC (8-12 weeks), liver enzymes (4-8), renal function every 6 momths

raynauds
first choice drug for RA
what is an important supplement with this
methotrexate
inclusion of folic acid to decrease toxicity rate
Sjogren syndrome is strongly correlated with what
increased incidence of lymphoma

giant cell arterities
describe Granulomatosis with polyangiitis
a type of vasculitis that causes dysfunction in the respiratory tract and glomerulonephritis caused by vasculitis, granulomatous inflammation, and necrosis
aggrivating factors for PFM
cold or humid
poor sleep
physical/mental fatigue
excess physical activity
lack of exercise
stress
ESR tests for
>100 might indicate what
how to get the upper limit lab value
OA vs RA
PMR, GCA, Wgeners
divide age by 2
limb changes associated with Kawasaki disease
edema, desquamtion, erythema of the palms and soles, induration of the hands and feet
fibromyalgia symptoms
point tenderness
fatigue
stiffness
anxiety
headaches
irritable bowel
parethesia
acute bacterial arthritis
defined
acute monoarticular arthritis usually seen in weight bearing joints that have previous joint injuries or injections
Dx of polymyositis
elevated muscle enzymes and aldolase
myopathic inflammation on biopsy
why is plaquenil useful in RA treatment
can be combined with other drugs
minimal side effects other than occasional GI
+5yrs has small risk of retinal toxicity
drug monitoring for NSAID use
annual monitoring for hepatic and renal function
annual monitoring of CBC
clinical presentation of fibromyalgia
nonarticular muscloskeletal pain
fatigue
sleep distrubance
trigger points
for at least three months
indicators of a prognosis in RA
reduced function
early xray changes
more joints
age
high rheumatoid factor
prolonged high ESR
treatment for wegener’s granulomatosus
steroids
cyclophosphamide
methotraxate
rituximab
what causes anemia in RA
hepcidin is elevated preventing iron from being made into HgB leading to anemia
scleritis
inflmmatory condition of the sclera associated with RA, vasculitis, granulomatosus, and henoch schonlein purpura
two specific uses for Hydroxychloroquine (plaquenil)
in RA as mild treatment or combination therapy
SLE to help with joint pain, rash, fatigue, and combination therapy with steroids for flares
other organs affected by polymyositis
joint, lungs, heart, GI
age and gender bias with polyarteritis
usually fatal, more common in men
ABx treatment for infectious arthritis
nafcillin + mysin (only 3 days due to ototoxicity)
ancef
vancomycin
may need debridment
how is cuteneous lupus diagnosed
where will you usuallly see lesions
does it scar?
DX by skin biopsy because ANA is usually negative
face, scalp, arms, upperchest
it can
muscle biospy findings associted with myositis
perivascular infiltrate of inflammatory cells
used to rule out inclusion body myositis
what is a definitive test for RA
CCP test, if its high you have RA
T/F 90% of drug included lupus will go away
common causes
what is the common presentation
true
progainamide, isoniazid, TNF blockers
inflammation of serous membranes (pericarditis, peritonitis, etc)
two less frequent systems affected by wegeners
skin (nodules, palpable purpura, ulcerations)
arthritis
telangiectasias
red spidery veins commonly seen on the nose, mouth, and chin; part of CREST syndrome
ESR >100 means what likely conditions
GCA
wegeners granulomatosus
lymphoma
mets to bone
what is this
what is the prognosis
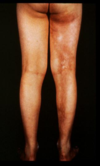
a type of limited scleroderma know as morphea
generally it has very good outcomes
musculoskeletal conditions associated with limited scleroderma
polyarthralgias common but not very inflammatory
no fricition rubs
mostly confined to hands
lower respiratory conditions associated with wegener’s granulomatosus
SOB, hemopytsis, cavitating lesions, tracheal lesions
ANA Profile (patterns)
Sm (smith)
SSA
SSB
RNP
SLE, UCTD (speckled)
Sjogrens, SLE (speckled)
Sjogrens (speckled)
UCTD, SLE (speckled)
podagra
gout attacking the first MTP joint of the foot
dactylitis
swollen fingers
osteoarthritis treatment
weight loss
exercise
nsaids
joint injections (steroid or synovial fluid)
joint replacement
ankylosing spondylitis Dx
Elevated ESR and CRP
HLA-B27 +
sacroilitis and bamboo spine on radiograph
most common bacteria causing infectious arthritis
staph, strep, gram negative bacilli
Systemic lupus erythematosus treatment
exercise
sunblock
NSAIDs
antimalarials
topical or oral steroids
MTX
Rheumatoid factor (RF) test for
what might increase RF without underlying pathology
inflammation, COPD, HCV, Lupus
age
secondary raynauds can be caused by what rheumatic disease
scleroderma
SLE
polymoysitis
sjogren
vasculitis
why would you test someone who SLE for APA
when they present with some kind of clotting probelm
calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)(pseudogout) Dx
CPPD crystals in joint fluid (positively bifringent)
fine, linear calcifications on xray
where is synovitis usually found with Lupus
similar to RA, small joints of the hands and feet
relationships between raynauds and PSS
usually present first with skin changes to follow
increased risk of gangrene or infarct
usually seen at 1 or 2 fingers
those who don’t have it have worse surivival
Sjogren syndrome treatment
keeping the eyes/mouth/vagina moist
pilocarpine can increase saliva flow
cyclosprine for eye symptoms
labs to monitor the progression of SLE
smith antigen antibodies
double stranded DNA antigens
depressed compliment
clinical factors associated with gout
more than on acute arthritis attack
development of maximal inflammation within 1 day
monoarticular arthritis
painful or swollen joint
erythema
suspected tophus
hyperuricemia
subcortical cysts without erosions
psychological management of PFS
stress management
biofeedback
relaxation
group/individual therapy
negative findings on PE for PFS
positive
muscle weakness, neurological exam, joint exam
trigger points, mild swelling, skin tenderness on pinch, hyperemia of skin
differentiate between GI involvement with limited vs PSS
uncommon to have lower GI involvement in limited
commonly has biliary cirrhossi
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis clinical presentation
usually presents with upper and lower respiratory symptoms with glomerulonephritis that takes place over 4-12 months
T/F low dose aspirin is bad for gout
true, it can exacerbate but high dose aspirin is a useful therapy
CXR findings associated with wegener’s granulomatosus
lung biopsy
nodules and cavititing infiltrate
necrotizing granulomatous process
giant cell arteritis treatment
should you wiat for biopsy before treatment
immediate high dose steroids with a 1-2 month duration
no
drugs for PFS
tricyclic antidepressants
muscle relaxers
SSRI
SNRI
antianxiolytics
gabapentin
tramadol
narcotics
types of uveitis
how do you differentiate
anterior, intermediate/posterior
anterior will have redness and dilated cillary vessels that go right up to the iris
posterior will have more vision defects (blurred vision, floaters0
what is the only condition that is treated with indomethacin
gout and pseudogout
polymyalgia rheumatica treatment
low dose corticosteroids for up to one year
treatment of psoriatic arthritis
NSAIDs work for mild cases
methotrexate, biologic DMARDS, TNF inhibitors for severe cases
surgery for end stage arthropathy
corticosteroids and antimalarials should be avoided
C-Reactive Protein tests for
what can confound the results
general marker for inflammation (RA, PMR) that is more specific than ESR
truncal obestity
antiphospholipid syndrome clinical presentation
thrombosis
SAB
rheumatoid arthritis clinical presentation
morning stiffness that take hours to go away
symmetrical poly arthritis that tends to effect the small joints
subcutaneous nodules
dry mucous membranes
scleritis
gender and age bias of PMR
what is it associiated with
over 50
women more than men
associated with giant cell arteriris
clinical presentation of giant cell arteritis
elderly patient
unilateral headache
scalp tenderness
jaw claudication
throat pain
diplopia
shoulder pain and stiffness from PMR
other uses for TNF
IBS
ankylosing spondylitis
psoriatic arthritis
what are the number 1 and two causes of a swollen, red joint
infection and crystal arthritis
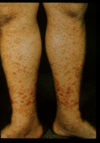
purpura
saddle nose deformity
a destruction of the nasal cartiliage found in Wegener’s granulomatosis
reactive arthritis
joint pain including ehtesitis, uveitis, urethritis, cervicitis usually precipitated by a GI/GU infection
T/F TNF blockers lead to production of anti-nuclear antibodies and drug induced lupus
true
why do many patients with RA have osteporosis
their inflammatory condition accelerates osteoclast activity
labs for PSS
SCL antibody (40%)
ESR usually normal
anemia is rare
mild increase in IgG
30% + RA factor
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (CCP antibody) tests for
RA, may be more sensitive to early onset than RF and CCP
define scleroderma
Chronic multi-system disease usually involving the skin, lungs and GI tract as well as the renal system.
includes widespread small vessle vacsculopathy and fibrosis
T/F renal involvement is common with limited scleroderma
false
Sjogren syndrome clincial presentation
dry eyes and mouth
enlarged parotid glands
age and gender bias for ankylosing spondylitis
onset in late teens but takes 10 years to diagnose
more common in men
Muscle Enzymes CPK, CK-MB, CK-MM, SGOT (AST), Aldolase test for
can be increasd by
myositis, PMR/GCA
can be increased by statins
systemic symptoms associated with joint pain that indicate a possible inflammatory disease
fever
rash
dry eyes/mouth
stomatitis
raynauds
pleuropericardial symptoms
renal involvement associated with wegener granulomatosus
proteinuria, hematuria, casts, focal segment glomerular nephriris on biopsy
SS of psoriatic arthritis
joint pain (depends on presentation)
psoriasis, usually years before ijoint involvement
calcinosis cutis
deposits of calcium found under the skin see in CREST syndrome
why cant you treat arthritis associated with IBD interleukin blockers
because the make IBD wose
extraglandular symptoms of sjogrens
fatigue, synovitis, rash, vasculitis, biliary cirrhosis, renal tubule acidosis, pancreatic insufficiency
organisms that can cause reactive arthritis
salmonella, shigella, chlamydia
symptoms of OA
pain localized to characteristic joints that is made worse by activity
stiffness in the AM lasting <15 that gets better with activity
gradual and additive onset
acute intermittent flares
HLA-B27 test for
ankylosing spondylitis
vascular damage indicators associated with Takayasu’s arteritis
diminished pulses
unequal BP
carotid bruits
limb claudication
HTN
PE findings with wegener’s granulomatosus
systemic symptoms
Upper res
lower res
eye
treamtne for psoriatic arthritis
NSAIDs
TNF blockers
IL blockers
treatment for osteonecrosis
no weight bearing or joint replacement if damage is too severe
what is the only rheumatologic condition that is treated by IVIG
myositis
cardiac involvement in PSS
significant cause of death is biventricular myopathy, CHF, and arrhythmais
what is undifferentied conntective tissue disease used for
it is kind of a catch-all for people who might have mild signs and symptoms
risk with colchicine preventative treatment of gout
can cause aplastic anemia
why is caffeine important to avoid in PFS
sleep distruption and vasoconstriction
progressive systemic sclerosis findings
40% 10 yrs survival rate
diffuse skin involvement with major organ involvement
raynauds not always present but usually follows
what is the benefit of TNF blockade for RA treatment
significant immprovement of S&S with methotrexate
significant improvement of functionality with MTX
stos joint damage
may decrease CV events
T/F sjogens patients are at higher riskf for leukemia
false, lymphoma
what is this
what condition is usually first see with this

sacroilitis
ankylosing spondylitis
labs for OA
imagings
nothing specific, ESR and rheumatoid factor appropriate with age
look for bondy sclerosis, loss of cartiliage, osteophytes
isses tha tend to be found in the shoulder
subacromial bursitis
adhesive capsilitis
OA
rotator cuff tear or tendonitis
biceps tendonitis
Serum Compliment – C3, C4, and others tests for
SLE
classifications of lupus
cutaneous
drug induced
neonatal
anti-phospholipid antibody syndrome
SLE
undifferentiated connective tissue disease
calcinosis might mimic what other joint ocnditions
how can you tell the difference
gout
gout crystals are radiolucent
treatment for Kawasaki disease
IVIG
aspirin
methylprednisolone
TNF
MTX
why is rapid treatment of GCA more important than PMR
GCA causes blindness and PMR does not
relaionship beween gout and kidnets
renal failure leads to hyperuricemia
hyperuricemia my lead to crystal deposition on renal parachyma
associated with HTN
can lead to urate stones
descrie polymyositis
inflammatory disease of the striated muscle fo the limbs, neck, pharynx commonly found in women and associated with an occult malignancy
Serum Uric Acid
hyperuricemia related to gout
labratory features of SLE
leukopenia, usually lymphopenia
anemia
thrombocytopenia
hypergammaglobulinemia
ana
compliment
Anti-nuclear antibodies (ANA) (titer) 1:160 or > tests for
SLE
RA
Sjogrens
Hepatitis
treatment of polymyositis
high dose methotrexate, steroids, or azathioprine
describe sjogren syndrome
an autoimmune condition that attacks the lacrimal and salivary glands that usually affects women between the ages of 40 and 60
Rhabdomyolysis treatment
IV fluids
mannitol
pathophysiology of fibromyalgia
abnormal signalling of the afferent nerve pathway in the dorsal horn
course of rheumatoid arthritis
chronic disease with acute flairs
progressive deformties and disability
progression is variable but major loss usually within 2 years
associated with shortened life expectancy
types of biologics for RA
TNF blockers
IL6 blockers
IL3 blockers
T cell blockers
B cell blockers
triggering agents for SLE
sunlight
diet
infections
stress
medications (sulfa antibiotics)
Serum Protein Electrophoresis used for
commonly used for multiple myeloma but cann be used to look for hypergammaglobulinemia that would indicate SLE
rheumatoid arthritis Dx
aspiration of joint fluid to exclude gout or septic arthritis
ESR and CRP elevation
RF and anti-CCP antibodies will be positive in many cases
juxtarticular lesions and soft tissue edema
HP/PE findings with ankylosing spondy
back pain worse in the AM, better with exercise
extra articular symptoms
how to differentiate viral arthritis from RA
RA will cause erosions
presence of causative agents
IgM antibodies against parovrius
+ anti CCP antiboides point to Ra
describe Kawasaki disease
systemic vasculitis precipitated by an infection or genetic predisposition that causes infiltration of plasma cells into the walls of the vessels
catastrophic ntiphospholipid syndrome
the 1% with Antiphospholipid syndrome that will progress to diffuse thromboses, thrombotic microangiopathy, and multi organ system falure
characteristics of myositis
symmetric proximal muscle weakness without pain
systemic symptoms
dysphagia
pulmonary and cardiac symptoms
periorbital edema
criteria for RA diagnosis
6 points for diagnosis
small joint synovitis
- 1-3 joints 2 pts
- 4-10 3 pts
- more than 10 5 pts
positive RF/CCP (2 pts)
Elevated ESR/CRP (1pt)
Lasts for more than 6 weeks (1pt)
enthesopathy
inflammation of the attachment points of tendons associated with ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis
treatment for scleroderma
calcium channel blockers for raynauds
ace inhibitors for renal crisis
steroids for myositis
nsaid and plaquenil for synovitis
common side effects of methotrexate
mucositis
transient elevated liver enzymes
leukopenia
thrombocytopenia
diagnostic tests for infectious arthritis
synovial fluid: gram stain, low glucose, elevated leukocyte count
blood: culture, elevated ESR and leukocyte count
describe takayasu’s arteritis
early adulthood vasculitis of the aorta and major branches with frequent relapse
treatment for GCA
usually high dose steroids for one month
may require immunosuppressive therapy such as MTX
resolves 6-24 months
describe the CREST syndrome associated with limited scleroderma
calcinosis cutis
raynauds
esophageal dysfunction
sclerodactyly
teleangiectasia
what constitutes chronic gout
10years of acute intermittent gout
tophi deposition
chronic swollen joints
joint destriction
absolutly require allopurinol or uloric
Systemic lupus erythematosus clinical presentaton
photosensity malar or discoid rash
oral ulcers
arthtitis
serositis
renal disease
hematologic or immunologic or neurologic disorders
neurological involvement of polyarteriis
mononeuropathy
diffuse poly neuropathy
CVA
Systemic lupus erythematosus Dx
clinical presentation
CBC (anemia, leukopenia/cytosis, thrombocytopenia)
BUN/creatinine
UA
ESR compliment
Sjogren syndrome Dx
Rheumatoid factor in 70%
ANA in 60%
anti-Ro antibodies in 60%
schrimir test for lacrimal glands
biopsy of the lower lip to confirm fibrosis and lymphcyte infiltration
T/F hyperuricemia is only present in people with active gout
what can be done wit these peole
false, 5% of asymptomatic people have it
don’t treat but consider removing exacerbating factors
hematology associated with SLE
hemolytic anemia
leukopenia
thrombocytopenia
what is the correlation between PMR and GCA
if you have PMR, you have a 10% chance to have GCA
Felty syndrome
a small subset of RA that features splenomegaly and neutropenia accompanied by severe, destructuve arthritits
age and gender bias associated with wegener’s granulomatosus
found in young to middle aged adults
slightly more common in men
dermatomyositis
a variant of polymyositis that affects the skin
describe fibromyalgia
a central pain disorder is mainly found in women and may occur with RA, SLE, or sjogrens
gouty arthritis DX
joint fluid analysis for urate crystals (rod shaped, negatively bifringent)
high serum uric acid is correlated but not diagnostic (flares can happen with normal serum testing0
education in regard to PFS
explain diagnosis
explain importance of lifestyle changes
explain lack of disability
describe giant cell arteritis
systemic arteritis affecting the medium and large vessels usually afflicting patients over 50 and coexisting with polymyalgia rhematica
nonspecific complaints that might indicate fibromyalgia
anxiety
depression
headaches
IBS
dysmenorrha
paresthesia
cutaneous involvement of polyarteritis
palpable purpure
livedo reticularis
splinter hemorrhages
what type of arthritis is often found in the wrist
rheumatoid
age and gender bias for psoriatc arthritis
30-50, even distribution between men and women
Total Hemolytic Compliment (THC) (CH50)
a low value might indicate autoimmune disease
characteristics of infectious arthritis
monoarticular
rapid onset
red/warm/swollen
LFT – AST/ALT
tests liver function after DMARDs or biologics
underlying diseases associated with psuedogout
hyperparathroid
hemochromatosis
hyperthyroid
amyloidosis
hypomagnesiemia
hypophophatasia
viruses that can cause arthritis
parovirus
chikingunya fever
Hep B or C
what is the most common vasculitis disease
GCA
musculosketal issues with PSS
useful therapies
polyarthragies
friction rubs suggest poor prognosis
flexion contractures common
nsaids, plaquenil, steroids
monarticular joint disease
septic
crystal
DJD
traumattic effusion
Pott disease
spinal turberculosis usually seen in immigrants
synovium
synovial membrane
describe psoriatic arthritis
arthritis preceed by psoriasis that is typically assymetical and can resemble RA or ankylosing spondylitis
Tuberculous arteritis
infection of peripheral joints from TB that can last week so or months and present like septic arthritis
nutrition changes for fibromyalgia
eat at least three protein rich meals a day
avoid caffine
drink water
lose weight
T/F RA doesn’t affect the neck
false, it can cause subluxation of C1-2 though it may take year to develope
describe microscopic polyangitis
vasculitis of the small blood vessels that presents with palpable purpura, splinter hemorhages, vesicobulbous lesions, lung and renal involvement
age and gender bias of gout
older men >50 with a poss genetic Hx, DM/HTN/hyperlipid
clinical presentation of scleroderma
polyarthralgia
skin chnages
esophageal dysfunction
describe reactive arthritis
an assymetrical arthritis of the lower extremities that typically strikes after a GI or GU infection
what is hydroxychloroquine used for in SLE
decrease flares
prevent organ involvement
manage steroid dose
rare but major side effects of methotrexate
interstitial pneumonitis
liver fibrosis of cirrhosis
infection
EBV induced lymphoma
Kawasaki disease Dx
clinical presentation
neutrophilia
elevated CRP
thrombocytopenia
no specific test
describe calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD)(pseudogout)
deposits of CPPD in the fibrous and hylaine cartilage of a joint causeing chrondrocalcinosis that commonly affect the wrist, knee, and elbow
mucous membranes assocaited with kawasakis
erythema, swelling and fissuring of the lips, strawberry tounge
what differentiates limited scleroderm from PSS
usually live longer (70% 10 yr survival)
anticentromere antibody rather than anti SCL 70
always have raynauds
sclerodactyl to the wrist

telangiectasias
raynaud phenomenon
paroxysmal digital ischemia caused by vasospasm in response to cold and emotional stress
alternative physical therapies for PFS
stim
massage
physical therapy
chiropractic
triggerpoint injections
joint issues that tend to be found in the back
muscle strain
lumbar herniation
scoliosis
spinal stenosis
OA of the back
reactive arthritis Dx
at least half of patients will be HLA-B27 positive
culture negative serous fluid
xrays may show permanent and progressive joint disease
therapy for cutaneous lupus
topical steroids
hydroxychloroquine
intralesional steroid injection
thalidomide
leflunomide
5 renal conditions associated with lupus
mesangial glomerulonephritis
focal glomerular nephritis
diffuse proliferative glomerular nephritis
ditto with necrosis
membranous glomerulonephritis
what muscles are typically effected by myositis
the shoulders
what joints of the hand will OA usually present in
RA
OA will usually be in the DIP and PIP
RA will usualyl be in the DIP and MCP
enthesopathy
inflammation of the attachment of a tendon to bone
Etanercept (Enbrel) is what type of drug
what can it treat
special considerations
TNF inhibitor DMARD
almost everything (RA, AS, PA, sjogrens, Wegeners)
increased risk for infection, TB, lymphoma, etc
Tuberculous arteritis Dx
synovial fluid smears and culture
synovial biopsy
what labs will have abnormal results in PFS
functional MRI
FM/2 blood test
Dx of pseudogout
presnts as gout, DJD, RA
chondrocalcinosis on xray
positively birefringent rod shaped crystals
more likley to be found in a damaged knee
upper respiratory conditions associated with wegener’s granulomatosus
sinusitis, nasal and oral ulcerations, saddlenoe deformity
biopsy findings for polyarteritis
acute inflammatory infiltrate with polymorphonueclear leukocyots and fibroid necrosis
treatment for pseudogout
NSAIDs
colchicien for acute attacks
steroids
differentiate between Arava and methorexate
arava is very similar in terms of effect and side effects but it does’t cause any pulmonary toxicity and may elevate BP
what type of cutaneous lupus that forms scars
discoid
what categories are present in the diagnostic critrea for RA
joint involvement (more points for more joints)
serology
duration of symptoms (longer is more points)
acute phase reactants (ESR and CRP)
most common symptoms related to GCA
debilitating temporal headache
Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (CCP antibody) tests for
RA, more specific that RF but less sensitive
risk factors for GI complcations with NSAIDs
older
HX ulcer and GI bleed or prior side effect
high dose NSAIDs
use with prednisone
CVD
antacids
three variants of scleroderma
progressive systemic sclerosis
crest
morphea
DIP psoraitic arthrtis
oligoarthicular involvement
polyarthritis involvement
spondlytis involvement
arthritis mutlilans
5%
70%
15%
5% but another type increases incidence by 40%
5%, destroys the joint
cutaneous PE findings associated with myositis
heliotrope rasj
gottrons papules
sun sensitive rash
lab tests for GCA
ESR >50, usually >100
elevated CRP
elevated LFTs (30%)
abnormal temporal artery biopsy
specific types of vasculitis
PMR/Giant cell arteritis
polyarteritis
wegeners granulomatosus
polyarteritis
lab tests for DIL
> antihistone antibodes
compliment is normal
anti-dna antibodies negative
triad of wegener’s granulomatosus
URt, LRT, renal involvement
when will the first attack of acute gout occur
describe the onset
how long does it last
between 40-60
classic acute onset usually monoarticular
7-10 days
rheumatoid arthritis treatment
low dose steroids to act as a bridge
methotrexate
best therapy is usually methotrexate with a biologic DMARD (TNF blocker)
what is the issue with treating cyclophosphamide for wegener’s
it is oncogenic
characteristics of psoriatic arthritis
enthesitis and dactylitis
describe ankylosing spondylitis
seronegative spondyloarthropathy that leads to eventual fusion of the vertebrae through syndesmophyes
T/F raynauds will get better over time
false, it is a fixed lesion
labs for wegener’s granulmatosis
anti neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies f
describe gouty arthritis
a recurring monoarticular arthritis caused by urate cystals in the joints that typically has an acte on set
what does IL-6 do
induces the final maturation of b cells into plasma cells
regulates the immune response to antigens
T/F combination therapy with DMARD and biologic is contraindicated for RA
false, they are more effective
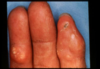
calcinosis
when will allopurinol be needed for lifelong treatment of gout
for urate over producers
GI involvement of polyarteritis
ischemic bowel
elevated LEFTs
T/F ANA is a definitive test for ESL
Positive ANA correlates with diagnosis but a negative does not exclude
Kawasaki disease clinical presentation
fever with four of the following
conjuctivitis
mucous membrane change
rash
cervical lymphadenopathy
peripheral limb changes
classic presenation of a malar rash spares what
the nasolabial fold
T/F TNF blockers are contraindicated in CAD
false, they are contraindicated in CHF
common joints of OA
DIP, PIP, 1st CP, spine, hips, knees
clinical features of SLE
fatigue
fever
cutaneous rash
synovitis
oral ulcers
pleural/pericardial inflammation
Takayasu’s arteritis Dx
ESR/CRP elevation
MRI to detect vasculitis
CTA to see narrowing
EMG findings associated with myositis
increased insertional activity
fibrillations
polyphasic motor unit potentials of low amplitude
what is the only hypercoagulable condition that will cause venous and arterial clot besides APA
factor V leiden mutation
pharmaceutical treatment for OA
NSADs
ice, heat
joint injection
Microscopic polyangitis treatment
corticosteroids with cyclophosphamid or rituximab
jak-stat inhibitors
small molecules that can stop the signaling molecules released by IL-6 from activating genes and producing RNA
Cox 2 inhibitors Celecoxib (Celebrex) are considerded what type of drug
what are they used for
what makes them special
an NSAID
OA
it blocks COX-2 enzyme to decrease prostaglandin formation and inflammation with less stomach distress than typical
acute bacterial arthritis
signs and symptoms
acute pain, swelling, heat in the affected joint worsening several hours
systemic symptoms
treatment for infectious arthritis
joint aspiration or synovial biopsy
treat with ABx to prevent damage and spread to other joints
what is Rituximab (Rituxan)
what is it used to treat
it is especially effective in what circumstance
biologic TNF inhibitor considered a DMARD
RA, SLE, spondyloarthropathies, Behcet’s disease, sjorgrens, wegeners
SLE when there is kidney or major organ involvement
gouty arthritis signs and symptoms
rapid onset of pain, typically with tender, warm, swollen, dusky red areas in the feet, ankles, and knees
APA therapy
APA and no clots - no Rx
APA and clots - coumadin with an INR 3-4 unless platelets are <50,000
continue anticoagulation even when APA negative
synovium
the inner lining of a synovial joint capsule that secretes synovial fluid
CREST scleoderma is an acronym for what
Calcinosis
Raynauds
Esphageal dysmotility
sclerodactyl
telangiectasias
T/F upper cervical vertebrae can be involved in RA
true
Antiphospholipid antibody tests for
APA syndrome in people autoimmune issues
composition of cartilage
70% water
type II collagen
proteoglycans
chondrocytes
livedo reticularis
mottled purple discoloration of the skin caused by blood clots tha lead to swollen venules in the skin
psoriatic arthritis types
spondylitis
RA like
Oligoarthritis
arthritis mutlialsn
what can methotrexate be used for
RA
SLE
Myositis
PMR/GCA
Wegeners
spondyloarthropathies
what does sjogren syndrome attack
exocrine glands (sweat, spit, tears, mucosa, pancreatic)
radiographic findings associated with RA
soft tissue swelling
bite juxtarticular lesions with no crystals
crooked fingers
drugs used to treat RA
TNF inhibitors
ACE inhibitors
DMARDs
chemo drugs
Gold Salts
IL-1 receptor agonists
systemic features of scleroderma
Reflux
hypomobile GI tract
pulmonary fibrosis
pulmonary HTN
renal involvement
why is it important to rule out inclusion body myositis
because it doesn’t respond well to treatment, patients just get worse and die
treatment for ankylosing spondy
nsaids
steroids
sulfasalazine, MTX, axathioprine
TNF inhibitors
IL 17A inhibitors
catastrophic APA syndrome
treatment
an emergeny clotting disorder with a high likelihood of death, gangrene in limbs or organs
pulse solumedrol, IV cytoxan, rituxan, plasmapheresis
Henoch-Schonlein Purpura
classical presentation
a systemic vasculitis associated with IgA deposites in vessel walls, often precipitated by group A strep exposure
palpable purpura in the legs, arthralgia, nausea, colic, melana

syndesmophytes
radiographic findings indicative of gout
no early signs
late signs will have have a bite out lesion under a rim of cortical bone with a splintered apperance
combined with a tophus they are diagnostic of gout
boutoneirre deformity
PIP flexion with DIP extension associated with rheumatoid arthrtiits

scleroderma
important indicator of sacriolitis on Xray
both sides of the SI joint must be effected
three common clinical signs of psoriatic arthritis
symmetric arthritis that resembles RA with DIP involvement
pitting of the nails and onycholysis
sausage fingers cause by tenosynovitis of the flexor tendon
bouchards nodes are indicative of what
usually OA but RA can sometimes present with more gelatinous cysts
labs for polyarteritis
elevated ESR/CRP
leukocytosis
screen for hep b and C
where will RA frequently be seen first on radiograph
around the ulnar styloid because there is no cartilage there to protect the bone
polyarticular joint disease
RA
spondyloarthopathies
undifferentiated connective tissue disease
DJD
gout
charactericstics of APA syndrome
spontaneous abortions
venous and arterial thrombeses
thrombocytopenia
livedo reticularis
septic arthritis (gonococcal) defined
what is the most common sign
a migratory inflammaltion of the wrist, ankle, knee, and elbow caused by gonorrhea
tenosynovitis and characteristic skin leasion
sclerodactyl
localized thickening of the skin over the hands, part of the CREST syndrome
eye conditions associated with wegener’s granulomatosus
episcleritis, uveitis
what is the hallmark conditions for ankylosing spondy
sacroilitis #1
enthesopathy and dactylitis common
peripheral synovitis
lab findings for ankylosing spondy
elevated CRP/ESR
sclerosis on SI oblique xrays
syndesmophytes
HLA B27
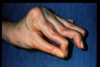
sclerodactyly
raynauds phenomena
cause
progression
arterial spasm that causes reduced blood flow
lupus, scleroderma, thyroid conditions
pallor, rubor, normal
important lab finding for gout
uric acid in blood below 6
what organs are usualyl affected by polyarteritis
any organ, but skin, nerves, joints, GI, kidents are most common
lungs are usually spared
what causes renal tubule acidosis in sjogrens
the inability of the kidneys to secrete bases
PE findings with GCA
acute or subacute onset with systemic symptoms
temporal headaches
scalp tenderness
jaw claudication
visual loss
aortic arch syndrome
thickened or tender temporal arteries
ischemic optic atrophy
PE for chrondromalacia patella
push down on the knee cap will hurt
common places for gouty tophus
thumb, big toe
T/F RA lung nodules can look like lung cancer
true
what percent of gout is from undersecretion
overproduction
90
10
labs for gout
hyperuricemia determined by 24 hr urine
swan neck deformity
extension of the PIP with flexion of the DIP caused by RA
clinical presentation of polymyositis
insidious, painless muscle weakness
dysphagia
skin rash (malar or heliotrope)
polyarthralgia
muscle atrophy
ANA Profile (routine)
patterns
tests for
rim, speckled, diffuse, homogeneous, nucleolar
SLE
osteoarthritis Dx
radiographs showing assymetrical joint narrowing, subarticular cysts, osteophytes
types of joint injections for OA
steroids
hylan products (synvisc)
extrarticular symptoms associated with ankylosing spondy
uveitis, psoriatic and reactive rask, IBD, aortitis, apical pulmonary scarring
pulmonary involvement of limited scleroderma.
treatment
Pulmonary hypertension late in the disease
poor prognosis, usually leasds to right side heart failure
viagra, iloprost, tracleer
Glucosamine and chondroitin are used for what type of arthritis
flax seed
OA
RA
lab studies for PMR
treatment
ESR >50 or elevated CRP
rapid low dose steroids will usualyl resolve in 6 months to 2 years
regional joint pain associated with the hip
OA
trochanteric bursitis
referred apin from the back
diagnostic criteria for acute gout
urate crystals in the joint fluid
OR
tophus with urate crystals
OR
6 clinical factors
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis diagnosis
slight anemia
mild leukocytosis
elevated acute phase reactants
proteinuria
RBC’s in blood
red cell casts
PMR indications on PE
systemic symptoms
stiffness with activity
muscle pain around the shoulder and hip
gouty arthritis treatment
elevation and rest
diet and alcohol reduction
NSAIDs (indomethacin) for intial treatment
colchicine
allopurinol
other syndromes assocaited with fibromyalgia
tension headaches
primary dysmenorrhea
irritable bowel
TNF blocking drugs
ETANERCEPT
ADALIMIMAB
INFLIXIMAB
GOLIMIMAB
CERTOLIZIMAB
T/F bursitis pain is worse at night
true
treatment of scleroderma
PPI for reflux
ACE inhibitors for renal disease
avoid triggers
CCB for raynauds
immunosuppresants for pulmonary HTN
Takayasu’s arteritis treatment
steroids
methotrexate or DMARDs as needed
bouchards nodes
cysts that form on the PIP due to bone spurs
common causes of osteomyelitis
hematogenous
infection
vascular insufficiency

purpura from wegeners granulomatosus
reactive arthritis treatment
phyiscal therapy
NSAIDs
ABx to reduce the chance of getting the disorder but don’t allieviate symptoms
differntiate between spondyloarthropathies and other artritis
spondy tends to get better with exercise
“more tolerable NSAIDs
nabumetone
salsalate
etodolac
acute bacterial arthritis
causes
bacteremia (typically with staph)
joint damage
compromised immunity
lost of skin integrity
four types of myositis
polymyositis
dermatomyositis
myositis associated with connective tissue disease
inclusion body myositis
rheumatoid arthritis defined
an auto immune disease that attacks the synovium and produces extra articular manifestations
alleiviating factors for PFS
warm/dry weather
hot shower
restful sleep
moderate activity
stretching
massage
prevenative therapy for gout
colchicine
NSAIDs
probenecid
allopurinol
steroids
labs for limited sclerodema
95% have anticentromere antibodies
ESR usually normal
anemia is rare
skin changes associated with progressive systemic scleroderma
early presentation with diffuse swelling and stiffness of the fingers
rapid progression
usualy involves skin above the wrist
rarely see telangetasias or subcutaneous calcium
the differnece between irritable bowel and inflammatory bowel
inflammatory bowel has noctural bowel movements
DMARDs
hydrocholoquine
methotrexate
leflunomide
azathioprine


