Respiratory system Flashcards
(26 cards)
What is the function of the respiratory system?
allows for the intake and exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the human body and the atmosphere
How does air enter the body to allow gaseous exchange?
Air moves in through the nasal or oral cavities, through the pharynx and larynx, into the trachea and then the bronchi where it is distributed through the lungs via the bronchial tree
Label the thoracic cage


What is the trachea?
Where does the trachea begin?
How is the trachea kept patent?
Where does the trachea end?
Mobile and cartilaginous tube
at the neck as a continuation of the larynx
by the presence of U-shaped bars of hyaline cartilage embedded in its wall
Trachea ends by dividing into right and left principal bronchi in the thorax
Describe how the bronchi of the lungs divides
Bronchi divide dichotomously, giving rise to several million terminal bronchioles that terminate in one or more respiratory bronchioles in the lungs
Label the tracheobronchial tree


Label the lungs in situ

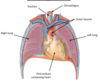
Where are the lungs suspended?
How are the lungs attached to the mediastinum?
Which lung is larger?
How many lobes does each lung have?
Why are the lungs not the same size?
Each lung is suspended free in its pleural cavity
Attached to the mediastinum by its root, where the main blood vessels and bronchi enter the lung
Right slightly larger than the left
Right has three lobes, left has two
Due to space taken on the left hand side of the thoracic cavity by the heart
Label the lungs and the bronchial tree


What type of image is this?

Bronchogram
Describe the following structures of the lungs:
Apex
Base
Costal surface
Mediastinal surface
Apex
Projects upwards into the neck above the clavicle
Base
Concave surface, sits on the diaphragm
Costalsurface
Corresponds to the concave chest wall
Mediastinal surface
Molded to mediastinal structures
Location of hilum, where bronchi, vessels and nerves enter and leave the lung (lung root)
Which vessel supplies the bronchi and connective tissue of the lungs?
Where do the alveoli receive deoxygenated blood from?
Where does the oxygenated blood leaving the alveolar capillaries drain into?
bronchial arteries, which are branches of the descending aorta
Alveoli receive deoxygenated blood from the terminal branches of the pulmonaryStudy arteries
Oxygenated blood leaving alveolar capillaries drains into the tributaries of the pulmonary veins
Label the blood supply of the lungs


What is a pleura?
A pleura is a serous membrane which folds back onto itself to form a two-layered membrane
What are the 2 parts of the pleura of the lungs?
Parietal pleura - Lines the thoracic wall, thoracic surface of the diaphragm, lateral aspect of the mediastinum
Visceral Pleura - Completely covers the outer surfaces of the lungs and extends into the depths of the interlobar fissures
How does the 2 parts of the pleura become continuous?
The two layers become continuous by means of a cuff that surrounds the structures entering and leaving the lung at the hilum
Label the development of the pleural membrane


label the following diagram


What seperates the 2 layers of the pleura
What does it contain and what is its function?
pleural cavity
Contains tissue fluid, covers the surface of the pleura
Reduces friction
Surface tension of the fluid allows close apposition of the lung surfaces with the chest wall
Aids in expanding volume of the lungs during breathing
What is the most important muscle of respiration?
What does it seperate?
Describe its shape
What does it consist of?
How does this muscle affect the thorax?
Diaphragm - thin muscular and tendinous septum
Separates the thoracic cavity above and the abdominal cavity below
Domeshaped
Consists of;
Peripheral muscular part
Centrally placed tendon
On contraction the diaphragm pulls down its central tendon and increases the vertical diameter of the thorax
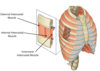
How are the fibres of the intercostal muscles arranged?
External
Fibres directed downward and forward from the inferior border of the rib above to the superior border of the rib below
Internal
Fibres directed downward and backward
Innermost = Deepest layer
Incomplete muscle layer that crosses more than one intercostal space
Label the intercostal muscles

Describe the mechanism of respiration
Consists of two phases: inspiration, expiration
Alternate increase and decrease of capacity of the thoracic cavity
As there is only a single entrance (trachea) an increase in capacity of the thoracic cavity results in air moving into the lungs under atmospheric pressure
How is the capacity of the thorax increased?
Vertical diameter = Diaphragm
Anteroposterior diameter:
Downward sloping ribs raised at sternal end
First rib is fixed, intercostals contract bringing ribs closer together
Transverse diameter:
Ribs articulate in front with the sternum and behind with vertebral column
Curve downward and resemble bucket handles


