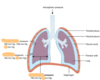
Respiratory Mechanics CPBC Flashcards
Fill in the gaps


what 3 areas of the brain participate in the control of breathing?
- medulla
- pons
- cortex, limbic system
What are the 2 respiratory groups of the medulla?
ventral respiratory groups
- pre-boetzinger complex –> central pattern generator
- boetzinger complex (aka SA node for breathing) –> expiratory neurons
dorsal respiratory groups
What are the 2 respiratory centers of the pons?
apneustic center –> stimulates inspiratory neurons of the dorsal and ventral respiratory group (medulla)
pneumotaxic center –> regulates volume and rate
how does ICH/TBI affect the breathing pattern
stimulation of the apneustic center of the pons –> gasping type breathing
What is the function fo the cortex/limbic system in control of respiration?
voluntary control/ emotions
where are the central chemoreceptors for breathing located and how are they stimulated?
in the medulla
blood CO2 diffuses into the CSF and increase [H+]/ decreased pH –> increase respiratory rate
where are the peripheal respiratory chemoreceptors located and how do they affect breathing?
cortid and aortic bodies
sense hypoxemia, hypercarbia, acidemia or decreased perfusion –> increase ventilation via the glossopharyngeal nerve
Where are the baroreceptors located and how do contribute to ventilation
carotid and aortic bodies
mostly concerned with circulation –> but sever hypotension will induce hyperventilation
what are the three types of breathing receptors located within the lungs?
- stretch receptors
- irritant receptors
- J receptors
what are the stretch receptors within the lungs?
located within the smooth muscles of the airways –> distention –> vagus nerve stimulated –> inhibits apneustic center
= inhibits respiration, prevents overdistention via the Hering-Breuer Reflex
how do the irritant receptors within the lungs affect respiration?
lay between airway epithelial cells
detect noxious gases, cigarette smoke, dust, cold air
cause bronchoconstriction and hyperpnea (=increased depth of breathing)
How do J receptors affect respiration?
lay in juxtacapillary and alveolar walls
stimulated by interstitial fluid or engorged pulmonary capillaries –> stimulates rapid, shallow breathing
are very sensitive –> even mild pulmonary edema not showing up on radiographs will stimulate recpetors –> first sign of volume overload is increased respiratory rate
Fill the gaps


Fill the gaps


Fill the gaps


Fill the gaps


Fill the gaps


What is the normal atmospheric pressure at sea level?
760 mmHg
The atmospheric pressure ___ as altitdue increases
decreases
What is the average pleural (thoracic) pressure?
- 4 cm H2O (but changes from top to bottom)
how is the lung distorted by its weight?
alveoli on top are stretched and expanded by the lung underneath
alveoli at the bottom are compressed by lung above
what is the range from pleural pressure from top to bottom of the lungs?
ranges from -10 to -2.5 H2O
what is the transpulmonary pressure?
airway pressure minus pleural pressure