Respiratory FINAL Flashcards
What are the structures within the respiratory system?
- Conductive System
- Transitional System
- Gas Exchange System
What is the conductive system composed of?
nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi.
What is the transitional system composed of?
Terminal Bronchioles
What is the Gas Exchange System composed of?
respiratory bronchioles and alveoli.
What component of the respiratory system is labeled by 1?

CONDUCTING
What component of the respiratory system is labeled by 2?

TRANSITIONAL
What component of the respiratory system is labeled by 3?

EXCHANGE
What does the Conductive System do?
- Brings air to the Respiratory Portion
- Cleanses, moistens, and warms incoming air.
- Hair and secretions in the nasal cavity trap particulate matter.
Blood in venous plexuses in mucous membrane of nasal cavity ____________________ of inhaled air.
regulates temperature
What is the transitional zone between the conducting (ciliated) and the gas exchange (alveolar system) areas of the respiratory tree.
TRANSITIONAL SYSTEM
The transitional system is composed only by the terminal bronchioles which are lined by….
Clara Cells
Non-ciliated secretory cells
Only a few ciliated cells
Healthy bronchioles do not have
Goblet Cells
What component of the respiratory system is depicted in this image?

EXCHANGE SYSTEM
What is the exchange system composed of? (shown in this image.)

Alveoli
Thin walled structures enveloped by a rich network of capillaries: the pulmonary capillaries.
Alveoli
Alveoli are lined by
epithelial type 1 (membranous) pneumocytes and type 2 pneumocytes
What are we looking at here?

Normal Sheep Lung
What are these examples of?

Cells of the Respiratory Tract
What are the Defense Mechanisms of the Respiratory System?
Non-Specific (non immune-mediated)
Specific (immune-mediated)
Describe the Non-Specific (non immune-mediated) defense mechanism of the respiratory system.

Describe the Specific (immune-mediated) defense mechanism of the respiratory system..

The conductive system is mostly lined by….

The conductive system is composed of
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
The respiratory portion of the nasal cavity is lined by
ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells.
What is indicated by the arrow?

tubulo-alveolar glands
The lamina propria contains tubulo-alveolar glands, mainly serous, with lesser numbers of mucous and mixed glands.
What is shown within the rectangle of this nasal cavity slide?

The lamina propria
The submucosa supports the lamina propria (shown within rectangle)
The oflactory epithelium contains
oflactory sensory cells
What is the bone supported cavity within the skull that is divided by nasal cartiliginous septum into two halves, left and right.
Nasal Cavity
Each half of the nasal cavity has three regions. What are they?
- Vestibular Region
- Respiratory Region
- Olfactory Region
What is this region of the nasal cavity?

Vestibular Region
What is the initial, external part of the nasal cavity with cutaneous mucous membrane, hairs, and skin glands.

The Vestibular Region.
The vestibular region is lined with….

stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
What region of the Nasal Cavity is this?

Respiratory Region
A. What is the largest part of the nasal cavity?
B. What is it lined with?

A. The Respiratory Region
B. Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells.
(this combination of cells is known as the Mucociliary apparatus, responsible for clearance.)
What is the Mucociliary Apparatus responsible for?
Clearance
What are the projections from the lateral wall that narrow the lumen of the nasal cavity and increase the area of contact of inhaled air with respiratory mucous membrane, thus regulating the quality and quantity of inhaled air.
Conchae Turbinates
What is this image depicting?
What is it responsible for?

Mucociliary Apparatus: Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium. (in trachea)
Responsible for Clearance.
What is this image depicting?

Mucociliary Apparatus: Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelum.
Goblet cells produce _________ granules.

mucinogen
Movement of cilia removes mucus with trapped airborne inhaled particles such as _______ and ___________.

dust and microorganisms.
What constitues a cleaning apparatus of upper respiratory passages?

Cilia and Goblet Cells
What is indicated in the oval?
What do the secretions of these cells do?

Goblet Cells
Secretions traps particulate matter
True or False
There are an increase number of Goblet Cells in smokers?
True. (hyperplasia)
A change from ciliated stratified epithelium to squamous stratified epithelium is called __________
Metaplasia
Ciliated Epithelial cells are connected by
Gap Junctions
The Olfactory Region: is lined with olfactory epithelium and is much _______ than respiratory epithelium. It lacks __________.
The Olfactory Region: is lined with olfactory epithelium and is much thicker than respiratory epithelium. It lacks goblet cells.
What epithelium is shown in slide A?

Respiratory Epithelum
What epithelium is shown in Slide B?

Olfactory Epithelium
What region is located in the dorsal part of the nasal cavity?
Olfactory Region
The Olfactory Region is lined by olfactory epithelium without __________

Goblet Cells
Olfactory Region:
Lamina propria contains _______________ and ______________ (non myelinated axons of olfactory neurons from nerve bundles Cr. N. 1.

Olfactory Region:
Lamina propria contains serous olfactory glands and fila olfactoria (non myelinated axons of olfactory neurons from nerve bundles Cr. N. 1.)
What is shown here?

Ciliated Pseudostratifed Columnar Epithelium with Goblet Cells (red arrows)
Both olfactory and respiratory regions are rich in venous plexuses known as __________ which are distended with blood.

Swell Bodies
What is the structure indicated by O?

Olfactory neuron
What is indicated by S?

Supporting Cell
What is indicated by A?

Axons of Olfactory neurons Cr. N. 1.
What is B?

Basal Cell
What is G?

Serous Olfactory Gland

Vemeronasal Organ: Chemoreception, Sexual Behavior
What are center arrows indicating?

Vomeronasal Organ
The Larynx includes…

Cartilage
Vocal Folds
Skeletal Muscle
Initial part of the Larynx is lined by….

Stratified squamous epithelium
After the vocal cords, the lining of the larynx changes to…

Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
What is this an image of?

The Trachea
The trachea is lined by

ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium
True or False.
In the trachea, the lamina propria and the submucosa are clearly demarcated.

FALSE.
In the trachea, the lamina propria and the submucosa are NOT clearly demarcated.
What is seen in the lamina propria/submucosa of the trachea?

Serous Glands
WTF is this?

Trachea.
Rings of _______, which are incomplete dorsally, support the tracheal wall.

Cartilage
A connective tissue ________ completes the wall of the trachea.

Adventitia
FUN FACT.
Birds have _________ rings of cartilage.

Complete
WTF is 1?

Cartilage
WTF is 2?

Esophagus
WTF is A?

Ciliated Cells
WTF is B?

Goblet Cells
WTF is C?

L. muscularis mucosae
WTF is D?

Serous Glands, Loose CT Vessels
WTF is E?

Cartilage
This is the Trachea.
WTF is A?

Cilia
This is the Trachea.
WTF is B?

Goblet Cell
This is the trachea.
WTF is C?

Lamina propria mucosae
This is the trachea.
WTF is D?

Basal Cells
Trachae branches into two bronchi. Bronchus has plates of ____________.

hyaline cartilage
The trachea bifurcates into the ________, which enter the lung and branch extensively.

Bronchi
WTF is this?

Bronchus
Bronchi are lined by….

Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
What is in the circle?

Mixed Bronchial Glands
What is the arrow pointing to?

Plates of hyaline cartilage
WTF is this?

Bronchioles
Bronchi branch into ______

Bronchioles
Bronchioles lack

cartilage and glands
Bronchioles are subdivided into

terminal bronchioles
and
respiratory bronchioles
Terminal bronchioles are lined by….

ciliated cuboidal cells with few to no goblet cells.
(a muscularis mucosae is still present in terminal bronchioles.)
What cells are located in the terminal and respiratory bronchioles, bulge at the surface, are a source of surfactant like substance, and metabolize airborne toxins.

Clara Cells
What is the arrow pointing to?

Clara Cell
What is the function of the respiratory bronchiole?
Conduction and Gas Exchange
WTF is this?

Respiratory Bronchioles
Respiratory Bronchioles are lined by

ciliated cuboidal epithelium, which becomes flattened distally
Respiratory Bronchioles have incomplete…

Respiratory Bronchioles have incomplete muscularis mucosae
Respiratory Bronchioles divide into….
Respiratory Bronchioles divide into alveolar ducts

WTF is this?

Alveolar Ducts
Alveolar ducts are part of the exchange system and they empty into

alveolar sacs and alveoli.
The walls of alveolar ducts are composed entirely of alveoli lined with…

simple squamous epithelial cells
The edge surrounding the opening of each alveoli of an alveolar duct contains

The edge surrounding the opening of each alveoli of an alveolar duct contains smooth muscle cells.
Alveolar ducts empty into _________ and alveoli.
Alveolar ducts empty into alveolar sacs and alveoli.

The presence of _________ gives the lip of the alveolus a knob like appearance on sections.
The presence of smooth muscle gives the lip of the alveolus a knob like appearance on sections.

Alveolar ducts branch into alveolar sacs which lack….
Alveolar ducts branch into alveolar sacs which lack smooth muscle.
Alveoli are lined by what two distinct epithelial cells?
Pneumocytes Type 1
Pneumocytes Type 2
What is this slide showing?

Pulmonary Edema: Alveolar Spaces filled with Proteinaceous Fluid.

Neighboring alveoli connect with each other via _______, providing equalization of pressure and collateral ventilation if a bronchiole is obstructed.
Pores

Pores allow __________ passage from one alveolus to another.
macrophage

What type of collagen is present in the alveolar wall?
Collagen type 3
What type of collagen is present in conducting airways?
Collagen Type 1
Pneumocyte type 1 cells are also known as
Squamous alveolar type 1 cells
Pneumocyte type 1 Cells compose ____ of the alveolar surface area.
Pneumocyte type 1 Cells compose 95% of the alveolar surface area.
Pneumocyte Type 1 cells are not ____
Pneumocyte Type 1 Cells are not mitotic.
What is the red arrow?
Grey arrow?

Pneumocyte Type 1
Pneumocyte Type 2
Pneumocyte Type II Cells are also known as
Granular alveolar Type II Cells.
Pneumocyte Type II Cells compose ___ of alveolar surface area.
Pneumoctye Type II Cells compose 5% of alveolar surface area.
Surfactant is produced via
Lamellar bodies
Pneumocyte Type II cells containt lamellar granules that contain recently synthesized….
Pneumocyte Type II cells containt lamellar granules that contain recently synthesized Surfactant.

This is a mono-molecular layer of phospholipoprotein…
Surfactant.
This functions to reduce surface tension, reducing effort needed to inflate alveoli, thus preventing alveolar collapse (atelectasis.)
Surfactant
This is constantly produced by Type II Cells
Surfactant
__________ stimulates production of surfactant in fetus just prior to parturation.
Cortisol stimulates production of surfactant in fetus just prior to parturation.
Absence of surfactant in newborns is known as
**Hyaline Membrane Disease **
What is this arrow pointing to?

Elastic Fibers
What is the Blood-Air Barrier composed of?
Vascular Endothelium
Basement Membrane of the Endothelial Cell
Basement Membrane of the Type I Pneumocyte
Cytoplasm of the Type I Pneumocyte
What is this TEM depicting?

Blood-Air Barrier
The lungs are covered by the _________ composed of connective tissue and lined by simple squamous epithelium.
Visceral Pleura
The thoracic wall, diaphragm, and mediastinum are lined by _________ which is continuous with the mediastinal and _________ covering the entire surfaces of the lungs.
The thoracic wall, diaphragm, and mediastinum are lined by parietal pleura which is continuous with the mediastinal and visceral pleura covering the entire surfaces of the lungs.
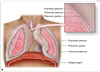
The pleura is composed of simple squamous epithelial cells also known as
mesothelial cells
WTF is this?

Trachea
What are the arrows pointing to in this slide of the Larynx?

Hyaline Cartilage
LARYNX: What is 1?

1 = Stratified Squamous Epithelium

LARYNX: What is 2?

2 = Mucous Glands

LARYNX: What is 3?

3 = Perichondrium

LARYNX: What is 4?

4 = Hyaline Cartilage

Identify and Describe this slide

Trachea.
Pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium, with goblet cells, submucosal glands, and hylaine cartilage.
LUNG: Identify Blue Arrow

Blue Arrow= Bronchus with Plates of Hyaline Cartilage

LUNG: Identify Green Arrow

Green Arrow = Bronchial Glands

LUNG: Identify Pink Arrow

Pink Arrow = Smooth Muscle

LUNG
Describe the slide

Bronchus lined by pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells.



