Resp/Neuro monitoring Flashcards
(114 cards)
What is the difference between ETCO2 and PACO2?
Approximately 5 torr, up to 10 torr
Define capnometry.
Encompasses all means of measuring carbon dioxide
Define capnography..
Recording of the measurement of carbon dioxide
Define capnogram.
Uses infrared analysis, A continuous display of carbon dioxide
What are the two forms of capnogram?
Nondiverting and diverting
Define nondiverting/mainstream monitor.
Measures gas directly within the breathing system
What are the advantages of nondiverting/mainstream monitoring?
Minimal time delays, no scavenging necessary
What are the disadvantages of nondiverting/mainstream monitoring?
Cannot measure gases other than carbon dioxide and nitrous oxide, increased deadspace
Define diverting/sidestream monitor.
Extracts gas from sample tubing near the patient end of the circuit and pushes it into monitor
What are the advantages of diverting/sidestream monitoring?
Minimal increase in deadspace, versatile gas analysis
What are the disadvantages of diverting/sidestream monitoring?
Need for scavenging, risk of contamination from secretions
Id the A-B portion of the waveform. What does this mean?

Baseline (anatomic deadspace)
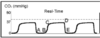
Id the B-C portion of the waveform. What does this mean?

Expiratory upstroke (deadspace and alveolar gas)

Id the C-D portion of the waveform. What does this mean?

Expiratory plateau (alveolar gas)

Id the D portion of the waveform. What does this mean?

End-tidal concentration

Id the D-E portion of the waveform. What does this mean?

Descent to original baseline (inspiration)

Capnogram – What is occurring?

- Rebreathing – Waveform fails to return to baseline
- Caused by inadequate fresh gas flow or depleted absorber
Capnogram – What is occurring?

- Prolonged expiration
- Caused by obstruction of expired gas flow or ventilation-perfusion mismatch
What respiratory commorbities could cause this? (3)

Asthma, bronchospasm, COPD, etc.
Capnogram – What is occurring?

Curare Clefts
- Spontaneous respiratory effort in an anesthetized patient who is mechanically ventilated and/or paralyzed
Be able to differentiate hyperventilation from hypoventilation.
Slide 90
Capnogram – What is occurring?

- Loss of end tidal waveform – Dislodged ETT or ETT disconnected
- Sudden loss of circulation, e.g. PE
What can increase ETCO2?
- Increased carbon dioxide delivery or production
- Hypoventilation
- Equipment problems
What can decrease ETCO2?
- Decreased carbon dioxide delivery or production
- Hyperventilation
- Equipment problems


