Repro Flashcards
(106 cards)
what is in the spermatic cord
nerves- cremasteric, ilioingual, sympathetic
arteries and veins- cremasteric, to vas, testicular
vas deferens, lymph, pampiniform plexus, processus vaginalis
coverings of spermatic cord
external spermatic fascia, cremaster fasia, internal spermatic fascia
venous drainage r/l testis, scrotum and prostate
l testis- renal vein
r testis- IVC
scrotum- scrotal veins
prostate- prostatic venous plexus>internal iliac
lymphatic drainager r/l testis, scrotum and prostate
r testis- para-aortic
l testis- para-aortic
scrotum- superficial inguinal
prostate- internal iliac/sacral
artery r/l testis, scrotum and prostate and penis
penis- pudendal
r/l testis- testicular artery
scrotum- scrotal artery
prostate- prostatic artery
what do seminal vesicles, prostate and bulbourethral glands release
seminal vesicles- fructose, alkaline fluids and coagulating agents. 65%
prostate gland- enzymes to break down clotting factors. 25%
bulbourethral glands- alkaline mucus. 10%
label the 4 missing sections on the prostate
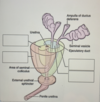
top left- transitional zone
bottom left- anterior region
top right- peripheral zone
bottom right- central zone
label the 4 missing ligaments
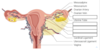
suspensory ligament
ovary
broad ligamet
round ligament
ovarian ligament
fill in the missing blood suppplies
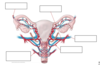
top: L- ovarian artery
R-uterine artery
Bottom: left- internal pudundal
middle- vaginal artery
right- internal iliac
label the anatomy
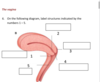
from top clockwise
internal os
posterior fornix
external os
vagina
anterior fornix
label the ligaments of the pelvic floor

top down:
pubocervical
transverse/cardinal
uterosacral
label the muscles of the pelvic floor

from top anticlockwise
ischiocavernosus
bulbospongiosus
perineal body
superficial transverse perineal muscle
label the deep muscles of the pelvic floor

top down
puborectalis
pubococcygeus
iliococcygeus
coccygeus
give the deep and superficial muscles of the pelvic floor
deep- puborectalis, coccygeus, iliococcygeus, pubococcygeus
superficial- ischiocavernosus, bulbospongiosus, perineal body, superverse transverse perineal muscle
what muscles make up levator ani
puborectalis, pubococcygeus, and iliococcygeus
venous drainage of ovaries, uterus, cervix, vagina
L ovary- ovarian, L renal
R ovary- ovarian, IVC
uterus- uterine venous plexus, internal iliac
cervix- uterine venous plexus, internal iliac
vagia- vaginal venous plexus
lymphatic drainage of ovaries, uterus, cervix, vagina
ovaries- paraaortic
uterus- external and internal iliac, para aortic
cervix- internal iliac/sacral
vagina- internal and extrenal iliac
which ligament is a remnant of gubernaculum
ovarian and round
normal position of uterus
anteverted and anteflexed
what do vas deferens and uterus develop from
vas deferens- mesonephric duct
uterus- paramesonephric duct
where do FSH and LH act, female and male
FSH
- male at sertoli cells to produce sperm and inhibin
- female at granulosa cells to produce oesterogen and inhibin
LH
- male at leydig cells to produce testosterone
- female at theca interna cells to produce progesterone and androgens
define
gonadarche
menarche
thelarche
adrenarche
gonadarche- activation of repro glands by FSH/LH
menarche- first periods
thelarche- onset breast development
adrenarche- adrenal activation
3 things that control timing of puberty
pineal gland, leptin, body weight
when does puberty start/male and female
male- 9-14
female- 8-13



