Renal Physiology Flashcards
What is a nephron?
It is a basic structural and functional unit of the kidney.
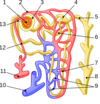
Name the components of the nephron.

As per diagram:
- Glomerulus, 2. Efferent arteriole, 3. Bowman’s capsule, 4. Proximal convoluted tubule, 5. Cortical collecting duct, 6. Distal convoluted tubule, 7. Loop of Henle, 8. Papillary duct, 9. Peritubular capillaries, 10. Arcuate vein, 11. Arcuate artery, 12. Afferent arteriole, 13. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
What is the purpose of the nephrons?
To regulate the concentration of water and soluble substances by filtering the blood, reabsorbing what is needed and excreting the rest as urine. A nephron eliminates wastes from the body, regulates blood volume and blood pressure, controls levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and regulates blood pH.
What is glomerulus?
It is a dense network of capillaries within the Bowman’s capsule where filtration occurs.
What is Bowman’s capsule.
It houses the glomerulus and is a space where the filtered water and solutes from the glomerulus enter.
What are the 3 layers of the glomerular capillary membrane that make up the filtration barrier and their characteristic?
From inner to outer:
endothelium: have holes called fenestrae for filtration
basement membrane: meshwork of collagen and proteoglycan fibrillae
epithelium (podocytes): These cells are not continuous but have long footlike processes (podocytes) that encircle the outer surface of the capillaries. The foot processes are separated by gaps called slit pores through which the glomerular filtrate moves.
What substances are not filtrated by the glomerular capillaries and what allows the glomerulus to be selective in its filtration?
Macromolecules such as proteins and RBCs (>50-100 angstrom), microsolutes such as calcium that are bound to proteins, and negatively charged particles (both macro and micro solutes) are not easily filtered due to their large size and/or electrostatic repulsion created by the negatively charged characteristic of the basement membrane of the glomerulus.
(Size and electrical charge determine filterability)
How does the blood enter into and exit out of the glomerulus?
Enters into the afferent arteriole and exits through efferent arteriole.
(Both are arteries and not vein)
What is responsible for creating the negative charge in the basement membrane of the glomerulus capillary membrane?
glycoproteins
What is GFR and its normal value?
It is the volume of plasma that is filtered from the glomerulus per minute.
120mL/min
What percentage of the CO is the renal blood flow and what is its volume?
20% of CO (1200mL/min)
The kidney receives the second highest percentage of CO, after the liver.
How much percentage of the glomerular filtration is converted to urine?
~1%
What four factors determine GFR?
1.The ultrafiltration coefficient
•This depends on capillary permeability and surface area available for filtration
2.Oncotic pressure
•Since there should be no free protein in Bowman’s Space the net direction of this force should oppose filtration
3.Net hydraulic pressure
•Drives fluid from capillaries into Bowman’s Space
4.Capillary plasma flow rate
•Higher flow = greater filtration
What is the net filtration pressure in the glomerulus?
+10mmHg
How does the factors below affect GFR?
glomerular capillary filtration coefficent
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure
glomerular capillary colloiod osmotic pressure
glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure
Increase in:
glomerular capillary filtration coefficent: increases filtration
Bowman’s capsule hydrostatic pressure: decreases filtration
glomerular capillary colloid osmotic pressure: decreases filtration
glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure: increases filtration
What three variables affect glomerular hydrostatic pressure?
(1) arterial pressure
(2) afferent arteriolar resistance
(3) efferent arteriolar resistance

