Renal: Gross Anatomy-Fletcher Flashcards
1
Q
The urinary System consists of?
A
- Kidneys (paired)
- Ureter (paired)
- Urinary Bladder
- Urethra
2
Q
Where is the urinary system located?
A
- Abdominal Cavity
- Pelvic Cavity
- Perineum
3
Q
Functions of the Urinary System
A
- Eliminate Nitrogen waste products
- Homeostatic regulation
- blood volume
- Acid-base Balance
- Synthesize hormones
- erythropoietin
- renin
- Coversion of Vitamin D to active form
4
Q
Where is the kidney located?
A
- Both sides of the vertebral column
- superior part of posterior abdominal wall
5
Q
Kidney
A
- Retroperitoneal
- surrounded by thick layer of fat
- Right kidney more inferior than left
- due to liver
- Lateral border
- rounded
- medial border
- concav notch=hilum-entrance to interior
6
Q
Renal Relationships
(Kidneys)
A
- Left kidney
- suprarenal gland
- stomach
- spleen
- pancreas
- splenic flexure of colon
- descending colon
- jejunum
- Right Kidney
- suprarenal gland
- right lobe of liver
- descending part of duodenum
- hepatic flexure of colon

7
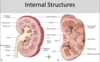
Q
Internal Structures
A
- Medulla
- inner layer
- dark-striated conical renal pyramids
- apices toward hilum
- contains:
- loop of Henle
- Distal Collecting tubules
- Cortex
- outer layer
- pale-granular
- contains:
- renal corpuscles
- proximal & distal convoluted tubules
- proximal collecting tubules
- Renal Columns
- extension of cortex b/w renal pyramids
- contain:
- blood vessels
8
Q
Draw Microanatomy of Medulla/Cortex of kidney
A

9
Q
Kidney: Collecting System
A
- Collecting ducts
- in renal pyramid
- point towards renal papilla (apex of pyramid)
- Minor calyces
- merge to form major calyx
- Major calyces
- merge to form funnel-shaped renval pelvis
- Renal Pevlis
- narrows to form ureter
- Renal sinus
- area containing:
- renal pevlis
- renal calyces
- major branches of renal vessels
- area containing:
10
Q
Ureter
A
- Retroperitoneal
- muscular tube
- 25 cm long (10 inches)
- Location
- proximal half-abdomen
- distal half-pelvis
- Passes:
- anterior to common iliac vessels when entering pelvis
- in females:
- ovary & uterine cervix
- in males:
- ductus deferens and seminal gland
- Takes urine through peristalsis to posterior aspect of urinary bladder
- passes oblique through bladder wall
11
Q
Path of ureter
A
- Passes:
- anterior to common iliac vessels when entering pelvis
- in females:
- ovary & uterine cervix
- in males:
- ductus deferens and seminal gland
- Takes urine through peristalsis to posterior aspect of urinary bladder
- passes oblique through bladder wall
12
Q
Renal & Ureteric Calculi
A
- Intermittent or complete bloackage of flow
- severe pain in lumbar and inguinal regions
- occurs most often at:
- renal pevlis-ureter junction
- pelvic brim
- bladder wall
13
Q
Urinary Bladder
A
- Hollow muscular sac
- Location
- posterior to pubic symphysis
- anterior to rectume
- vagina in females
- Receives, stores and expels urine
- Superior surface-peritoneum
- inferior neck (tapered part)
- leads into urethra
- rests on prostate
- Interior characterized by:
- rugae (folds)
- except smooth triangular area (Trigone) bounded by ureteric opening and internal urethral orifice
- rugae (folds)
14
Q
Urethra
A
- Tube used to void urine
- & discharge semen in males
15
Q
Male Urethra
A
- 20cm long
- 4 parts
- preprostatic
- in bladder wall
- prostatic
- passes thru prostate
- ends at external urethral sphincter
- receives ejaculatory ducts
- Intermediate/membranous
- passes thru external urethral sphincter
- spongy/penile
- psses thru penis
- ends at external urethral orifice on glans penis
- preprostatic
16
Q
Female urethra
A
- 4 cm long
- corresponds to non-spongy part of male urethra
- closely associated with anterior vaginal wall
- ends at external urethral orfice in vestibule of vagina
17
Q
Kidney Developement
A
- 3 sets of kidneys develop from intermediate mesoderm
- Pronephros
- Mesonephros
- Metanephros
18
Q
Pronephros
A
- Form in cervical region
- degenerates during 4th week
19
Q
Mesonephros
A
- Forms in Thoracolumbar region
- late 4th weeks
- duct opens into cloaca
- distal dilated hindgut
- Degenerates entirely in females
- duct remains in males and becomes apart of reproductive system
20
Q
Metanephros
A
- Definitive kidney
- form in sacral region
- 5th week
- begins as diverticulum (Ureteric bud) from caudal end of mesonephric duct
- grows into condensation of mesoderm=metanephrogenic blastema
- stalk of ureteric bud
- lengths to form ureter
- bud undergoes repeated divisions to form:
- renal pelvis
- calyces
- colecting ducts
- Bastema cells form
- non-vascular part of renal corpuscles
- convoluted tubules
- loop of henle
21
Q
Positional changes of kidney
A
- Week 6-9
- kidney move cranially to lumbar
- caudal to suprarenal glands
- Receives blood from:
- common iliac arteries
- aorta
- New renal arteries form
- caudal renal arteries degenerate
22
Q
Urinary Bladder: Developement
A
- urorectal septum
- divides cloaca into:
- ventral urogenital sinus
- dorsal rectum
- divides cloaca into:
- Ventral Urogenital Sinus
- cranial vesical part
- forms bladder
- Endoderm of sinus
- forms epithelium
- Adjacent mesoderm forms:
- muscles
- Connective tissues
- cranial vesical part
- As bladder enlarges
- dorsal wall absorbs distal end of mesonephric ducts
- ureters open seperately into bladder
23
Q
Urethra: Developement
A
Uorgenital Sinus
- Middle Part
- Females–forms entire urethra
- Males forms:
- preprostatic
- Prostatic
- Intermediate urethrae
- Inferior Phallic part
- Males:
- spongy-penile urthrea after incorporated into penis
- Males:
- Distal part of spongy urethra develops from:
- ECTODERMAL CELLS
- forms canal


