RENAL Flashcards
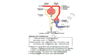
body fluid “60-40-20” RULE
60% of BW: Water
40% of BW: ICF
20% of BW: ECF (INTERSTITAL FLUID 15%, PLASMA 5%)
Marker for Total Body Water
MArker for ECF

Marker for plasma

Marker for IF
MArker for Intercellular fluid

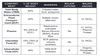
Explain thr volume and concentration changes across compartments during LOss of Isotonic fluid ie Diarrhea
ECF volume: decrease
ECF osmolarity : no change
ICF volume: no change
ICF osmolarity: no change
Explain the volume and concentration changes across compartments during excess fluid ie Infusion of isotonic fluid
ECF volume: increase
ECF osmolarity : no change
ICF volume: no change
ICF osmolarity: no change
Explain the volume and concentration changes across compartments during volume contraction ie Loss in dessert
ECF volume: decrease
ECF osmolarity : no change
ICF volume: no change
ICF osmolarity: no change
Explain the volume and concentration changes across compartments during Volume expansion ie Excessive NaCl intake
Explain the volume and concentration changes across compartments during Adrenal sufficiency ie decrease Aldosterone secretion
Aldosterone: inc Na reabsorption along with water.
Decrease aldosterone levels would reselt in salt and water wasting
ECF volume: decrease
ECF osmolarity : no change
ICF volume: no change
ICF osmolarity: no change
Explain the volume and concentration changes across compartments during SIADH
ECF volume: increase
ECF osmolarity : decrease
ICF volume: increase
ICF osmolarity: decrease
Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH) is characterized by excessive unsuppressible release of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). Unsuppressed ADH causes an unrelenting increase in solute-free water being returned by the tubules of the kidney to the venous circulation
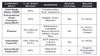
Workhorse of the Nephron
PCT
Reabsorption in the PCT
66% of filtered Na, K, H20
100% of filtered glucose and amino acids
most susceptible to hypoxia and toxins
PCT
Loop of HEnle
Descending Limb
permeable to water
Impermeable to solutes
loop of henle
Ascending limb
- permeable to solutes
- impermeable to water
where does NA K 2Cl transport located
Thick ascending limb of henle also called Diluting segment
Also called Cortical diluting segment and the site for macula densa
Early Distal tubule
Site of action of Aldosterone
Late distal tubule
Cells contain in the LAte Distal TUbule
Principal cells and Intercalated cells
Pricipal cells REABSORB AND SECRETE?
reabsorb : Na
Secrete: K
Intercalated cells reabsorb and secrete?
reabsorb : K
Secrete: H
Role of ADH
↑ ADH → ↑ AQP-2 channels → ↑water reabsorption
- Results in ↑ intravascular volume → ↑VR, CO, BP
- Results in ↓ urine volume, ↑ urine concentration
Movement from Glomerular Capillaries to Bowman’s Space
GLomerular filtration

Movement from Tubules to Interstitium to Peritubular
Capillaries
(Tubular) Reabsorption