Regulation of gene expression Flashcards
what are three reasons for gene regulation?
adaptation
development
conservation of energy
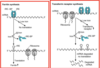
A Zinc finger is the target of a drug. What is being stopped inside the cell?
Zinc finger = protein motiff
- each of two Zn fingers of the estrogen receptor contains Zn ion coordinated with 4 cysteine residues
- binds a specfic DNA in the major groove- nucleotide recognition signal
elucidate the mechanism of mRNA editing on protein function
regulation of Gene expression in prokaryotes. give three scenerios
- Lac operon
- No glucose/ lactose–or—only glucose
- no Lac operon
- Glucose and Lactose
- Increase Lac operon expression
- No cAMP-CRP expression
- w/o coactivator transcription is low
- No glucose but Yes to Lactose
- allolactose activates repressor
- increase Lac operon
- Yes cAMP-CRP
- No glucose/ lactose–or—only glucose
when Trp is high in the bacterial cell the Trp expression is
low, b/c Trp is a corepressor. terminates transcription
what can activate a set of genes?
inducer-
what can activate many genes with common regulatory elements?
Transcription factor
what is the transcription level of the DNA when part of the promoter on a nucleosome?
there will be no transcription if a promoter region is a part of a nuclesome
when genes are activly transcribed only on paternally or maternally inherited chromosomes
genetic imprinting
what occurs when the lysine are methylated and acetylated?
gene expression occurs
what happens when lysine is acetylated and serine is phosphorylated?
genes are expressed
what occurs in histones for heterochromatin and silencing of gene expression?
methylation of the lysine

trimethylation of H3 lysine9 attracts
heterochromatin-specific protein (HP1)
which induces a spreadin wave of Lys9 trimethylation followed by further HP1 binding
what is involved in increasing and decreasing acetylation in histones?
HATs -add acetyl groups on
HDACs - remove acetyl groups
inactivation of the X c’some in a female is an exapmle of
genetic imprinting
After examining the chromosomes of a patient you see excessive silencing of genes on both copies of the chromosome 15. The child has an insatiable appetite and low muscle tone
prader willi syndrome-
- paternal c’some 15 is silenced.
- this is a complication because the maternal 15 csome is normally silenced
- three possible scenerios
- imprinting- 1%
- maternal uniparental disomy 29%
- deletion of paternal region 70%