Regulation of blood pressure + flow Flashcards
Describe the distribution of cardiac output at rest and how this changes during exercise
Gut gets a lot of the blood supply when resting
Gut > kidneys > skeletal muscle > bone/brain > skin > heart

Name each part of the blood vessel structure

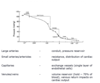
Name the blood vessels in order of their pressure starting from the highest
Blood pressure os determined by the relationship between CO + TPR (total peripheral resistance)
Calculate mean arterial blood pressure + cardiac output
MAP = CO X TPR
CO = stroke volume X heart rate
Describe the role of myogenic mechanisms in controlling vascular resistance

Describe the role of endothelium-derived vasoactive factors in controlling vascular resistance
Endothelium-derived vasorelaxants
- prostacyclin
- nitric oxide
- endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factor
Endothelium-derived vasconstrictors = endothelin
Describe the factors involved in controlling coronary blood flow and the consequences of reduced blood flow to cardiac tissue
Neural = minor direct influence
- SNS stimulation causes beta-mediated increase in HR + stroke volume which increase oxygen consumption
Local = major influence of metabolites
- hypoxia, hypercapnia, adenosine cause vasodilatation
Hormones
- adrenaline - vasodilator, stimulates metabolism
Describe the role of sympathetic nerves in controlling vascular resistance
When the SNS is activated, synaptic vesicles release noradrenaline.
Noradrenaline binds to alpha1 receptors = vasoconstriction
Noradrenaline binds to beta2 = vasodilatation
ATP + NPY = vasoconstriction
Describe the consequences of reduced blood flow to cardiac tissue
If flow cannot be maintained (e.g. by blockage of a coronary artery) then ischaemia, pain results (angina). Worst case outcome is complete blockage leading to myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Describe the cardiovascular consequences of moving from a supine to a standing position

Describe the role of the renin-angiotensin system in the long-term regulation of blood pressure



