Red & White Lesions- Dr. Flores Flashcards
Frictional Hyperkeratosis
- occurs in areas that are commonly traumatized
- chronic rubbing or friction
- lips
- lateral tongue
- buccal mucosa
- macrophages & epithelial cells produce IL-8
- causes overexpression of keratinocyte chemokine (KC)

What condition?

Frictional Keratosis
(hyperkeratosis without dysplasia)
Management of a white lesion suspected to be from mechanical irritation
- remove source of irritation
- will regress in absence of stimulus
- patient returns in 2-3 weeks
- If lesion has not regressed=biopsy
What condition?

Frictional Hyperkeratosis
Leukoplakia
- when you cannot
- identify source of white lesion
- diagnose as any other condition
- White lesion that does not rub off
- Clinical TERM only
- no diagnostic meaning
- never seen on biopsy report as diagnosis
- no diagnostic meaning
- most common premalignant oral manifestation-85%
Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis
- on edentulous alveolar ridge
- Hyperkeratosis w/o dysplasia
- similar to frictional hyperkeratosis
- usually in patients who do not wear dentures
- retromolar pod
- Hyperkeratosis w/o dysplasia

Hairy Tongue
- overgrowth of the dorsal tongue
- filiform papillae
- Predisposing factors:
- Broad spectrum antibiotics
- oxygenating mouth rinses
- smoking
- radiation
- stem cell transplant
- Management:
- identify & eliminate predisposing factor
- improve oral health
- tongue scraper

What condition?

Benign Alveolar Ridge Keratosis
What condition?

Hairy Tongue
What condition?

Hairy Tongue
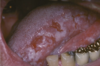
Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis
- Associated with
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- most common malignancy from smokeless tobacco
- Verrucous carcinoma
- snuff dipper’s canncer
- uncommon
- low-grade malignancy
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Clinical features
- stretching reveals snuff pouch (tobacco pouch)
- soft fissured gray-white lesion that blends in with surrounding mucosa
- induration (hardened), pain, and ulceration are NOT associated
What condition?

Smokeless Tobaccoo Keratosis
What condition?

Smokess Tobacco Keratosis
What condition?

Smokeless Tobacco Keratosis
Oral Submucous Fibrosis
- Pale, Marble-like stiff mucous in betel quid users
- precancerous condition
- Chief complain
- trismus and generalized oral burning sensation
- intolerance to spicy foods
- Betel Chewers Mucosa
- not precancerous
- Brown-red mucosa
- Betal quid lichenoid lesions
- tooth staining
- attrition
- perio

What condition?

Oral Submucous Fibrosis
Nicotinic Stomatitis
- aka Smoker’s Palate
- associated with tobacco smoking
- develops in response to the heat
- Dry mud apperance
- Palatal mucosa is grey w/numerous pappules w/red center
- Reverse smoker’s palate
- should resolve w/stopping in 1 month

What condition?

Nicotinic Stomatitis (Aka Smoker’s Palate)
What condition?

Nicotinic Stomatits (smoker’s palate)
What condition?

Nicotinic Stomatitis (smoker’s palate)
Actinic Cheilitis
- Actinic Cheilosis
- farmer’s lip
- sailor’s lip
- common premalignant alteration of LOWR LIP Vermilion
- results from long-term UV exposure
- Clinical:
- rare in younger than 45 y.o.
- Males 10:1
- slow developing lesion
- overtime Scaly lesion develops sometimes w/ulceration
- suggests SCC
What condition?

Actinic Cheilitis
What condition?

Actinic Cheilitis
White Sponge Nevus
- aka Cannon Disease
- mutation- Keratin 4 & 13
- white plaque on buccal mucosa, nasal, and anal mucosa
- Unique:
- eosinophilic condensation in perinuclear region of cells in superficial layers of epithelium