Red Eye Flashcards
1
Q
Acute angle closure glaucoma
A
- Severe pain (may be ocular or headache)
- Decreased visual acuity, patient sees haloes
- Semi-dilated pupil
- Hazy cornea

2
Q
Anterior uveitis
A
- Inflammation of the anterior part of the uvea (involves the iris, ciliary body and choroid)
- Presentation:
- Unilateral symptoms
- Dull, aching painful red eye
- Ciliary flush
- Acute onset
- Blurred vision and photophobia
- Floaters and flashes
- Small, fixed oval pupil, ciliary flush
- Excessive tear production
- Acute associated with HLA-B27 conditions:
- IBD
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Reactive arthritis
- Chronic associated with:
- Sarcoidosis
- Syphilis
- Lyme disease
- TB
- HSV
- Management:
- Steroids
- Cycloplegic-mydriatic medications (i.e. cyclopentolate, atropine)
- Immunosuppressants (i.e. DMARDs, TNF inhibitors)
- Laser therapy, cryotherapy or surgery in severe cases

3
Q
Scleritis
A
- Inflammation of the full thickness of the sclera - more serious than episcleritis
- Presentation:
- Severe pain (may be worse on movement) and tenderness
- Photophobia
- Eye watering
- Reduced visual acuity
- Abnormal pupil reaction to light
- Tenderness to palpation of the eye
- May be underlying autoimmune disease:
- RA
- SLE
- IBD
- Sarcoidosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangitis
- Can lead to perforation of the sclera
- Management:
- Consider underlying systemic condition
- NSAIDs
- Steroids
- Imunosuppression

4
Q
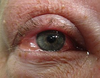
Conjunctivitis
A
- Purulent discharge if bacterial, clear discharge if viral
- Roughly divides into three:
- Viral (adenovirus, HSV)
- Bacterial (S. aureus, S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae)
- Allergic (hypersensitivity to specific airborne allergens)
- To differentiate
- Bilateral vs unilateral
- Onset
- Discharge
- Swabs to diagnose
- If allergic treatment involved:
- Identify allergen and eliminate
- Mild: artifical tears (dilutes allergen)
- Moderate: Mast cell stabilizer or topical antihistamine; and oral antihistamine (i.e. chlorphenamine)
•Severe: add short course of topical steroids
5
Q
Subconjunctival haemorrhage
A
- Rupture of vessels within the conjunctiva and release of blood between that and the sclera
- Hx of trauma or coughing bouts
- Conditions which predispose include:
- HTN
- Bleeding disorders
- Whooping cough
- Medications (warfarin, NOACs, antiplatelets)
- NAI
- Management:
- Harmless and resolve within 2 weeks
- Important to consider potential causes

6
Q
Endophthalmitis
A
- Typically red eye, pain and visual loss following intraocular surgery
7
Q
Orbital cellulitis
A
- Usually systemically unwell with fever
- Lid and conjunctival swelling, proptosis, restricted eye movements and tenderness over sinuses, RAPD present, reduced visual acuity and reduced colour vision
- Mortality from sepsis, cerebral abscess, meningitis, orbital or periorbital abscess and cavernous venous thrombosis
- Bloods and cultures alongside CT orbits/sinuses/brain
- IV antibiotics and ENT assessment for sinus drainage

8
Q
Herpes keratitis
A
- Viral infection with HSV
- Presentation:
- Painful red eye
- Photophobia
- Vesicles around the eye
- Foreign body sensation
- Watering eye
- Reduced visual acuity
- Diagnosis:
- Fluorescein stain showing dendritic corneal ulcer (image shows a dendrite)
- Slit lamp examination
- Corneal swabs or scrapings for culture or PCR
- Management:
- Aciclovir
- Ganciclovir
- Topical steroids

9
Q
Corneal ulcer/abrasion
A
- Causes:
- Contact lenses
- Foreign bodies
- Finger nails
- Eyelashes
- Entropion (inward turning eyelid)
- Presentation:
- Hx of contact lens or foreign body
- Painful red eye
- Foreign body sensation
- Watering eye
- Blurring vision
- Photophobia
- Diagnosis:
- Fluorescein stain - yellow stain collects in abrasions/ulcers
- Slit lamp examination
- Management
- Simple analgesia
- Lubricating eye drops
- Antibiotic eye drops (i.e. chloramphenicol)
- Another appointment to check healed (7 days time)

10
Q
Trauma
A

11
Q
Orbital vs preseptal cellulitis
A

12
Q
Differential diagnosis of red eye
A
- Painless Red Eye
- Conjunctivitis
- Episcleritis
- Subconjunctival Haemorrhage
- Painful Red Eye
- Glaucoma
- Anterior uveitis
- Scleritis
- Corneal abrasions or ulceration
- Keratitis
- Foreign body
- Traumatic or chemical injury
13
Q
Episcleritis
A
- Benign and self-limiting inflammation of the episclera
- Presentation:
- Typically not painful but can be mild pain
- Segmental redness
- Foreign body sensation
- Dilated episcleral vessels
- Watering of eye
- No discharge
- Management:
- Usually self-limiting
- Simple analgesia
- Cold compresses
- Safety-net advice


