Reading 53 - Option Markets and Contracts Flashcards
(40 cards)
What does a fiduciary call portfolio consist of?
- A long position in a European call option
- A long position in a pure-discount riskless bond
**gets its name because it is faithful to the notion of preserving capital**
What does a protective put portfolio consist of?
- A long position in a European put option
- A long position in the underlying stock
What is the formula for put-call parity for European options?
***Critical Concept****

What is the general formula used to solve any “synthetic” options?

What are the steps to creating a synthetic European call option?
- Buy a European put option on the same stock with the same exercise price (X) and the same maturity (T)
- Buying the stock
- Short the present value of X worth of a pure-discount riskless bond
What are the steps to creating a synthetic European put option?
- Buying a European call option
- Shorting the stock
- Buying (i.e. investing in) the pure-discount riskless bond
What are the steps to creating a synthetic stock position?
- Buy a European call option
- Short (i.e. writing) a European put option
- Buying ( i.e. investing in) the pure-discount riskless bond
What are the steps to creating a synthetic pure-discount riskless bond?
- Buying a European put option
- Buying the stock
- Shorting (i.e. writing) a European call option
A 1 yr call option on Cross Reef Inc. with an exercise price of $60 is trading for $8. The current stock price is $62. The risk-free rate is 4%. Calculate the price of the synthetic put option implied by put-call parity.

What are 2 reasons why investors might want to create synthetic positions in securities?
- To price options by using combinations of other instruments with known prices
- To earn arbitrage profits by exploiting relative mispricing among the four securities. If put-call parity doesn’t hold, an arbitrage profit is available.
What is the equation we use to calulate the the size of the Up (U) or Down (D) of the possible price changes in a binomial option model?
Either the U or D will be given. The equation to solve for the other is:
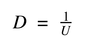
How do you calculate the risk-neutral probability of an up-move or down-move binomial option model?
***Critical Concept****
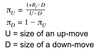
What are the 3 steps in calculating the value of an option on a stock?
- Calculating the payoff of the option at maturity in both the up-move and down-move states
- Calculating the expected values of the options in one year as the probability-weighted average of the payoffs in each state
- Discounting the expected value back to today at the risk-free rate.
Use the attached binomial tree to calculate the value today of a one-yr call option on the stock with an exercise price of $30. Assume the risk free rate is 7%, the current value of the stock is $30, and the size of an up-move is 1.333.


How is an option’s delta calculated?
***Critical Concept***
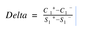
What are the steps in valuing an option using a two period binomial model?
***Critical Concept***
- Calculate the stock values at the end of two periods
- Calculate three possible option payoffs at the end of two periods
- Calculate the expected option values at the end of two periods (t=2) using the up and down move probabilities
- Discount the expected option values (t=2) back one period at the risk free rate to find the option values at the end of the first period (t=1).
- Calculate the expected option value at the end of one period (t=1) using up and down probabilities
- Discount the expected option value at the end of one period (t=1) back one period at the risk free rate to find the option value today.
What are the 3 basic steps to valuing an option on a fixed income instrument using a binomial tree?
- Price the bond at each node using the projected interest rates
- Calculate the intrinsic value of the option at each node at the maturity of the option
- Bring the terminal option values determined in step 2 back to today.
How do you calculate the expiration value of a caplet of European style options???
**Critical Concept***

How do you calculate the expiration value of a floorlet of European style options???
***Critical Concept***

What are the 6 assumptions made in the Black-Scholes-Merton (BSM) model?
- The price of the underlying asset follows a lognormal distribution
- The (continuous) risk free rate is constant and known
- The volality of the underlying aset is constant and known
- Markets are “frictionless” (i.e. no taxes, transaction costs, limits to short selling)
- The underlying asset has no cash flows
- The options valued are European options.
What are the 5 inputs to the BSM model?
***Critical Concept****
- Asset price (Delta)
- Exercise price
- Asset price volatility (Vega)
- Time to expiration (Theta)
- The risk-free rate (Rho)
What are the five sensitivity factors (“greeks”) of the BSM?
- Delta
- Gamma
- Vega
- Rho
- Theta
What does Delta measure?
It describes the relationship between asset price and option price.
* A call option’s delta is positive b/c as the underlying prices increases, so does the call options value
* A put option’s delta is negative b/c the put value falls as the asset price increases.
What does Vega measure?
***Critical Concept****
It measures the sensitivity of the option price to changes in the volatility of returns on the underlying asset.
***Since calls and puts are more valuable the higher the volatility, vega is positive for puts and calls.





