Reactivity of Alkenes Flashcards
(16 cards)
Where do alkenes occur?
What building blocks are they made from?
In plants (essential oils), steroids, lipids

Monoterpines have how many isoprene units? Diterpines?
2, 4
What is the process called when you break large alkanes into smaller alkanes and alkenes?
Cracking
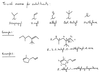
What is the name for 2C, 3C, 4C, and 5C alkenes?

What do you call it when you have…
… 2 CH3 connected to CH?
… CH2 connected via double bond to a CH?
CH2 connected to a CH connected to CH2?
3 CH3s connected to C?
CH2 connected to C?
As two molecules collide, what three forces operate?
Positive charge on one attracts any negative charge on the other (and repels any positive)
Occupied orbitals of one repel occupied orbitals of another
Occupied orbits (especially Highest Occupied Molecular Orbital [HOMO]) of each interact with the unoccupied orbitals (especially Lowest Unoccupied Molecular Orbital [LUMO]) of the other
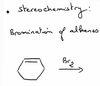
What happens in the electrophilic addition of bromine to an alkene? What does the intermediate look like?
Why does the bromine not attack the bromine of the intermediate?

Bromine is still more electronegative than carbon (the + on the intermediate is about the molecule). Delta+ is therefore on the carbon, which is where the Br- will attack…

Bromination of unsymmetrical olefins - how would the following differ?
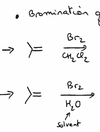
[NB: CH3 groups apparently stabilize the delta+, which is why water preferentially attacks that carbon][It is the “most substituted carbon = carbon of the alkene that is attached to the most carbons (or “fewer number of hydrogens”, if you prefer). the “less substituted” carbon is the carbon of the alkene that is attached to the fewest carbons (or “greater number of hydrogens”)]

What product do you get from the following reaction?



Addition of mercury…
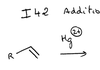

Addition of hydrogen halides: reaction and intermediate step?


Epoxidation: how does an alkene react with m.CPBA?
Why do you get this reaction?

Weak oxygen-oxygen bond (as with Br2)

Epoxidation via m.CBPA: what face of the alkene’s pi bond are the new C-O bonds formed?

Show the homolysis of HCl…

Why does the following difference happen… [addition of HBr to olefins]

[placeholder]


