RACS True/False Quiz 2018 Flashcards
No difference in PROMs, complication or revision rates between mechanical and kinematic alignment TKR groups at 2 years.
True
But long-term data are still lacking
Mechanical alignment in TKR is created by making a femoral cut perpendicular to the anatomical axis of the femur
False
Increased failure rate in patients with femoral components in > 8º of anatomic valgus, in addition to tibial components positioned in > 3º of varus relative to the midline
True
Femoral components in kinematic knee are aligned in 2 to 4º more valgus and tibial components that are positioned in 2 to 4º more varus, while maintaining similar hip-knee-ankle angles
True
Studies show marked difference in Knee Society Scores at 3/12, 6/12, and 5 years postoperatively when compared CAS (computer assisted surgery i.e Navigation) to non-CAS TKA
False
Young and Burgess lateral compression never causes bleeding requiring angioembolization
False
Patterns most commonly requiring angioembolization are the Young and Burgess LC and APC types and Tile type C
Approximately 85% of bleeding associated with pelvic fractures is from veins or bones
True
Ligation of the internal iliac artery during laparotomy is an effective way to control pelvic arterial haemorrhage
False
Due to rich collaterals
Hemodynamic instability on presentation (defined as systolic arterial pressure ,90 mm Hg after an infusion of 2 L of lactated Ringer solution and the initiation of transfusion of packed red blood cells) as an indication to immediately perform angiography with embolization
True
Fractures through the sciatic notch are thought to be associated with a high rate of arterial injury
True
Because of the proximity of the superior gluteal artery
Patients who get embolization after pelvic injury have higher mortality rates
True
Because of substantial high-energy trauma with multiple injuries (Mortality of 16-50% reported)
Survival substantially improves when embolization is performed within 6 hours of arrival
False
Within 3 hours
Name the most commonly embolized arteries in pelvic fractures in decreasing order
Internal iliac & its branches, Sup Gluteal, Obturator, Internal pudendal
Inadequate response to initial resuscitation is very sensitive but not specific to predict arterial bleeding in angiography
True
100% sensitive and 30% specific
Pressures of only 10 mm Hg are require for tamponade of venous bleeding in the pelvis
True
Harder bearings (e.g. cobalt-chromium and ceramics) have lower wear rates than soft bearings because of lower surface roughness and less vulnerability to deformational forces
True
Ultra high–molecular weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) and XLP, have a lower Young modulus of elasticity and therefore exhibit higher deformation under force
False
Higher Young modulus of elasticity
UHMWPE has the highest surface roughness factor resulting in higher frictional forces during articulation and the generation of more wear particles than other bearing surfaces
True
Large cobalt-chromium femoral heads (>32 mm), when coupled with both UHMWPE and XLP, have demonstrated low volumetric wear rates because larger femoral heads have more surface area for articulation
False
Larger surface area= higher volumetric wear
Ceramic on-ceramic implants, given the nature of their smoother surfaces, have the best lubrication performance and can establish fluid-film lubrication at various femoral head sizes
True
Ceramic and metal are hydrophilic which aids in forming fluid film and fluid film lubrication
XLP is irradiated at 200 kGy to increase the cross-linking potential between free radicals
False
50-100. Higher doses will cause breakdown of the mechanical structure
The threshold for osteolysis resulting from polyethylene debris has been considered 0.10 mm/y for linear wear and 80 mm3/y for volumetric wear
True
Trunnion corrosion related to larger femoral head sizes, longer length of trunnion, smaller trunnion diameter, longer neck length, higher taper angle, lower flexural rigidity, and dissimilar alloy pairings
True
The bare area of the glenoid is thought to converge with the center of the inferior glenoid circle
True
Coracoid process transfer procedures act mainly as a bone block to prevent further dislocation
False
Sling effect by the conjoined tendon contributed 76% of the restored stability in the end range of motion & 56% in the midrange of motion
Latarjet procedure proved to be superior to Bristow in the presence of a significant bone lesion
True
Classic Latarjet procedure restored a 30% defect to within 5% of the intact glenoid surface area, whereas the congruent arc modification allowed full restoration to the intact condition
True
Coracoid osteolysis is often observed after anterior glenoid grafting. Osteolysis is usually around the inferior screw & more obvious when the reconstructed glenoid defect is > 15%.
False
More around the superior screw and when the defect is <15%
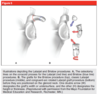
Bony Bankart lesion is seen in 20% of first time and 90% of recurrent dislocations
True
Hill-Sachs lesions, are found in 67% of first-time dislocations and up to 100% of recurrent dislocations
True
15% glenoid bone loss in a patient with off-track lesion is an indication for Latarjet procedure
True

In paediatric ACL injuries peripheral physeal drilling is associated with a lower risk of growth arrest compared with central drilling
False
Central is associated with less risk
In paediatric ACL injury In all epiphyseal technique distal post fixation may distribute a tethering force across the physis
True
The risk of ACL rupture is approximately two to eight times higher in females than in males
True Due to endocrine, biomechanical factors such as increased Q-angle and genu valgum, a high body mass index, unbalanced quadriceps strength, GLL , patella alta, a high tibial slope, and a low notch width index
Non surgical treatment in patients <14 years of age with ACL injury and normal physical exam is not effective
False
Non op Tx: functional bracing, activity modification, and physical therapy
The ACJ is a true synovial joint with the articular cartilage, a capsule, and several stabilizing ligament
True
Patient should start full ROM exercises immediately after ACJ stabilization
False
6/52 in sling then gradually start ROM
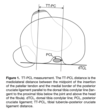
The center of the trapezoid attachment is roughly 26 mm from the ACJ
True
Conoid insertion is 46 mm from lateral end of the clavicle
Stryker notch view allows better visualisation of ACJ
False
Zanca view
Patient with GIII ACJ separation who is still symptomatic after 4/52 of non operative treatment and has media-lateral instability and scapular dyskinesia should be offered surgery.
True
50% of patient post ACJ stabilisation demonstrate some degree of loss of reduction
True
53% to be exact, 20% clavicle or crocoid fracture, 6% infection
Meniscal homologue and any other interposed tissue should be excised after performing clavicle excision in Weaver Dunn procedure
True
Achilles tendon is the largest and strongest tendon in the human body
True
The aponeuroses from each of 2 heads of gastrocnemius muscles combine to form the Achilles tendon, approximately 5-6 cm proximal to the Achilles insertion
True
Achilles tendon fibers undergo a clockwise rotation, imparting maximal stress 2 to 5 cm proximal to the Achilles insertion (hypovascular zone).
False
Counterclockwise
Gastrocnemius-soleus (GCS) provides 83% of the plantar flexion torque to the ankle
False
93%
In patients who have chronic Achilles tendon ruptures that have healed in continuity, a Z-shortening procedure has been described to restore normal tension to the GSC
True
Primary repair of a chronic Achilles tendon rupture with gap <3cm should not be attempted
False
The axis of pull of the FHL tendon most closely replicates that of the Achilles tendon
True
FHL tendon advantages: Stronger than PB or FDL, in phase, in anatomic proximity to TA, Muscle belly of FHL may provide vascularity
Transferring FHL in chronic TA rupture causes no disruption to inversion/eversion
True
Dual-mobility systems increase the jumping distance by decreasing the femoral head offset
True

Osteolysis is uncommon, with wear rates of <0.1 mm/yr.
True
Constrained tripolar designs carry less risk of impingement compaired to non constrained tripolar
False
More risk of impingement
When press-fit constrained acetabular components are used, the shell and the host bone contact area is accepted to be <50%.
False
Must be > 50% in Tripolar otherwise high failure rate at the bone shell interface: type I failure
Retentive failure is a term used specifically for dual mobility cup failure associated with dislocation
True
Constrained liners cause increase wear, ROM and impingement
False
Increase wear and impingement Decreased ROM

Greater trochanteric (GT) pelvic impingement is a GT impingement on the ischium during a combination of hip flexion, abduction, and external rotation
True
Pelvic inclination does not affect loads on the lumbar spine
False
Hip joint disorders that limit terminal hip extension can aggravate symptoms due to hyperlordosis, narrowing of the foramina, and consequent lumbar nerve root compression
True
Sciatic nerve has 28 mm of excursion during hip flexion
True
Hamstring syndrome is the experience sciatic nerve irritation and symptoms in the lower buttock in the presence of Hamstring tear
True
Because of inflammation
The branches from the Sciatic nerve to the long head of the biceps femoris and semitendinosus muscle emerge in the mid thigh
False
Near ischial tuberosity
Pudendal nerve entrapment and/or irritation can occur at different locations such as the intrapelvic region, piriformis muscle at the sciatic notch, sacrospinous ligament and sacrotuberous ligament
True

Deep gluteal syndrome describes the entrapment of the inferior gluteal nerve in the deep gluteal space
False
Sciatic nerve
Structures causing entrapment: Fibrous bands containing blood vessels, gluteal muscles, hamstring muscles, the gemelliobturator internus complex, bone structures, vascular abnormalities, and space-occupying lesions

Long-stride walking test is positive in cases of lesser trochanter impingment on ischium.
True
Pain is produced posteriorly and lateral to ischium

Inbone ankle replacement is designed to be a primary ankle replacement
False
A revision
Inbone ankle replacement has a low survival rate
True
77% survival @ 2years due to talus osteonecrosis secondary to talus reaming
The STAR (Scandinavian Total Ankle Replacement) ankle is the only three piece mobile-bearing design
True
4th generation STAR is showing survival of 70% at 10 years
False
>90%
Second generation total ankle replacement required syndesmosis fusion
True
porous metal-backed surfaces to improve osseous integration; replacement of the tibiotalar, talofibular, and medial-malleolar talar articulations; and/or improved stability with the fusion of the syndesmosis
Minimal bone resection, superior bony ingrowth, retention of ligamentous support, and anatomic balancing are some of 3rd and 4th generation total ankle replacement improvments
True
The revisions for 3rd and 4th generation total ankle replacements were attributed to poly wear and infection.
False
aseptic implant loosening, talar & tibial components subsidence and talar osteonecrosis
Zimmer biomet trabecular metal ankle replacement requires a lateral transfibular approach therefore minimizes wound healing complications
True
It also mimics the natural curvature of the tibiotalar joint and results in less bone removal and more surface area contact.
The average age of patients with ipsilateral femoral neck & shaft fractures is 50 years, and 75% of patients are female
False
The average age of patients is 35 years, and 75% of patients are male
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, ipsilateral knee injury is rare
False
20% to 40% of patients have ipsilateral knee injuries, including ligamentous injury, tibial plateau fracture, patellar fracture, or knee dislocation
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, femoral neck fractures will be always diagnosed on pelvis CT scan
False
Can be missed in CT scan, so special CT scan with fine-cut (2-mm) CT scan through the femoral neck should be considered in addition to fluoroscopic AP in internal rotation after nailing
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, Fixation with a single intramedullary device has a higher rate of malreduction in comparison to two devices
True
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures,The most significant factor to determine the femoral neck non union is the accuracy of reduction
True
Varus malunion has a higher rate of non union (>5 degrees of varus)
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, Miss-a-nail technique is placing the cannulated screws posterior to the antegrade nail.
False
Anterior
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, The risk of malunion or nonunion are less than the risk malunion and non union in pts with isolated neck of femur fractures.
True
5% risk of each of malunion or nonunion in patients with femoral shaft & ipsilateral neck fracture
In patients with ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft faractures, Femoral shaft fracture in this combined injury has a higher rate of non union than isolated fracture
True
20% of non union due to high energy trauma with a higher incidence of compound fractures
15% of patient with femoral shaft fracture as a result of high energy trauma will have ipsilateral NOF #
False
9%
NOF # in ipsilateral neck and shaft fracture are usually a Pauwel type III
True
For NOF # compared to THA, hemiarthroplasty has reduced surgical time, less blood loss, decreased risk of instability, and fewer postoperative complications
True
THA has been shown to produce better pain relief than hemiarthroplasty and is associated with lower long-term reoperation rates
True
THA for hip fractures confers the same risk of complications than elective THA
False
Higher risk
Elderly patients can yield up to 40% reduction in muscle Strength after 4 weeks bed rest
True
Decreased mortality after NOF # is demonstrated when surgery is performed within 48 hours of injury
True
Cemented stems in comparison to cementless show some improved postoperative pain and hip function with less implant-related complications but longer surgical times
True
No statistical differences in mortality, hospital stay, operation time, residual pain, or complications between cemented and noncemented prostheses
True
Remember it is about failed hemiarthroplasty
Chronic institutionalized patients have higher risk of infection 67% caused by gram-positive bacteria
False
Gr-ve
55% of dislocated hemiarthroplasties were observed to have inappropriate femoral offset
True
Posterior approach has been proven to have higher dislocation rates in hemiarthroplasty
False
Leucocyte Esterase (LE) strip test is more sensitive than alpha-defensin test
False
Both are 100% specific
Mortality increases after complications of hemiarthroplasty as infection or dislocation
True
Oblique pulley in the thumb is most important for preventing bowstringing of the flexor pollicis longus
True
Core suture material is relatively unimportant compared with the suture technique
True
The strength of the repair is proportional to the number of core sutures and the caliber of the sutures that cross the repair site
In hand flexor tendon repair Peripheral stitch increased repair strength by 10% to 50% and substantially reduced gap formation
True
In hand flexor tendon repair Adding an epitendinous suture decreased the rate of reoperation by 84%.
True
In hand flexor tendon repair Advancing the tendon 5 mm can cause a quadriga effect
false
>1cm
The midaxial incision in finger should lie parallel and volar to the midline of the finger
False
Dorsal
25% of A2 and all of A4 may be incised with little functional deficit
True
In hand flexor tendon repair Gap formation of >5 mm also decreased the strength of the repair site and led to ultimate failure
True but the figure is more than 3mm of gap
Spaghetti wrist is the term used to describe injury in zone IV or V involving multiple tendons and the median nerve
True