Quantum chemistry- Core 1 Flashcards
(45 cards)
Name the different parts of Bohr atom as shown on the picture.
What are properties of this model?
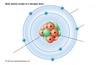
Going clockwise:
Energy level (shell)
An electron (on an orbit)
Neutron (in a nucleus)
Proton (in a nucleus)
Electron behaves as a particle and position is predictable.
What is mass number?
Number of protons + number of neutrons
What is atomic number?
Atomic number is number of protons. It also equals to number of electrons as atom is neutral overall.
Give relative masses and charges for:
proton, electron, neutron
Proton:
Relative mass: 1
Relative charge: +1
Neutron:
Relative mass: 1
Relative charge: 0
Electron:
Relative mass: 1/1840
Relative charge: -1
What determines the chemical properties of an element?
Where do elements with similar chemical properties are usually found?
Chemical properties are determined by electron configuration, so number of electrons in an outer shell.
Elements with similar properties are found in the same group of periodic table.
What is the order of filling orbitals?

What is the difference between a photon and a wave?
A wave is a means of transfer of energy between 2 points without there being any transfer of matter.
A photon is a particle and it is a quanta of energy (discrete packet of energy).
Give me equation relating speed, frequency and wavelength
c=fλ
c= speed of light (3x10^8 m/s)
λ= wavelength (m)
f= frequency (s^-1)
What is frequency?
The amount of times our wave passes through a point in one second.
What is the wavelength?
wavelength is the distance between two consecutive troughs or two consecutive peaks.
Give an equation for energy of a photon.

What are the ranges of wavelengths for each type of light in EM spectrum?

What is spectroscopy all about?
Shining light at a substance and then analysing the light that was absorbed or that comes out.
You get a spectrum.
How is absorption spectrum done?
Gas is heated up and then photons of different wavelengths are emitted as electrons go back to their ground states.
You get series of thin lines on black background.
How is absorption spectrum obtained?
gas is cooled down and then light passes through a substance. Absorption spectrum shows which frequencies of light were absorbed against a broad range of electromagnetic spectrum.
Describe what is meant by quantization of energy levels?
Energy levels are quantized which means that only discrete frequencies can be absorbed or emitted by an atom, which is backed up by having only a few lines recorded on emission or absorption spectra.
Only certain photons excite or de-excite electrons to higher or lower energy levels respectively.
What is rydberg equation? What is it used to describe?
v= RH (1/n21- 1/n22 )
v= frequency (s^-1)
n1, n2= lower energy level and higher energy level
It is used to classify energy difference for every line in
H- EMISSION SPECTRUM
Describe to me wave-like behaviour of an electron in the atom.
- objects that are small can display wave-like properties.
- This is as a consequence of de Broglie equation where sufficiently small mass can produce significant wavelength to observe these properties.
- electrons are spread out and we can’t easily predict their position. We can only use probabilities that they can be found in a volume of space known as orbita.
What is a standing wave? What is the requirement to produce standing wave in an atom?
A standing wave is a stable wave where it interferes with itself constructively. Whole number of wavelengths needs to fit around the circumference of an orbit to produce this stable wave
Give me propreties of waves and describe what are these properties?
Difrraction- when a wave passes through a slit or obstacle, it spreads out. The effect is at its highest if wavelength is similar to the size of an obstacle
Refraction- the wave changes speed after it passes between media with different densities which often results in change in direction
Reflection- a wave bounces off a medium and travels in the opposite direction in the same medium.
Interference- the overall displacement of two waves at a point equals to the vector sum of their individual displacements at a point. They can interfere constructively or destructively.
What is a wavefunction?
A wavefunction describes how an electron wave behaves with position and direction. It is solution to the SchrÖdinger equation.
What is the Bohr interpretation of a wavefunction?
Bohr interpretation of a wavefunction states that if we square a wavefunction at a point in space, it will give us probability of finding an electron at that point in space.
If it is high, the probability is high, if it is low it is quite unlikely.
What is de Broglie equation? Which quantities does it relate?
The de Broglie equation relates wave-like properties (wavelength) to particle like properties (momentum). If particle is sufficiently small in mass, its wavelength will be significant to display wavelike properties

State the Heisenberg uncertainty principle and describe what does it show?
It shows that for a qunatum particle, if we know its momentum (energy) quite well, then we have a large uncertainty in position and we can’t predict it accurately.







