Quantum Flashcards
(41 cards)
1
Q

A

2
Q

A

3
Q
Explain the EPR paradox
A

4
Q
Write a super position over n qubits
A

5
Q
What are qunatum gates?
A
Unitarian matrices
6
Q
Define Unitarian matrix
A

7
Q

A

8
Q

A
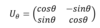
9
Q
Write Not, Z, Cnot, C-U
A

10
Q
How can we apply H on the first cubit?
A
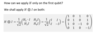
11
Q
What important property does quantum gates have?
A

12
Q

A

13
Q
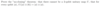
A

14
Q
Describe how, by sending two classical bit and an EPR pair, we can teleportize a state.
A

15
Q
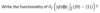
A

16
Q

A

17
Q

A

18
Q

A

19
Q
Describe deutch-Jozsa
A

20
Q
define Simon’s algorithm
A

21
Q
Describe Simon’s algorithm
A

22
Q
What is the conclusion?
A

23
Q
So, how can we find a
A

24
Q

A

25
Why must be such r?

26
what is the relation of the cyclic *r* to **factorization`**

27
Prove


28
Explain the chinese remainder theorem

29


30


31
Describe the superposition given after applying QFT to a super position on m qubits.

32


33
How does it help us with the QFT?


34
Describe the factorization algorithm

35
# define **periodic, period** and **offset.**

36
?What does it tell us if the input vector is periodic?

37


38
What's the problem with the period algorithm?
In step 4 we find the cyclic pattern which enables to use the method for finding the order k, and then to reach r.
Think is, r may not be a power of 2, and thus k won't be an integer.

39
Assume r divides M. what is the chance of hitting a **good** s, an arbitrary s, and what is the change of the gcd of all s's we picked to be different than k.
hitting good s - 1 - certain
hitting specific s - 1/sqrt(k)
different than k gcd of all j's for s tries - k/2^s
40
What if r does not divide M?

41




