Quanta and Waves part I Flashcards
(59 cards)
Under which condition will a wave undergo a phase change of λ/2 upon reflection?
The wave will be travelling from a medium with a lower refractve index and reflected by a medium with a higher refractive index.
A stationary wave pattern is shown below.
What is the wavelength of the wave?

The wavelength is 1m.
(There are three half-wavelengths in 1.5m)
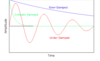
Shown below is an example of a ‘black body radiation curve’ which shows the irradiance of all wavelengths of radiation emitted by an object.
What is the relationship between the ‘peak wavelength’ emitted by an object and its temperature in kelvin?

The shorter the ‘peak wavelength’ of the object, the higher the temperature of the object.
Quantatively, this relationship is known as ‘Wein’s law’ and is given by the relationship
T x λp = 2.9 x 10-3
There exists some well known experimental evidence for wave-particle duality.
Can you name some experimental evidence which shows the
- Particle nature of waves
- Wave nature of particles.
- The photoelectric effect
- Electron diffraction patterns
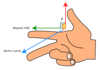
Describe the motion of a charged particle which enters a magnetic field:
- Perpendicular to the field
- Parallel to the field
- At an angle
- The particle will travel with circular motion only.
- The particle will continue with linear motion parallel to the field only.
- The particle will travel with helical motion (circular perpendicular to the field and linear parallel to the field).
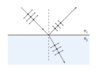
Shown below is an example of interference by division of amplitude- a lens is ‘bloomed’ with a non-reflective coating.
Derive the expression d = λ/4n where ‘d’ is the thickness of coating required to give destructive interference.

Optical PD = λ/2 for destructive interference
also from the diagram, Optical PD = 2nd
therefore
2nd = λ/2
d = λ/4n
The relationship describing a travelling wave is shown below.
y = 4.0 sin2π(8t – 5x)
What is the relationship describing a reflected wave of the same type with half the amplitude, travelling in the opposite direction?
y = 2.0 sin2π(8t + 5x)
What is the relationship between Brewster’s angle and the refractive index of a material?
n = tan ip
What is the condition for destructive interference in terms of optical path difference?
Constructive interference occurs when
Optical path difference = (m+1/2) λ
Describe the effects of damping in simple harmonic motion. Consider:
- Underdamping
- Overdamping
- Critical damping
- The effects of underdamping are quite small and result in a slow reduction in amplitude.
- The damping is so great that no complete oscillations are seen. (sometimes called heavy damping)
- This means that the oscillator comes to rest in the minimum possible time
Describe how aurorae are produced in the earth’s upper atmosphere
Cosmic rays enter the earth’s magnetic field and spiral with helical motion along the field lines until they enter the earth’s atmosphere at the north and south poles.
Collisions with atoms in the earth’s atmosphere produce energy in the form of light, known as aurora. (Borealis, Northern lights. Australis, Southern lights)
Nils Bohr and Louis de Broglie suggested that electrons can be considered as ‘standing waves’ in orbit around the nucleus of an atom.
Using the circumference of an orbit (2πr) being equal to n de Broglie wavelengths (nλ), derive an expression for the quantised angular momentum of an electron.
2πr = nλ
2πr = nh/p (since λ = h/p)
2πr = nh/mv (since p = mv)
mvr = nh/2π
What does it mean if a wave is said to be plane polarised?
The electric field vector (of the light) oscillates in a single plane.
(NOT ‘direction’)
The phase difference (Φ) between two points on a travelling wave separated by a distance of half a wavelength (x = λ/2) is equal to how many radians?
Φ = x/λ x 2π
so if x = λ/2
Φ = π radians.
Starting with the relationships
y = A sin ωt and v = Aω cos ωt
show that the velocity of a particle undergoing simple harmonic motion can be expressed as
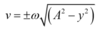
- y = A sin ωt and v = Aω cos ωt
rearranging gives
- sin ωt = y/A and cos ωt = v/Aω
since sin2ωt + cos2ωt = 1
- y2/A2 + v2/A2ω2 = 1
multiplying through by A2ω2
- y2ω2 + v2 = A2ω2
now rearrange for v2
- v2 = A2ω2 - y2ω2
take ω2 out as a common factor
- v2 = ω2(A2 - y2)
square root both sides
- v = ±ω√(A2 - y2)
What is the unit of phase angle, Φ?
Radians (rad).
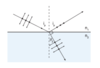
What effect would having a thinner ‘wedge’ (d) have on the spacing between bright fringes (∆x) in the following experiment?

A thinner wedge would make the spacing further apart.

What is the condition for destructive interference in terms of phase?
Two waves meet completely out of phase by half a wavelength- crest meets trough.
The phase difference Φ = π radians.
The relationship shown below can be used to determine the wavelength of a laser going through a double slit.
What effect would be seen on the interference pattern if a smaller wavelength of light was used?
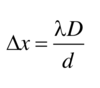
The distance between adjacent bright fringes, Δx, would be smaller (the fringes would be closer together).
The relationship shown below can be used to determine the wavelength of a laser going through a double slit.
Define each of the quantities in the relationship.
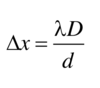
Δx = distance between adjacent bright fringes (m)
λ = Wavelength of the laser light (m)
D = distance from double slit to screen (m)
d = distance between slits (m)
Considering the relationship shown for velocity in SHM, describe the conditions when the velocity is at a maximum and at a minimum.

Velocity is at a MAXIMUM when y = 0 (This simplifies the equation to vmax=ωA).
Velocity is at a MINIMUM (zero) when y = A or -A.
Derive an expression for the kinetic energy of an object undergoing simple harmonic motion.

What is the condition for constructive interference in terms of optical path difference?
Constructive interference occurs when
Optical path difference = mλ
Explain the production of ‘cosmic air showers’ when cosmic rays enter the atmosphere.
The cosmic ray strikes a nucleus creating secondary particles (usually hadrons such as the pion) which in turn collide with other particles and so on creating a ‘shower’ of particles which are detectable a ground level (such as muons, positrons and neutrinos).
‘Cosmic air showers’ provided the very first evidence for sub nuclear particles and the quark model of matter.