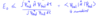QM - Postulates of quantum Flashcards
Describe Ψ
The state of a system is fully described by a mathematical function Ψ called a wavefunction
Give an example of bra ket notation
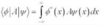
Define a normalisation constant
A normalisation constant N is a constant such that the integral of Ψ(x)Ψ*(x) dx over all space = 1

Define an observable
An observable is a measurable property such as bond length or kinetic energy
State the postulate regarding observables and operators
Every observable B is represented by an operator B̂ and all operators can be built from the operators for position and momentum
Give and describe the operator for momentum
p̂
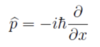
Give and describe the operator for position
x^ = multiply by x
State the hamiltonian
H^ is the total energy operator, T^ is the kinetic energy operator and V^ is the potential energy operator

Show how to derive the expression for kinetic energy
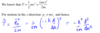
State the general form of an eigenvalue equation
B̂f = bf
Where the operator B̂ acts on the eigenfunction to regenerate f multiplied by the eigenvalue b (a constant)
Define an exact wavefunction of the Schrodinger equation
If Ψ(x) is an eigenfunction of H^, it is termed an exact wavefunction
Describe orthogonal and orthonormal wavefunctions

Give the expectation value for an operator B̂ for a wavefunction Ψ
The expectation value is denoted by and is given below.
Note: dτ symbolises integration over all space
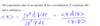
Give if the wavefunction in question is an exact wavefunction, ie an eigenfunction of H^ and also an eigenfucntion of B^ such that B^Ψ = bΨ

Give if the wavefunction in question is normalised

State the Schrodinger equation
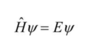
State the postulate regarding
When a system is described by a wavefunction Ψ, the average value of the observable B is equal to the expectation value of the corresponding operator B^
Describe the variation principle
For any trial wavefunction Ψ, the expectation energy can never be less than the energy of the ground state E0