Pulp and Periapical Diseases Flashcards
most common result after trauma
pulp hyperaemia
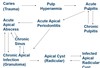
-itis indicates
inflammation
abscess indicates
infection
more severe than -itis (inflammation)
infection spread from pulp
out of pulp chamber through the apex to the apical region
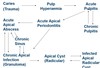
chronic apical abscess from acute apical absess
Abscess can subside so no longer be acute, but still active infection so becomes a chronic infections with flare ups

granuloma is
overgrowth (commonly seen on extraction attached to roots)
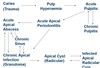
sinus is
infection around apex/abscess which perforates through bone and soft tissues and drains out into mouth
chronic blister/burst
less pain but can leave bad tast - may not be aware of it
cyst development
long term chronic apical granuloma can develop into a cyst - most not all cases, unsure why
can grow large in sizes but is painless

cyst is
fluid filled cavity
do cysts cause pain
when they get infected
4 symptoms of pulp hyperaemia
- Pain lasting for seconds
- Pain stimulated by hot/cold or sweet foods
- Pain resolves after stimulus
- Caries approaching pulp but tooth can still be restored without treating pulp (reversible pulpitis)

6 symptoms of acute pulpitis
- Constant severe pain
- Reacts to thermal stimuli
- Poorly localised pain
- Referral of pain can be very strange
- No/minimal response to analgesics (cannot get into pulp chamber)
- Open symptoms less severe
- Severe gross caries and crown breaks away, release of pressure so pt has less pain

pulp hyperaemia progressed further
how to dx of pulp acute pulpitis
- History – most useful
- Visual examination
- Negative Tenderness to Percussion (usually)
- Pulp testing is ambiguous
- Radiographs
- Diagnostic’ Local Anaesthetic
- Removal of Restorations
acute apical periodontitis dx - how
- Easy to make – can pinpoint
- Tenderness to Percussion – extremely tender, tooth may feel high in the mouth
- Tooth is non-vital (unless traumatic)
- Slight increase in mobility
- Radiographs
- Loss of clarity of Lamina Dura
- Radiolucent Shadow – May indicate an ‘old’ lesion e.g. Flare up of apical granuloma
- Delay in changes at the apex of the tooth
- Widening of apical periodontal space

causes of traumatic peridontitis
parafuction (tooth clenching or grinding)
clenchers will be unaware, grinder will know
dx of traumatic periodontitis
- Clinical Examination of the Occlusion
- Functional positioning
- Posturing
- Tender to Percussion
- No history of trauma
- Normal Vitality
- Radiographs
- May show generalised widening of periodontal space
2 tx of traumatic periodontitis
- Occlusal adjustment e.g. filling too high
- Therapy for parafunction e.g. gum shield/splint, advice on clenching
what is the commonest pus producing infection
acute apical abscess

4 possible pus producing infections in oral cavity
- acute apical abscess - most common
- Periodontal abscess – directly in periodontium, not as result of pulpitis (symptoms similar but tooth still vital)
- Pericoronitis – inflammation around a crown, usually PE 8s
- Sialadenitis – infection of saliva glands (usually major one), symptoms: facial swelling, redness, pus coming out gland
oragnisms involved in dental abscess
- Polymicrobial
- Anaerobes play an important part
Unusual infections
- Staphylococcal lymphadenitis of childhood
- Cervico-facial actinomycosis – rare, very chronic pus producing infection, usually after XLA
how to tell the stage of the abscess
clinical features will reflect the stage of the abscess
- Initially almost identical to Acute Apical Periodontitis (Prior to eroding through bone and into soft tissues)
- Looks for path of least resistance – tends to be mouth, but can be through face

3 symptoms of dental abscess
- Severe unremitting pain
- Acute tenderness in function
- Acute tenderness on percussion
BUT no swelling, redness or heat (yet….)

5 cardinal signs of inflammation
heat
redness
swelling
pain
loss of function
symptoms once the abscess perforates through bone
- Pain often remits (unless it’s in the palate)
- Swelling, redness and heat (in the soft tissues) become increasingly apparent
- As swelling increases pain returns
- There is an initial reduction in tenderness to percussion of the tooth as pus escapes into the soft tissues
sites of swelling due to abscess depends on
- The position of the tooth in the arch
- Root length
- Muscle attachments
-
Potential spaces in proximity to lesion
- Submental Space
- Sublingual Space
- Submandibular space
- buccal space
- Infraorbital Space
- Lateral Pharyngeal Space (a.k.a. Parapharyngeal Space)
- Palate

acute apical abscess tx
Provide Drainage
- Soft tissue incision intraorally
- Soft tissue incision extraorally minimise scarring
- Remove source/cause
- Extract tooth
- Pulp extirpation
- Periradicular surgery unusual
- Providing drainage and eliminating cause is trying to tip the balance to body of winning fight against infection*
- *Need for antibiotics determined by: avoid
- Severity
- Absence of adequate drainage
- Patient’s medical condition
assessment for need for antibiotics
- Local factors
- Toxicity pt systemically unwell, no longer local problem
- Airway compromised
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Trismus (limited mouth opening)
- Lymphadenitis
- Location (worrying areas e.g. floor of mouth – can cause issue breathing)
- Systemic factors
- Immunocompromised pts
- Acquired causes (e.g. HIV – debatable now depend on their tx)
- Drug Induced (e.g. Steroids, Cytostatics)
- Blood disorders (e.g. Leukaemias)
- Diabetes – well controlled should be fine, poorly controlled more likely
- Extremes of age
- Immunocompromised pts
6 local factors for consideration for antibiotic use
- Toxicity pt systemically unwell, no longer local problem
- Airway compromised
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Trismus (limited mouth opening)
- Lymphadenitis
- Location (worrying areas e.g. floor of mouth – can cause issue breathing)
3 systemic factors for consideration for antibiotics
- Immunocompromised pts
- Acquired causes (e.g. HIV – debatable now depend on their tx)
- Drug Induced (e.g. Steroids, Cytostatics)
- Blood disorders (e.g. Leukaemias)
- Diabetes – well controlled should be fine, poorly controlled more likely
- Extremes of age
what is reversible pulpitis
Denotes a level of inflammation in which returning to a normal state is possible if noxious stimuli removed (due to caries, trauma or filling)
Mild-moderate tooth pain when stimulated, no pain without stimulus, subsides within seconds (<5 secs), no mobility, no pain on percussion
what is irreversible pulpitis
Denotes a higher level of inflammation in which dental pulp has been damaged beyond point of recovery
Sharp, throbbing, severe pain upon stimulation, and pain may be spontaneous or occur without stimulation, pain persists after stimulation removed (>5 secs); tx: RCT or extraction
describe periapical granuloma (chronic apical periodontitis)
Mass of chronically inflamed granulation tissue at apex of tooth (plasma cells, lymphocytes, and few histiocytes with fibroblasts and capillaries).
NOT a true granuloma because not granulomatous inflammation! (Note that granulomatous inflammation has epithelioid histiocytes mixed with lymphocytes and giant cells), has no giant cells
what is teh etiology of periapical (radicular) cyst?
7 stages
- Caries, trauma, periodontal disease
- Death of dental pulp
- Apical bone inflammation
- Dental Granuloma
- Stimulation of epitheialial rests of Malassez (by the chronic inflammation in the area)
- Epithelial Proliferation
- Periapical Cyst Formation
it is non vital


