Psychopharmacology Flashcards
When switching from SSRI or SNRI to MAOI, which of the following medications requires a 5-6 week washout period?
A. Paroxetine
B. Sertraline
C. Citalopram
D. Venlafaxine
E. Fluoxetine
E. Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine (Prozac) requires 5-6 week washout period due to its extremely long half-life. All other SSRIs, and SNRIs, and TCAs require a standard 2-week washout period.
MOA: Memantine?
Use?
NMDA receptor antagonist; inhibits glutamate stimulation and theoretically limits overactivation of and toxicity to remaining cholinergic neurons
Used in moderate to severe neurocognitive disorders (dementia)
Which TCA has been found in considerably higher concentrations in breat milk, compared to other medications in the same class?
A. Doxepin
B. Amitriptyline
C. Clomipramine
D. Nortriptyline
E. Nitroxazepine
A. Doxepin
Infant plasma concentrations are considerably higher for doxepin than for other TCAs.

SSRIs cause what type of sexual dysfunction?
Affects both libido and orgasms
SSRI-induced sexual dysfunction occurs in both women and men.
Ginseng’s affect on mental and physical performance when combined pt is on lithium
Ginseng has been reported to interact with certain psychiatric medications (including phenelzine, lithium, and neuroleptics), causing irritability, insomnia, and mania.
What type of symptoms characterizes the toxicity of clomipramine?
Cardiac arrhythmias, convulsions, coma
TCAs block the reuptake of norepinephrine or 5-HT
Pathophysiology of schizophrenia
Overactivity of nigrostriatal and tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic pathways
Nigrostriatal = neurons projecting from substantia nigra to dorsal striatum (caudate and putamen)
Tuberoinfundibular = arises from hypothalamus and projects to pituitary; dopamine released by these neurons inhibits prolactin release from pituitary
What is the most appropriate medication for melancholic depression in the geriatric population?
A. Isocarboxazid
B. Tranylcypromine
C. Doxepin
D. Phenelzine
E. Nortriptyline
E. Nortriptyline
TCAs (doxepin) and MAOIs. (tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine) are more poorly tolerated in geriatric patients and are generally considered second- or third-line agents in this patient population.
However, nortriptyline is still used as a first-line agent for elderly melancholic patients.

An overdose of antipsychotics can lead to seizures. Which of these drugs are the most likely to cause seizures?
A. Haloperidol and olanzapine
B. Olanzapine and aripiprazole
C. Lurasidone and perphenazine
D. Clozapine and chloropromazine
E. Risperidone and asenapine
D. Clozapine and chloropromazine
Clozapine leads to seizures in 4% of patients taking >600 mg. Chlorpromazine is the most likely to cause seizures among typical antipsychotics.
A 45 yo woman presents to ER with diarrhea, diaphoresis, and agitation. She takes citalopram for depression and sumatriptan for migraines. On exam, the patient exhibits involuntary, rhythmic contractions in her lower extremities. At the end of the exam, she says she started a new medication a few days ago. Which of the following medications is most likely contributing to her clinical presentation?
A. Haloperidol
B. Acetaminophen
C. Warfarin
D. Lorazepam
E. Tramadol
E. Tramadol
Centrally acting synthetic opioid analgesic. Binds to mu-opioid receptors and weakly inhibits reuptake of NE and 5-HT. Weak inhibition of serotonin reuptake increases total amount of serotonin in the body. Taking tramadol in combo with citalopram (another serotonin reuptake inhibitor) and sumatriptan (a selective agonist of serotonin receptors) increases the amount of serotonin in the body, causing serotonin syndrome.
Which antidepressant has the greatest evidence of beneficial effects in pts with depressed mood and eating disorders?
A. Sertraline
B. Fluoxetine
C. Bupropion
D. Nortriptyline
B. Fluoxetine
Which antidepressant is least likely to cause significant drug-drug interactions in the elderly?
A. Fluoxetine
B. Paroxetine
C. Sertraline
D. Fluvoxamine
E. Venlafaxine
E. Venlafaxine

Which of the following is NOT a method for maintenance tx of rapid cycling bipolar disorder:
a. Stop the triggering factor(s)
b. Have thyroid status stabilized
c. Lithium monotherapy
d. Valproic acid
e. SSRI
E. Antidepressants, particularly SSRIs, may prompt rapid cycling

MOA: Galantamine
AChE inhibitor and allosteric nicotinic modulator
What prescription medication is approved by the USFDA for treatment of excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and cataplexy associated with narcolepsy?
Sodium oxybate (Xyrem)
Which of the following antidepressants increases dopamine significantly?
A. Duloxetine
B. Trazodone
C. Selegiline
D. Reboxetine
E. Venlafaxine
C. Selegiline
MAOIs like selegiline increase NE, 5HT-3, and DE.
Bupropion has a slight dopamine increase as well.
Most SSRIs increase serotonin predominantly, and TCAs generally increase serotonin and NE.
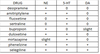
Duloxetine (Cymbalta)
Who is it used for?
Side effects?
Who should avoid it?
- Who is it used for? people with depression, neuropathic pain, and in fibromyalgia
- Side effects? similar to SSRIs but more dry mouth and constipation relating to its norepinephrine effects
- Hepatotoxicity more likely in patients w/ liver disease or heavy alcohol use
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS) reversal?
Bromocriptine (strong dopamine D2 receptor agonist and partial dopamine D1 receptor agonist) or dantrolene (stimulates muscle relaxation by modulating skeletal muscle contractions at a site beyond myoneural junction and by acting directly on the muscle itself)
MOA: Mirtazapine
Tetracyclic compound used in treatment of depression.
It is a noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressant (NaSSA).
Unrelated to TCAs
Blocks presynaptic alpha-2-adrenergic receptor, which results in 5-HT-1A activation and causes an increased release of dopamine
Treatment for enuresis in children
Imipramine (TCA)
Increase the synaptic concentration of serotonin and/or norepinephrine by reuptake inhibition
Carbamazepine is most likely to cause which of the following lab abnormalities?
A. Elevated amylase
B. Elevated potassium
C. Elevated phosphate
D. Low ionized calcium
E. Low sodium
E. Low sodium
SIADH –> hyponatremia
What substance should be avoided in patients who are taking antiplatelet and anticoagulant medications?
Ginkgo biloba
Which of the following medications commonly requires regular monitoring of symptoms like bruising and bleeding?
A. Carbamazepine
B. Levetiracetam
C. Lithium
D. Lamotrigine
E. Topiramate
A. Carbamazepine
These symptoms of bone marrow suppression are caused by carbamazepine and can lead to agranulocytosis or aplastic anemia.
Aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and agranulocytosis occur so rapidly that a daily blood count would be rquired to detect them.
Although not FDA-approved for the treatment of alcohol use disorders, topiramate can reduce the number of heavy drinking days, increase the number of abstinent days, and reduce serum GGT levels, which is an objective marker of alcohol abuse. Topiramate achieves these outcomes by which of the following neuropharmacological pathways?
Antagonizing glutamate and suppressing alcohol-induced dopamine release
When a patient chronically consumes alcohol, the ethanol decreases the firing of GABA neurons. This rxn results in increased release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens, reinforcing habitual alcohol use. These “less-inhibited” GABA neurons cause the ventral tegmental area to be “hyper-excitable.”
Topiramate is an anticonvulsant that can assist in reversing this altered neural pathway. Topiramate is thought to inhibit ventral tegmental area GABA neuronal activity due to increased GABA tone in the nucleus accumbens. At the same time, topiramate also antagonizes glutamate and suppresses the release of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. Reducing dopamine in the nucleus accumbens reduces the “reward” from alcohol use.
Lithium has been associated with which of the following side effects?
a. Eosinophilic colitis
b. Acne
c. Neutropenia
d. Pancreatitis
e. Myocarditis
b. Acne
Neutropenia, myocarditis, and eosinophilic colitis = associated with clozapine
Pancreatitis = rare but potentially deadly side effect of valproic acid
First line agents for ADHD?
Stimulants (methylphenidate and amphetamines)
Although exact MOA in ADHD is unknown, they affect both dopaminergic and noradrenegic systems, resulting in release of catecholamines within CNS
What drug is safe to use with bupropion?
a. Clozapine
b. Theophylline
c. Clomipramine
d. Paroxetine
d. Paroxetine
Paroxetine and other SSRIs are commonly used with bupropion. Bupropion is commonly used. to augment an SSRI or to combat the sexual side effects of SSRIs. Both paroxetine and bupropion inhibit CYP 2D6. Any drug that reduces the seizure threshold like clozapine, theophylline, or clomipramine should be avoided.
Furthermore, the use of stimulants, alcohol,or cocaine increases the risk of seizures when combined with bupropion.
Which medication can cause a false positive for phencyclidine on a urine drug immunoassay due to a similar chemical structure?
A. Amitriptyline
B. Venlafaxine
C. Naproxen
D. Sertraline
E. Trazodone
B. Venlafaxine
- Amitriptyline - LSD
- Naproxen - barbiturates
- Sertraline - benzos
- Trazodone - amphetamines
Best medication to start falling asleep?
a. Ramelteon
b. Trazodone
c. Zolpidem
d. Triazolam
e. Zaleplon
a. Ramelteon
Ramelteon mimics melatonin’s sleep-inducing properties. It has a high affinity for melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors in the brain. The 1/2 life of ramelteon is between 1 and 2.5 hours. Ramelteon reduces time to sleep.
Carbamazepine for bipolar disorder… which of the following tests should be done every 3 months during tx with this drug?
a. Platelet count
b. Serum electrolytes
c. SGOT
d. ECG
e. Urinalysis
c. SGOT
- Aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hepatotoxicity
44 y o woman comes for tx of major depression. BMI is 28. She states she has lost 50 lb in the past year and is determined not to gain it back. Which of the following medications would be best choice to treat her depression, given these circumstances?
a. Amitriptyline
b. Doxepin
c. Nortriptyline
d. Phenelzine
e. Sertraline
e. Sertraline
a 30 yo woman is diagnosed as bipolar. At the same time that this illness is diagnosed, it is discovered that she is pregnant. Which of the following drugs has the highest risk to the fetus?
a. Valproic acid
b. Lithium
c. Chlorpromazine
d. Haloperidol
e. Fluoxetine
a. Valproic acid
Most common side effect of galantamine
A. Headaches
B. GI disturbances
C. Hypotension
D. Visual disturbances
E. Cough
B. GI disturbances
GI side effects are common with the use of galantamine and other cholinesterase inhibitors
First trimester exposure of which SSRI is associated with an increased risk of cardiac defects, atrial and ventricular septal defects?
A. Sertraline (Zoloft)
B. Citalopram (Celexa)
C. Paroxetine (Paxil)
D. Fluoxetine. (Prozac)
E. Fluvoxamine (Luvox)
C. Paroxetine (Paxil)
Which of the following meds can reduce suicidality in pts with bipolar mood disorders?
A. Clozapine
B. Levetiracetam
C. Lithium
D. Paliperidone
E. Valproate
C. Lithium


