Psychiatry - Pharmacy Flashcards
Psychiatric
Pharmacy
Medication Used in Psychiatry?
- Antidepressants
- Mood stabilisers
- Antipsychotics
- Others
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants?
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) – 1st choice
- Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA)
- Serotonin noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (SNRI)
- Noradrenergic & specific serotonergic antidepressants (NaSSAs) – mirtazapine
- Noradrenaline reuptake inhibitors (NARI)
- Monoamineoxidase inhibitors (MAOI)

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants?
Can be used for other mental health illnesses in addition to depression:
- Panic disorder
- Generalised anxiety disorder
- OCD
- PTSD
Cautious use in those with BPAD

Psychiatric Pharmacy
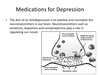
Anntidepressants - MOA

- Change neurotransmitters levels in the brain
- Certain neurotransmitters (i.e. serotonin and norepinephrine) can improve mood and emotion though how and why is not fully understood
- They treat the symptoms of depression, they do not necessarily address causes - usually used in combination with therapy
- ADx have to be taken for at least 3-4 weeks before they notice any improvement in their symptoms, because increasing the levels of neurotransmitters is a gradual process

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Anntidepressants - MOA
SSRIs
- Work by selectively inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin
- Most widely prescribed type of antidepressants, because they cause fewer side effects. Not addictive!
- An overdose is also less likely to be fatal
- Common side effects of SSRIs include:
- Mainly GI e.g. nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea (GI upset)
- Headache
- Insomnia
- Sexual dysfunction
- Anticholingeric - blurred vision, dizziness, sedation, dry mouth
- Insomnia
- Hyponatraemia in elderly
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Anntidepressants - Types of SSRIs

- Fluoxetine
- Citalopram
- Sertraline
- Paroxetine
- Escitalopram
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
Initiation & Discontinuation of SSRIs
- May take a few week to work (trial for at least 4-6 weeks, 6 weeks in older pts, if partial response try for another 2 weeks)
- Stop SSRIs if develop rash and must get help if agitation/suicidal feelings occur
- Patients should be reviewed 1-2 weeks after starting treatment
- After remission of symptoms, continue for at least 4-6 months (12 months in the older patient)
- Maintenance treatment may be needed in those with recurrent depression
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
Serotonin Syndrome

- Occurs within hours of starting SSRI or dose increase
- Restlessness
- Tremor
- Myoclonus
- Confusion
- Headache
- Rapid HR, changes in BP
- Severe cases can be life-threatening – urgent medical attention if high fever, seizures, irregular heartbeat, unconsciousness

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants SSRIs
Discontinuation Syndrome
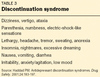
- Irritable/restlessness
- Nausea – “GI chills”
- Paraesthesia
- Ataxia
- Hypomania, anxiety and restlessness
- Reduce the dose gradually over about 4 weeks or so to try to avoid this. In patients who have taken the drug long-term, they may need 6 months or so to withdraw gradually

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
SNRIs
- Newer type of antidepressant
- Works in similar way to SSRIs but reuptake serotonin and noradrenaline
- There are currently two SNRIs prescribed in the UK:
- Venlafaxine
- Duloxetine
- Side effects, cautions and interactions are similar for both SSRIs and SNRIs
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
TCAs
- Older type of antidepressants
- No longer recommended as a first-line treatment
- Can be dangerous if an overdose is taken
- Cause more unpleasant side effects than SSRIs and SNRIs

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
MAOIs

- Older type of antidepressant with a wide range of side effects
- Only to be used if other types of antidepressants are not effective
- Need to avoid certain foods and drinks, such as red wine, older cheeses, pickled fish, which contain a protein called tyramine because consuming tyramine while taking MAOIs can cause a dangerous rise in blood pressure (cheese reaction)

Psychiatric Pharmacy
Antidepressants
Others
- Flupentixol has antidepressant properties when given by mouth in low doses. Flupentixol is also used for the treatment of psychosis
- Mirtazapine a presynaptic alpha2-adrenoreceptor antagonist, increases central noradrenergic and serotonergic neurotransmission. It has few antimuscarinic effects, but causes sedation during initial treatment
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Mood Stabilisers?

- Used to treat bipolar disorder
- They suppress swings between mania and depression
- They are also used in PD and schizoaffective disorder
- The main mood stabilisers are:
- Lithium
- Sodium valproate (as semi-sodium)
- Carbamazepine
- Lamotrigine
- Other drugs used as mood stabilisers:
- Benzodiazepines
- Antipsychotic drugs

Teratogenic!
Psychiatric Pharmacy
Mood Stabilisers?
Lithium

- Lithium is the “classic” mood stabiliser
- Therapeutic drug monitoring is required to ensure lithium levels remain in the therapeutic range: 0.6- 0.8-1.2mmol/L.
- Signs and symptoms of toxicity include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and ataxia (lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements)
- Side effects are:
- Polyuria/polydipsia
- Lethargy, tremor, sedation
- Weight gain
- Blurred vision
- Hair loss
- Cardiac problems
- Long-term effects: subclinical hypothyroidism