Psych Soc Flashcards
Social Loafing
- tendency that people have to put in less effort in a group setting
- especially true when group is evaluated on a whole
“foot-in-the-door technique” of persuasion
- involves getting a person to agree to a small request, followed by makeing a much larget request
- Ex: asking customer to purchase small item in store, followed by making a much larger request to buy something else
Heuristics
- refers to mental shortcuts or simplified iterations of principles that can help us make decisions, but can also lead to poor judgement
If Weber’s law states that a subject detects a noticable difference when shifting from 5kg to 8kg mass, how many kg must be added to a 15kg mass to replicate effect?
A) initial ratio = [5:8]
B) new ratio = [15:24] – ∴ a 9 kg mass must be added to a 15 kg mass to notice the same difference
The House Money Effect
- after a prior gain, people become more open to assuming risk when the new money is not treated as one’s own
Harry Harlow Experiment (Rhesus Monkeys)
- experiment examined parent/child attachment, social isolation, and dependency in rhesus monkeys
- Attachment:
• Results:
– infant monkeys preferred spending time clinging to cloth mother vs. wire mother (even when wire mother was only one to provide food, still visited cloth mom just to eat)
– wire vs. cloth paired monkeys consumed and grew in similar amounts, but wire monkeys sought less soothing from their moms
– monkeys paired w/wire mom displayed abnormal behavior—»behavior could not be corrected by pairing them w/cloth mom after development of abnormal behavior
• Conclusion: contact comfort was crucial to psychological devleopment and health of infants
Weber’s Law
- states that the just-noticeable difference for a stimulus is proportional to the magnitde of the stimulus, and this proportion is constant over most of the range of possible stimuli
Prejudice
- a preconcieved notion about a person, group, or thing
- specifically target people (unlike stereotypes), groups, etc
- EX: if i see someone wearing red and form a negative opinion about that person
Relative Deprevation Theory
- posits that individuals who perceive themselves as having less resources than others will often act in ways to obtain these resources
- individuals lash out against others due to perceived deprivation of resources that they believe they are entitled to (i.e. minority groups w/discrimination)
Accommodation
- Term for how we adjust our schemas to incorporate new experiences to remeber
- Acronym: accommodation has cc” for change or create”
Compliance
- Compliance: when an individual changes his or her behavior in response to a direct request (usually a person or group that doesn’t actually have authority to enforce that change)
Wernicke’s Aphasia
- Damage to Wernike;’s area—»causes the loss of speech comprehension
- patients can speak, but words are non-sensical—»problem with creating meaningful, intelligible speech
Expert Power
- refers to the power conferred by the socially symbolic status of being a credentialed expert in the field with specialized knowledge
- group believes the person has a special knowledge or skill, and is trustworthy—»appeal to high-knowledge/high-motivation people
Classical Conditioning
- Unconditioned stimulus (US) and the subsequent uconditioned response (UR) to it are used to turn a neutral stimulus into a conditioned stimulus
- Ex: Pavlov’s dog’s expt.
- US: meat
- UR: salvation at sight of meat
- neutral stimulus: bell rung before meat
- CR: salvation upon bell ring
Place Theory
posits that one can hear different pitches b/c different sound waves trigger activity at different places along the cochlea’s basilar membrane
Symbolic Interactionism
- focuses on symbolic meaning that people develop and rely upon in the process of social interactions
- Ex: smoking—»symbolic interactionism of smoking is point of contention; some social circles see smoking as trendy while others see it as symbol of poor self-regard and ignorance
- EX: The symbolic meaning of marijuana usage, developed through social interactions, explains why individuals become sustained marijuana users.
Cognitive Biases
- ways in which our perceptions and judgements systematically differ from reality
- thought to be unavoidable freatures of our cognitive system, and may even be adaptive in some cases
Fundamental Attributional Theory
is when an individual interprets another’s actions incorrectly by overemphasizing internal characteristics instead of external events
attrition bias
occurs when participants drop out of a long-term experiement or study
Coercive Power
- power exerted through the threat of force/punishment—»most direct form of power
- effective form of power for all types of individuals regardless of knowledge/motivation
Internal Validity
- the degree to which causal conclusions can be drawn from a study (can include accounting for confounding variables)
Freud’s Id, Ego, & Superego in terms of consciousness

Would an external locus of control mentality have a positive or negative effect on self-efficacy?
- it would have a negative efect—»it might increase an individual’s self-esteem, but not their self-efficacy
Discrimination
- a change in behavior (i.e. speaking/questions asked) based on race and gender
- EX: profesors speaking w/minority females are more likely to use shorter sentances w/more instructions, and asked questions that assumed a lack of skill
urbanization
patterned movement from rural areas to cities
EX: ppl in rural areas dont have enough resources to support the growing population, so ppl move to city
Group Polarization
- tendency that groups have to make decisions that are notably more extreme than the intial individual opinions of members
What are some characteristics of societies w/high levels of Anomie?
- rapid changes in society
- low levels of income
- high heterogeneity
Meritocracy
a system under which individuals are rewarded on the basis of individual skill, talent, or achievement
-EX: testing system that reqards students for sucess on the test
Deindividuation
- describes how ppl lose sense of self-awareness in large group settings
- provides high degree of arousal and low sense of responsibiltiy
- main contributing factors: anonymity, diffused responsibilty, and group size
what is stranger anxiety? At what age is this displayed?
Stranger Anxiety: the fear of strangers (or other-race faces, etc.) that infants commonly express around 8 months of age
variable interval schedule
- occurs when behavior is reinforced after an average, but unpredictable, amount of time has passed
- Ex: pigeon recieves food pellet for pressing button, and another pellet is administered on average every 30s (i.e. could be 10s, 40s, etc.)
why do affluent countries typically have a higher mortality rate despite being higher than poor countries in all other measures of quality of life?
- affluent countries often have higher median ages—»leads to higher mortality rate due to more age-related deaths
Face Validity
- refers to whether a study comprehensively accounts for all the relevant facets of the phenomenon it is intended to investigate
Reconstructive Bias
type of bias related to memory—»our memories of the past are not as accurate as we think, especially memory during high stress periods
Moderating Variable
- one that influences the strength of a relationship between two other variables
- Ex: relation between class size and test performance
- Class time spent learning = mediator variable
- SES of parents = moderating variable
- private vs. public school = confounding variable
Gambler’s Fallacy
- mistaken belief that, if something happens more frequently than normal during some period, it will happen less frequently in the future or vice versa
- Ex: someone who bets on red b/c last 5 spins all landed on black
self-serving bias
- a person interprets things in a way to bolster self-esteem, including how they carry out attribution
- cognitive bias
Gestalt’s Principles of Perception
- Law of Proximity: asserts that we tend to perceive objects close to each other, rather than as a large collection of individual pieces
- Law of Similarity: states that objects that are similar to each other in terms of color or other properties will be grouped together
- Law of Closure: states that people tend to infer complete shapes even if a shape is incompletely sketched out or blocked by another object -prinicple of good continuation states that we perceive intersecting objects as forming coherent wholes
Reliability Vs. Validity
Reliability: refers to how consistent and repeatable an experiment is
Validity: a measure of how well a given experiment actually measures what it set out to measure
opiods mimic what endogenous hormone? where is this hormone produced?
- opiod analgesics mimic the effect of endorphin hormones—»naturally inhibit pain by blocking the release of NTs at nociceptors
- produced in the anterior pituitary gland
Arousal Theory
- Posits that people behave or act in certain ways to maintain a level of optimal arousal which varies from person to person
- Yerkes-Dodson Law: states that performance of a behavior tends to be negatively impacted at high and low levels of arousal -optimal level is at midpoint of upsidedown u-curve w/arousal on x-axis
Internal Locus of Control
- term to describe when a person interprets what happens to them and why things happen to them as something that they have control over in their lives
Nominal Level of Measurement
- variables with no inherent order or ranking
- Ex: gender, race, etc.
what would a drive-reduction & cognitive theorist argue is most strongly correlated with depression?
- Drive reduction theories suggest that depression stems from a reduction in the motivating forces of arousal
2. cognitive theorist would argue that arousal is essential to sustaining most behaviors
Folkways
- norms that govern everyday behavior
- Ex: holding a door open
Taboos
- unacceptable by almost every culture
- Ex: cannibalism/incest
“door-in-the-face” technique of persuasion
- an intiial request is unreasonably large, ∴ rejected—»this request is followed by a smaller, more reasonable request, which is likely to be accepted.
Negative Reinforcement
reinforcing behavior by removing a stimulus (usually negative–i.e. chores) after the good action is completed
The Stroop Effect
- phenomenon in which it is harder for an individual to reconcile differnt pieces of information relating to colors than to reconcile similar pieces of information
- EX: more difficult to say GREEN (shown in red color) vs. GREEN (shown in green color)
Content Validity
- the extent to which a study appears to assess what it is intended to assess
External Validity
- the degree to which the findinds of a study are generalizable to the population as a whole
- typically involves issues regarding the size and representativeness of the sample
Ratio level of measurement
- measurement = quantitiative responses
- ordered at equally-spaced intervals
- possible score of 0 (complete abscence of quantity)
- Ex: the number of times a person has been to church in the last month
Anomie Theory
- states that individuals who experience weakened social values are less likely to behave in ways that are helpful to that society
- breakdown of social bonds, norms—»use strain theory to study how social breakdown of anomie can lead to social deviance and crime, which in turn reinforces social stratification and dysfunction
General Strain Theory
- holds that individuals who have experienced negative events feel negative emotions, which lead to negative behaviors
Unconditioned Stimulus
- stimulus that produces the unconditioned response
- ex: US = food in Pavlov’s expt (unconditioned response = salvation)
Attrition Bias
- systematic error when participants drop out of a study over time affecting the results
The Stanford Prison experiment illustrated that those who assume abuses in criminal institutions are done by those w/dispositional propensities to violence are commiting what type of error?
- Fundamental Attribution Error—» experiment showed that anyone can act in the way participants did under the right conditions (NOT personality characteristics)
- type of bias that tends to place less importance on the context of behavior, and instead places unneccessary emphasis on dispositional/internal qualities to explain behavior.
Operant Conditioning
- type of associative learning that uses reinforcement to encourage a behavior and punishment to discourage it
- Types of punishment/reinforcement…
a) Positive Punishment: adding an unpleasant stimuls to discourage behavior
b) Negative Punishment: removing a pleasant stimulus to discourage behavior
c) Positive Reinforcement: adding a pleasant stimulus to encourage behavior
d) Negative Reinforcement: removing an unpleasant stiimuls to encourage behavior
Mediating Variable
- one which explains the relationship between two other variables
- Ex: if its found that caucasian patients are perscribed more pain medication than hispanic patients, and that there were differences in insurance coverage between the two groups, than insurance converage is considered the mediating variable
Ordinal/Interval Level of Measurement
- variables with an ordered series, without possible measure of 0
- Ex: blood group, performance, degree of belief in the afterlife
Test-Retest Bias
- happens when participants take the same exam over and over again, affecting their responses
Neustress
- neutral type of stress
- happens when you are exposed to something strtessful, but it doesnt actively or directly affect you (i.e. knews about natural disaster on other side of world)
ecological validity
- refers to how findings from an experimental setting can be generalized to the environmental considerations in the real world
Wernicke’s Area
- breain region that controls the comprehension of speech and written language
- located at the back of the temporal lobe (posterior to sylvian fissure)
Functionalist Theory (Social Stratification)
- Functionalism: views society as a system of interconnected parts that carry out a specific role that enables them to cooperate to maintain social equilibrium for society as a whole
- functionalist theories assert aspects of culture are necessary and need-based—»social stratification is necessary & results from the need for those w/special intelligence/skills to be a part of those important occupations
What are the ethical considerations that apply to all research studies?
- informed consent
- expt conducted in least harmful way possible that is consistent w/the research goals (“degree” of harm evaluated by IRB)
Reward Power
ability to motivate action/pursuade by promising rewards (opposite of coercive)
Stereotyping
- a cognitive action, not a behavior
- a prevalent, but oversimplified idea about a certain group w/similar characteristics (race, gender, sexual orientation)
- stereotypes sometimes may be right, but since they are generalizations the obscure the nuances btwn individuals in a stereotyped group
- EX: if i believe all the people who wear red are loud and annoying
Eustress
positive type of stress that happens when you perceive a situation as challenging, but motivating (usually enjoyable
Mores
- norms that are deemed highly necessary to the welfare of a society/consequences if violated
- Ex: health behavior standards —» if person doesnt seek help, might be shunned by family/friends
Social Desirability Bias
- bias related to how people respond to research questions—»if you have an awareness of what the research is going to ask, might cause you to respond a certain way
- Ex: study in which participants feel pressured to respond in way that minimizes ethnocentrism and promotes cultural relativism
Conflict Theory
- emphasizes role of coercion and power in producing social order —» society is fragmented into groups competing for resources
- social order is maintained by those w/most power (i.e. political, economic, or social capital)
- Ex: conflict theory asserts bias and inequality are underlying aspects of education
what are the emotions that have been found to be universally expressed?
- anger
- happiness
- disgust
- sadness
- fear
- surprise
Selection Bias
type of bias related to how many people are chosen to participate —» people who can relate to whatever you are studying are more inclined to sign up and be studied
Self-Serving Bias
- tendency to attribute good outcomes with internal factors (i.e. hard work) & ascribe bad outcomes to external factors (i.e. boss not giving raise = poverty)
How is compliance induced within a target group?
- Copmliance is induced in groups that view themselves as similar
Relative Poverty
- refers to condition where person lacks the minimium income/resources needed to maintin the average standard of living for a community or society
- Ex American poverty
Anomie
- refers to society feeling fragmented and lacking cohesiveness
- breakdown of social bonds (i.e. social norms btwn individuals & communities)
- characteristics of anomie (social breakdown) can lead to social deviance and crime—»reinforces social stratification and dysfunction
Attributional Theory
relates to an attempt by an individual to interpret actions by assigning causes to them
reciprocal determinism
- Albert Bandura—»theory that a person’s behavior both influences and is influenced by personal factors and the environment
Subjective Norms
- refer to the perceived social pressure to engage or to not engage in a behavior
3 High-Level Sociological Theories of MCAT
- Symbolic Interactionism: focuses on symbolic meaning that people develop and rely upon in the process of social interactions
- Conflict Theory: emphasizes role of coercion and power in producing social order —» society is fragmented into groups competing for resources
3. Functionalism: views society as a system of interconnected parts that carry out a specific role that enables them to cooperate to maintain social equilibrium for society as a whole
Assimilation
- term that occurs when an individual from one culture gradually takes on characteristics of another culture
Resercher (Experimenter) Bias
- occurs when a study’s design is biased—»process where the scientists performing the research influence the results, in order to portray a certain outcome.
How would one improve the internal validity of an experiment?
- by adding additional measurement points to prevent interference from counfounding variables
representative heuristic
- tendency to make decisions about actions or events based on our standard representations of those events
- cognitive bias
Binary Nominal Level of Measurement
- variables with only 2 options
- Ex: pass/fail, belief vs. not believe in god, etc.
Types of Validity:
- Construct
- external
- criterion
- Construct Validity: the manner in which the terms of the study are defined
- External Validity: refers to the generalizabiltiy of the research to settings beyond the study
- Criterion Validity: refers to whether a variable is able to predict a certain outcome
Construct Validity
- Construct Validity: the manner in which the terms of the study are defined
Criterion Validity
Criterion Validity: refers to whether a variable is able to predict a certain outcome
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
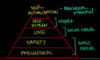
Conditioned Stimulus
- stimulus that is presented after the US in order to ellicit the UR
- Ex: CS = bell in Pavlov expt (CR = salvation)
Cannon-Bard Theory of Emotion
- posits that cognitive and physiological responses to a stimulus occur simultaneously and independently of one another, with a behavioral response following them
* physiological arousal does not have to occur for individuals to feel an emotion - lacks any element of cognitive appraisal/conscous thought about how one’s situation may impact emotions
- Ex: aggressive emotions from listening to angry music—»simultaneous subjective feeling of aggression and physiological arousal that are separate and independent
Persuasion
- Persuasion: a form of social influence in which an individual or group is encouraged to adopt an idea, atitude, or course of action
- Ex: pursuasion techniques often used by advertisers to achieve compliance from consumers (i.e. buy their product)
Cognitive Dissonance
- the unpleasent feeling a person experiences when holding two contradictory beliefs at the same time—» posits that peopel desire consistency btwn their thoughts, values, and actions, and seek to explain the justifications people use for actions that do not align with their values and evoke cognitive dissonance
- EX: father (who’s also a high school teacher) tells son not to go to college to save money, but also responded that higher education is extremely important in a survey
- EX: tendency of bystanders to avoid intervening in conflict even though they would want others to intervene for them
negativity bias
- when the negative aspects of a situation are focused upon, not the good aspects
- Ex: only focusing on bad grades while ignoring the good ones
- cognitive bias
fixed-ratio schedule
behavior is reinforced after an average, but unpredictable, number of responses
- EX: rat gets treat every 3rd push of level
French & Raven’s Bases of Power Model
- social psychologist model that defined multiple bases of power to capture the idea that power can stem from various sources and be exerted in diverse ways
- Power: general sociology term, that refers to an individuals abilitiy to compel other people to do things.
5 power bases are…
A) Coercive B) Legitimate C) Expert D) Referent E) Reward
in a study where participants spend 10, 20, or 30 sec looking at a complex image.the image is then removed and replaced w/an identical image except for one small change. researchers measure how long it takes them to find the change. what is the IV?
IV = the time spend looking at the original image
Normative vs. Informational Influence
- Normative Influence: an influence to conform with the expectations of others to gain social approval
- Informational Influence: an influence to accept information from others as evidence about reality a
test-test Reliability:
test-test Reliability: refers to fact that good tests will yield stable results over time - EX: taking MCAT 1x/year w/out studying over time, you would get basically the same results every time b/c MCAT has goog test taking reliabiltiy
inter-rater Reliability:
inter-rater REliability: means that if an assessment is carried out by different researchers, they should generate similar results - EX: SAT essay graded on scale of 1-6—»good inter-rater reliability b/c same essay is given the same score regardless of which person scores it
Erikson’s Stages of Development

Groupthink
- refers to when a group of people has such a strong desire for harmony and conformity that the group makes irrational decisions
Variable Ratio Schedule
- occur when behavior is reinforced after an average, but unpredictable, number of responses
- tend to produce the highest response rates
- EX: rat tree dispenser set to dispense a treat after an average of 1/10 presses, but the exact number of presses btwn rewards varies
distress
negative type of stress that builds over time and is bad for your body—»occurs in percieved stressful situations, body is primed to respond to threat










