Protein Structure (BIO, BC, OC) Flashcards
(14 cards)
Primary structure of proteins is what kind of sequence of amino acids ? Peptide bonds are (?) linked?
Structure Primary structure of proteins is the Linear sequence of amino acids. They are Covalent (Peptide) linked bonds.
Secondary Structure of Proteins. What kind of bonds? Configurations? How do they fold?
Local structure, stabilized by hydrogen bonding
α-helices – hydrogen bonds run up and down, stabilizing the structure
β-pleated sheets – stabilized by hydrogen bonds connecting the sheets
Antiparallel vs. Parallel configurations
The way the linear sequence folds on itself
Determined by the backbone interactions (primarily hydrogen bonds)
Hydrogen bonds between backbone atoms
Tertiary Structure of Proteins have what kind of characteristics?
- 3-D structure stabilized by hydrophobic interactions, acid-base interactions (salt bridges), hydrogen bonding, and disulfide bonds
- Depends on distant group interaction
- Stabilized by hydrogen bonds, van der Waals, hydrophobic packing, disulfide bridge formation
-
Disulfide bond formation happens on the exterior of the cell (covalent bond of two cysteines).
- Extracellular space prefers the formation of disulfide bonds (the oxidizing environment)
- Hydrophobic interactions and polar interactions between side chains
Quaretenary Structure of Proteins have what characteristics?
Interactions between subunits (multiple polypeptides)
Hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds between side chains (i.e. cysteine side chains making disulfide bonds)
In Summary of Protein Structure:
Primary Structure = determined by
Secondary Structure = determined by
Tertiary Structure = determined by
Quaternary Structure = determined by
Primary Structure = determined by peptide bonds
Secondary Structure = determined by backbone interactions (hydrogen bonds)
Tertiary Structure = determined by distant interactions between groups (van der Waals, hydrophobic packing, disulfide, hydrogen bonding)
Quaternary Structure = determined by same bonds from tertiary structure
Protein is ONLY FUNCTIONAL when in the proper conformation. What is a force that helps stabilize the protein?
A force that helps stabilize the protein is the solvation shell
Solvation shell = layer of solvent surrounding the protein (can be the water solvent interaction with polar AAs, etc.)
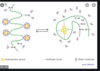
What is Denaturation & causes this & what protein structures are affected?
- when a protein loses active conformation and becomes inactive
- Occurs by changing pH, temp, chemicals or even enzymes
- If you denature by heating, you destroy all the structures of the protein except the primary structure (primary structure is conserved)
Hydrophobic Interactions/ Solvation Layer in relation to entropy
Hydrophobic Interactions/Solvation Layer (entropy) (BC)
The hydrophobic regions of the protein aggregate, which releases the water from cages 🡪 This increases the entropy of water, which is the major thermodynamically favorable component of protein folding

Isoelectric Point of an ACID AA is determined by?
I
pI is determined by averaging the pKa values that refer to the protonation and deprotonation of the zwitterion

Isoelectric Point of a Neutral AA is determined by?

Isoelectric Point of Basic AA is determined by?

Gel Electrophoresis … what will have a harder time moving ?
Positively charged anode at bottom, negatively charged cathode at top
Larger molecules will have harder time moving, thus separation created by size with the smallest molecules towards the bottom

Native Page Vs SDS Page

Native Page Vs SDS page



