Protein basics Flashcards
Nonpolar AAs
GAVLIMP TP
“GAVin LIMPs out of the restroom with TP on his shoe”
- Glycine
- Alanine
- Valine
- Leucine
- Isoleucine
- Methionine
- Proline
- Tryptophan
- Phenylalanine
Polar (+) AAs
HAL
“HAL is alway positive”
- Histadine
- Arginine
- Lysine
Polar (-) AAs
AG
“Polls AGrregate negative answers”
- Aspartate
- Glutamate
Polar (neutral) AAs
“Those Girls Think About Shopping Constantly”
- Tyrosine
- Glutamine
- Threonine
- Asparagine
- Serine
- Cysteine
Essential AAs
PVT TIM HALL
- Phenylalanine
- Valine
- Threonine
- Tryptophan
- Isoleucine
- Methionine
- Histidine
- Arginine*
- Leucine
- Lysine
Arg during growth/dev.
T ≠ Tyrosine (derived from Phe via Phe Hydroxylase)
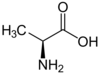
Alanine
Ala (A) = Nonpolar
Side Chain: -CH3 (methyl)
Codons: GCX (4)
1 of 2 highly glucogenic AAs (also glutamine)
Non-Ess: Glc→Pyr→Ala
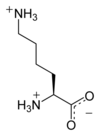
Arginine
Arg (R) = Polar (+), Basic
Side Chain: -(CH2)3-Guanidine
Codons: CGX + AGA, AGG (6)

Aspartate (Aspartic acid)
Asp (D) = Polar (-)
Side Chain: -CH2COOH
Codons: GAU & GAC (2)
Non-Ess: OAA→Asp

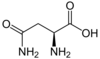
Asparagine
Asn (D) = Polar (neutral)
Side Chain: -CH2(CO)NH2
Codons: AAU & AAC (2)
Non-Ess: OAA→Asp→Asn
Cysteine
Cys (C) = Polar (neutral)
Side Chain: -CH2SH
Codons: UGU & UGC (2)
**Form disulfide bonds**
Non-Ess: Glc→3PG→Ser→Cys

Glutamine
Gln (Q) = Polar (neutral)
Side Chain: -(CH2)2(CO)NH2
Codons: CAA & CAG (2)
1 of 2 highly glucogenic AAs (also alanine)
Non-Ess: TCA→a-KG→Glu→Gln

Glutamate
(glutamic acid)
Glu (E) = Polar (-)
Side Chain: -(CH2)2COOH
Codons: GAA & GAG (2)
Non-Ess: TCA→a-KG→Glu

Glycine
Gly (G) = Nonpolar
Side Chain: -H
Codons: GGX (4)
Non-Ess: Glc→3PG→Ser→Gly

Histidine
His (H) = Polar (+)
Side Chain: -CH2-imidazole
Codons: CAU & CAC (2)

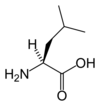
Isoleucine
Ile (I) = Nonpolar
Side Chain: -CH(CH3)CH2CH3
Codons: AUU, AUC & AUA (3)