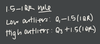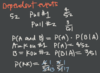Probability & Statistics Flashcards
(94 cards)
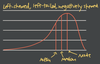
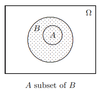
What is one-way data?
Data that’s focused on or collected about just the single individual.
Variable data given for individuals.
One independent variable, called individuals, and one OR more dependent variables, called the variables

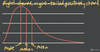
What does this graph represent?

Bar Chart
What does this graph represent?

Histogram
What does this graph represent?

Line graph
What does this graph represent?

Ogive
What is Two-way data?
Two independent categories on which the variables are dependent.

What is the relative frequency table?
A table that shows percentages instead of actual counts of outcomes of one experiment.
Displays data in Two-way or One-way tables as percentages.

What is Joint Distribution Table?
A table that compares two different distributions.
It helps us see a correlation between the two variables (distributions).

What is Marginal Distribution?
The Total row or the Total column in a Joint Distribution.

What is Conditional Distribution?
Distribution of one variable, given a particular value of the other variable.

What is the joint distribution section of this table?
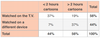
The joint distribution or the joint probability distribution is the probability that a pair of events can happen. All of the possible pairs of events happen in the body of the table

What is the marginal distribution section of this table?
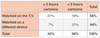
The marginal distribution comes from the total column OR total row.

What is the Frequency Table?
A table that displays how frequently or infrequently something appears.
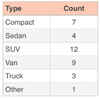
What is a dot plot?
Shows frequency of small datasets.

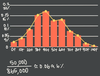
What is a Histogram
(or Frequency Histogram) ?
Just like a Bar Graph, except that we collect the data into buckets or bins, and then sketch a bar for each bucket.
Representation of the distribution of numerical or categorical data in bins.
What is a Stem Plot?
Data grouped together by the first digit(s) in each number.
The “stems” are the numbers on the left, in this case, the 6 and the 7.
The “leaves” are all the other numbers on the right.

What is Mean?
The average.

What is median?
The value in the middle when you line up all the data in order.

What is Mode?
The value that appears most often.

What do we need to look at first when we analyze data?

What is spread?
How and by how much a data set is spread out around its center.
We call measures of spread measures of dispersion or scatter.
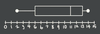
What is Range?
The difference between the largest and smallest value.
What is Quartile?

What is Interquartile range?
The difference between the median of the upper half
and the median of the lower half.