Pregnant and nursing patient Flashcards
What is labelled?

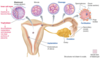
What is labelled?

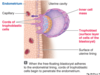
What is labelled?
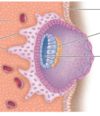
What is labelled?
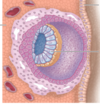

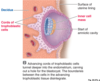
What is labelled?

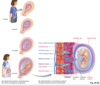
What is the functions of the placenta?
- The placenta forms the functions of the kidneys and digestive and respiratory systems.
- Nutrients and O2 brought to the fetus in the maternal blood are acquired by the mother’s digestive and respiratory systems, and the CO2 and wastes transferred into the maternal blood are eliminated by the mother’s kidneys and lungs, respectively.
- The mother’s digestive tract, respiratory system, and kidneys serve the fetus’s needs as well as her own.
- The means by which materials move across the placenta depends on the substance.
- Many drugs, environmental pollutants, other chemical agents, and microorganisms in the mother’s bloodstream can also cross the placental barrier, and some of them may harm the developing fetus.
What does The placenta temporlariy become during pregnancy?
The placenta becomes a temporary endocrine organ during pregnancy.
During pregnancy three endocrine systems interact to support and enhance the growth and development of the fetus, to coordinate the timing of parturition (birth), and to prepare the mammary glands for nourishing the baby after birth. What are these 3 hormones?
- Placental hormones
- Maternal hormones
- Fetal hormones
Hormones secreted by the placenta play a critical role in maintaining pregnancy.
What are the most important hormones?
- Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
Why is the placenta unique among endocrine tissues?
- Transient tissue
- Secretion of its hormones is not subject to extrinsic control. Instead, the type and rate of placental hormone secretion depend primarily on the stage of pregnancy.
What does the Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) do?
Peptide placental hormone that acts to prolong the life span of the corpus luteum (CL).
What does the corpus luteum do?
- CL of pregnancy is an ovarian endocrine unit that grows larger and produces increasingly greater amounts of estrogen and progesterone for ~10 weeks post-implantation.
- Maintenance of a normal pregnancy depends on high concentrations of estrogen and progesterone.
- Persistence of estrogen and progesterone maintains the thick, pulpy endometrial tissue and menstruation ceases during pregnancy.
What does a male fetus hCG stimulate?
hCG stimulates precursor Leydig cells in the fetal testes to secrete testosterone, which masculinises the developing reproductive tract.
Where is hCG eliminated?
hCG is eliminated in the urine.
What can hCG be an underlying trigger for?
hCG may be the underlying trigger for “morning” sickness






