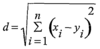Pre-exam Flashcards
(316 cards)
What is model underfitting?
When the model has yet to learn the true structure of the data. Performs poorly on both training and test sets.
What is model overfitting?
The model is too large and fits the data so well that it is no longer able to generalize
When a model is overfit, what happens to the test and training error rate?
Test error rate increases Training error rate continues to decrease
What are some reasons overfitting can occur?
Fitting noise points Not enough representative data
What is MDL?
The minimum description length (MDL) principle is a formalization of Occam’s razor in which the best hypothesis for a given set of data is the one that leads to the best compression of the data. - wikipedia
What is a validation set used for when building decision trees?
The data set is divided into two smaller subsets: 1 for training (2/3) and the other for testing the generalization error (1/2).
What is prepruning?
A method used on decision trees to stop growing the tree before it is fully grown.
What is post pruning?
Pruning a decision tree after it has been constructed.
What are 3 methods used for evaluating the performance of a classifier?
- Holdout (part data training, part data testing) 2. Random subsampling (repeating holdout several times) 3. Cross validation (each record is used the same # of times for training and 1 time for testing) 4. Bootstrap - sample w/ replacement
What is a rule antecedent?
The condition for a rule.
What is a rule consequent?
The end result for a rule (a class).
In a rule set, what is coverage?
The fraction of records in a data set that trigger the rule (satisfy the antecedent).
e.g. rule is triggered 5 times out of a data set of size 10 would yield a coverage of 0.5.
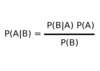
In a rule set, what is accuracy?
The fraction of records triggered by the rule whose class labels are equal to y.
The fraction of records that satisfy both the antecedent and consequent out of the number of time the rule satisfies the antecedant.
What is a mutually exclusive rule?
The rules are independent of each other.
Every record is covered by no more than 1 rule (a recorord is not covered by 2 or more rules).
What are exhaustive rules?
Accounts for every possible combination of attribute values Each record is covered by at least one rule
What is a default rule?
It has an empty antecedent and a default class. It is triggered when all other rules have failed (if used).
What are ordered rules?
Rules that are ordered in decreasing priority (what ever is defined such as accuracy, coverage, etc…). Also known as a decision list.
What are the two methods for extracting classification rules?
- Direct methods which extract rules directly from the data 2. Indirect methods which extract rules from other classification models such as decision trees. `
Explain the sequential covering algorithm.
- Start from an empty rule 2. Grow a rule using the Learn-One-Rule function 3. Remove the training records covered by the rule 4. Repeat step 2 and 3 until a stopping criterion is met.
What are the two rule growing strategies?
General to specific Specific to general
What are some advantages of rule based classifiers?
As highly expressive as decision trees Easy to interpret Can classify new instances rapidly Performance is comparable to decision trees
What is a rote-learner?
Memorizes the entire training data and performs classification only if attributes of a record match one of the training examples exactly
What is an instance-based classifier?
Stores the training records Uses the training records to predict the class label of unseen cases
What is a Voronoi diagram?
It’s basically a model for KNN. It splits the solution space.. on a line = equal distance to parents on an intersectoin = equal distance to 3 parents