Pre Camcards Flashcards
Formula for precentance effience
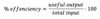
Mechanical Wave
NEEDS a MEDIUM

Diode
Absolute Presure

Newtons 1. law
An object at rest remains at rest, or if in motion, remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force
STP

Error Type?

Random Error
Reduced: By using avarge of multible measurements
A wave trough is
BølgeDAL
Force of Tension

Area under Displacement-Force curve shows
WORK in joules
Is the centripital force a fundamental force
NO
It most often is in the form of tension
Capacitance

Formel for x komponent i vektor
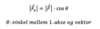
Formulas for constructive and destructive interference for 2 waves with equal frekvenses

Resistance Formula

Angular Displacement

Archimedes’ principle
“Every object is buoyed upwards by a force equal to the weight of the fluid the object displaces.”

Capicitor


Filament Bulb
- Følger ikke Ohms lov
- More current ⇒filament gets hotter⇒atoms vibrate more⇒more colisions with flowing electrons⇒increasing resistance
Magnetic Flux Desity

Hvor og hvorfor bruges en comutator

Ultimate Tensile strength

Electric Power

Formula for specific heat capacity c

Electric force FE between 2 charges

Elastic Colision
Total Ekin is conserved
Critical Damping

Formula for power displaced in a recister R

Fundemental Frequency
MINIMUM frequency of standing wave

Resistors in series circuits
- Total resistance is equal to the sum of the individual resistances.

Direction of magnetic field
North to South

Why is high voltage used in power transmition

Consecvense of following formula

What holds Nucleus together
STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE
Electric Field Strength (E)

Lenz law is consecvens of
Conservation of ENERGY
Critical Angle

Factors affecting directions of an induced voltage

Magnetic Fields are resutls of …….
MOVING CHARGES
Behaviour of Alpha in magnetic field

Electric Charge

Work Energy priciple



Background radioation
- Radon gas
- Kosmic radiation (some get trough earths mag-field)
- X-ray
-
Nuclear weapons testing
*
Dopplerecffect formula for observed frekvency fo, when source moves
+ when source moves away
- when source moves towards

Which wave type needs a medium
LONGITUDINAL
Error Type?

Systematic Error
Tæller man displacement i formel for Epot, spring fra ny eller gammel hvile postion i følgende situation

Ny, hvis man ikke Egrav, pot

Resistors in parallel circuits
- Individual resistances diminish to equal a smaller total resistance rather than add to make the total.

HIGH or LOW Thermal Conductivity


Electromagnetic Induction
Current can be induced to flow due to a CHANGING magnetic field
Total Internal Reflection

Formula for RESISTIVITY

Gauge pressure
Pressure measured relative to atmospheric pressure

First law of Thermodynamics
Superposition principle

Lift
Upward-acting force on an aircraft wing or airfoil.

Hvad er formlen for Amperes Law og hvad bruges den til
- B at a distance r from a long straight wire carrying current I
- µ0 er permeability of free space. B afhænger af ledningens materialle
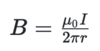
Sammenhæng mellem angular velorcity og speed
Enhed for angular velorcity er radians/secound

Pefectly in-elastoc colision
MUST stick together after colision
Flemings RIGHT hand rule
DYNAMO EFFECT

Describe

0.6 V is THEASHOLD VOLTAGE
Important with this

Finger curled in direction of CURRENT
Current in parallel circuits

Gravertational Field Strength (g)

Lenz Law

Resistance: Impurities of metal, temperature

Factors affecting rate of conduction

Sammenhæng mellem Young’s modulus og k
- A is area
- L is nominal lenth

Particles affected by STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE

Paramagnetisk
- Bliver magntisk ved pårvirkning af eksternt magnetisk feldt
Coulomb’s Law with permittivity of free space

Defernition of a wave
“A disturbance propagating through space”

Lamp
Thermal Radiation is what wave type

Formula for TERMINAL VELORCITY

Stress is defined as

Alpha Decay

Distinction between liquid and gasses
- Gasses are compressible
- Liquids are negligibly compressible
Measurement close to true value
Accurate Measurement
What is this

Potential Divider Curcuit
CONVECTION FLOW

Relationship between wave lengh, frecvency and the speed of light

Strain is defined as

Radition Types

Voltage in parallel circuits
- Voltage is equal across all components in a parallel circuit

Induced magnetism

Normal Force FN
- Contact force
- Always acts perpendicular to contact surface
What is REFRCTION and REFLECTION


Relationship between agular velocity and speed

Upon REFRACTION what is changed
- Speed
- Frekvency
- Wave length
- Speed CHANGES
- Frekvency CONSTANT
- Wave length CHANGES
What type of transformer is this

STEP-DOWN transformer
NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION IN TERMS OF MOMENTUM

Responsible for beta day
WEAK NUCLEAR FORCE
Speed of sound
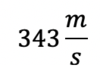
Potential Difference

Constructive and Destructive Interference

Formula for rotational kinetic energy

Formula for Magnetic Flux

Quarcs in hadrons


MELTING and BOILING
Equation for simple hamonic oscilation

Kinematic formula without vf

Specific Gravity
S.G is equal to % of object submerged
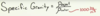
GAMMA DECAY

What are the 3 conservations in mechanics
- Conservation of Emek=Epot+Ekin ( in isolated system)
- Conservation of Momentum
- Conservation of Angular Momentum
Formel for y komponent i vektor

Where do we place the zero point of gravitational potential energy
Makes all values of the gravitational potential energy negative.

In-elastic colision
Total Ekin is NOT conserved
Electric Field (E)
- Q1 creates E1 ⇒ E1 exerts force on Q2

Formula for the magnitude of the centripital acceleration ac

Relative penetrating abilities of Alpha, Beta and Gamma

The area under accelleration-time graph shows
Change in velorcity
Formula for Fluid presure

Maxwells RIGHT hand rule
Direction of Magnetic Field around a current carying wire

Newtons 2. law


Resistor
Behaviour of Alpha, Beta and Gamma in a electric field

PITCH relates to…….
Frekvency

Ammeter
Amplitude A defernition
“Maximum magnitude** of **displacement “
Formula for TORQUE
Direction of TORQUE is find by right hand rule

Formula for wave lenths at the n’th harmonic node for a standing wave
L is distance from start node to finish node (pipe lenth)
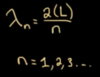
Formula for Buoyant force
Because bottom of an object is always deeper in a fluid than the top of the object

What type of transformer is this

STEP-UP transformer

Only way to change speed of waves
Change the properties of the medium it travels in
Kinematic formula without time

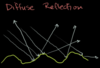
Diffuse reflection
Formula for momentum p
Momentum is a vector

The limit of proportionality
Point beyond which Hooke’s law is no longer true
Formula for impulse J
Impules is a vector

What type of wave is sound
Longitudinal wave
Compresion wave
Relationship between number of primary coils, secoundary coils, primary voltage and secoundary voltage
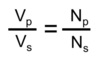

Variable Resistor




Antinode and node

LOUDNESS relates to ……
AMPLITUDE
Kinetmatic formula without displacement

100% transformer efficiency and conservation of energy gives following formula


DAMPED oscillations
Planck’s equation
E: energy of the photon absorbed or emitted
f: frequency of the photon
h: is Planck’s constant, 6.626•10-34 J•s

Relationship between Amplitude and Intensity

Kinematic formula without acceleration

Defernition of Terminal veloricity
Max v attainable by an object as it falls through a fluid

NTC Thermistor
- NTC stands for “Negative Temperature Coefficient”
- Resistance decreases as temperature increases

Difference between PD and EMF
- PD is the work done in taking a unit charge from one point of the circuit to another
- EMF is work done by a source in taking a unit charge round the complete circuit
Energy Transfer

Formula for specific charge of electron

Centripital Force



Cell

Boyles Law
Beta-_PLUS_ deay

Current in series circuits
The amount of current is the same through any component in a series circuit.

Place of node and antinode in half open pipe

The conservations during radioactive decay

Factors affecting magnitude of an induced voltage

Range around measurement within true value is expected to lie
Uncertainty
Behaviour of Beta-MINUS in magnetic field
Use Flemmings LEFT hand rule

Internal Resistance

Gravertational force FG between 2 masses

Formula for center of mass
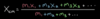
Voltage in series circuits
- Total Voltages is equal to the sum of all voltages

Flemings Left hand rule
MOTOR EFFECT
and
FREE MOVING CHARGES IN B-FIELD

Voltage

Weight
Weight W is the force of gravity Fg exerted on an object



Pascal’s principle

Relationship between agular displacement and distance

LDR’s
Photo Resistors
- LDR stands for light dependent resistors
- In dark resistance is very _high_ (1M
-
Resistance decreases as the intensity of light they are exposed to increases
*

The area under velorcity-time graph shows
Displacement
Drag
Modstand fx. luftmodstand, vandmodstand osv.
Hooke’s Law

“Specific”
Per unit mass

Bridge Rectifier
Formel for Fskrå på en skrå overflade

Simple Harmonic Oscilator
- Restoring force is proportional to displacement
- Can be decribed with sine and cosine functions
Average Power

Vigtig Formula for gliding stopping due to friction

Trick for pulley-table problems
Treating systems as single object

Conservative Forces
- Only depends on initial and final position
- Eg. Gravitational and spring
- NOT Drag or friction
Natural Frequency

Formula for Kinetic Energy
What is this

Velorcity Selector
What realtionship can be used instead of the formula of conservation of Ekin in problems with elastic colisions

Snells Law

If force i applied away from the center of mass of an object, then the object will
Rotate
Defernition of EMF
Work done in driving unit charge around a complete circuit
Formula for wave lenths of standing wave in half open pipe at n’th harmonic node

Interpretation of output voltage graph


Traveling distance of Decay in air
- Alpha : 5 cm
- Beta : 15 cm
- Gamma : several meters
Whar is the range of frekvencies the human ear can observe

Formula for potential energy in a non-uniform gavitational field

Place of Antinodes in open pipe

Coherent Waves
Constant Phase Difference
Repeated measurement is the same
Precise Measurement
Determining wave lenth


Magnetic Domains are due to
Unpaired elektron spin

The angular velorcity in the equation of a harmonic movement for a sping is equal to

Describe
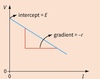
Finding EMF and internal recistance
- Mesure Terminal PD and corosponding I
Formula for moment of inertia, when all mass is a same r

Stokes Law

Mass of alpha vs. electron
10 000 : 1

Parallax Error
Formel for static friction coeffitient µs

CONDUCTION

Formel for FN på en skrå overflade

MOTOR EFFECT
Current carying wire experience force, when placed in a magnetic field

Latent heat of fusion and Latent heat of vaporizartion

Deffinition of a calorie
Energy needed to heat 1 g water 1 0C
Work formula

Period T defernition
“Time required for an entire cycle”
Moment is the same as
TORQUE
Formula for TOTAL MOMENT OF INERTIA

Is kinetic energy a vector
- No it is only a scalar
- It is also ways positive
Diffraction Equation

What type of wave is light
Transverse wave

Body executing SIMPLE HARMONIC motion
Specular reflection

Formula for NET impulse Jnet

In perfect circular movement:
Velocity is……
Angular Velocity is …..
Velocity is changing
Angular Velocity is constant
Mass
Mass m is a measure of the inertia of the object

Evaporation


The steady current, delivering same average power as A.C
THE ROOT MEAN SQUARE


Battery

Voltmeter
What is rarefaction
Det modsatte af compresion

Work MUST be done to seperate atoms
Formula for DRAG FORCE

Magnetic Flux

Field strengh general deferniton

Formula for potential spring energy

Problem causing reading to differ from true value
Error
Directions of electric field lines

Refraction Index

CONVECTION

Voltage is induced when ……..
- Wire cuts fieldlines
- Magnetic Field changes
Perfect Diode
- Acts like a perfect conductor when voltage is applied forward biased
- Acts like perfect insulator when voltage is applied reverse biased.

Definition of Current
Charge per time (ladning per tid)

Torque acting clockwise is…….
NEGATIVE
Elastic Limit
Minimal value of the stress which produces plastic deformation
4 FUNDERMENTAL FORCES OF PHYSICS

Defernition of FLUID
Fluids take shap of container
Formel for kinetic friction coeffitient µk

Behaviour of gamma in magnetic field


Brownian motion
AC
Alternating Curent (veksel)

Acceleration in SIMPLE HARMINOC MOTION
Young’s modulus
Measures the resistance of a material to being elastically deformed

Newtons 3. law
If an object A exerts a force on object B, then object B must exert a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction back on object A.

Beta-MINUS Decay

Defernition of a PHOTON
The elementary particle, or quantum, of light
Potential energy in uniform gravitational field


Fixed Resistor
- Følger Ohms lov
- Antager konstant temperatur
Instentanious Power

Gravitational Potential
WORK pr. unit MASS bringing a MASS from infinity to the point

Relativ ionising abilities of Alpha, Beta and Gamma

DC
Direct current (jævn)
Particles NOT affected by STRONG NUCLEAR FORCE

Randomness of decay
Radioactive decay is a stochastic/random process at the level of single atoms. According to quantum theory, it is impossible to predict when a particular atom will decay
Inetia
- Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist change in velocity
- Inetia deppends on mass
Dopplerecffect formula for observed frekvency fo, when observer moves
+ when obs moves towards source
- When obs moves away from source

Lonzents Force Law


Between State Change
How is electromagnetic waves different from waves at sea
Consist of 2 waves oscillating perpendicular to one another

Faradays Law of Induction

Relationship between wave frekvency f and wave period T

Potential Divider Equation

What must the surface be in order to produce ECHO
- SMOUTH
- HARD
Difference between scalars and vectors

Sping constant from force and extention

Ferromagnet
- Permanent magnetisk
The centripital force here is due to

MOTOR FORCE


