Practice Test w/pic Flashcards
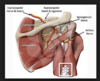
At the suprascapular notch, the suprascapular artery typically passes directly _______ to the transverse scapular ligament
Anterior
superior
posterior
inferior
Superior
At the suprascapular notch, the suprascapular artery typically passes directly _______ to the transverse scapular ligament
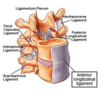
The posterior longitudinal ligament is positioned _______ to the spinal cord
medial
lateral
anterior
posterior
Anterior
The posterior longitudinal ligament is positioned _______ to the spinal cord
As the femoral artery (external iliac) exists the pelvis, it is positioned _____ to the inguinal ligament and _____ to the
iliopsoas muscle
anterior/anterior
anterior/posterio
posterior/anterior
posterior/posterior
Posterior/anterior
As the femoral artery (external iliac) exists the pelivs, it is positioned posterior to the inguinal ligament and anterior to the

The inferior gluteal nerve exits the greater sciatic nerve directly __________ to the piriformis muscle.
superior
inferior
medial
lateral
inferior
The inferior gluteal nerve exits the greater sciatic nerve directly ______ to the piriformis muscle

With the popliteal fossa, the popliteal artery is positioned directly ______ to the popliteus muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
With the popliteal fossa, the popliteal artery is positioned directly ______ to the popliteus muscle
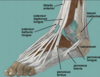
The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes _____ to the lateral malleolus prior to attaching in part to the lateral aspect of the base of the 1st metatarsal
anterior-superior
anterior-inferior
posterior-superior
posterior-inferior
posterior-inferior
The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes _____ to the lateral malleolus prior to attaching in part to the lateral aspect of the base of the 1st metatarsal
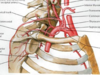
The subclavian artery and vein pass _____ to the clavicle
anterior-superior
anterior-inferior
posterior-superior
posterior-inferior
posterior-inferior
The subclavian artery and vein pass _____ to the clavicle
The radial nerve passes directly ____ to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus
anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
anterior
The radial nerve passes directly ____ to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus

The axillary artery and cords of the brachial plexus pass directly _____ to the pectoralis minor muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
The axillary artery and cords of the brachial plexus pass directly _____ to the pectoralis minor muscle
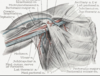
The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery pass directly ______ to the shaft of the humerus
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
posterior
The radial nerve and profunda brachii artery pass directly ______ to the shaft of the humerus
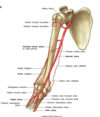
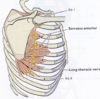
The long thoracic nerve is positioned directly _______ to the serratus anterior muscle
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Lateral
The long thoracic nerve is positioned directly _______ to the serratus anterior muscle
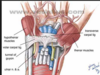
The ulnar nerve and superior ulnar collateral (or posterior ulnar recurrent) artery pass directly ______ to the medial epicondyl of the humerus
anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
Posterior
The ulnar nerve and superior ulnar collateral (or posterior ulnar recurrent) artery pass directly ______ to the medial epicondyl of the humerus

Near the wrist, the radial artery is positioned directly _____ to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.
Medial
lateral
superficial
deep
Lateral
Near the wrist, the radial artery is positioned directly _____ to the tendon of the flexor carpi radialis muscle.

The ulnar artery and nerve pass directly _____ to the transverse carpal ligament.
Superficial
deep
superior
inferior
Superficial
The ulnar artery and nerve pass directly _____ to the transverse carpal ligament.
The radial artery passes directly ______ to the trapezium and base of the first metacarpal.
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Posterior
The radial artery passes directly ______ to the trapezium and base of the first metacarpal.
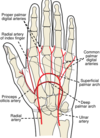
The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle passes directly ____ to the dorsal tubercle of the radius.
Superior
inferior
medial
lateral
Medial
The tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle passes directly ____ to the dorsal tubercle of the radius.

The obturator externus muscle passes directly _____ to the neck of the femur
Anterior
posterior
superior
inferior
posterior
The obturator externus muscle passes directly _____ to the neck of the femur
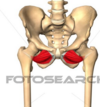
During its posterior course, the medial circumflex femoral artery passes directly ___ to the pectineus muscle
Medial
lateral
superior
inferior
Lateral
During its posterior course, the medial circumflex femoral artery passes directly ___ to the pectineus muscle
Immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve is positioneddirectly __________ to the femoral artery.
anterior
posterior
medial
lateral
Lateral
Immediately inferior to the inguinal ligament, the femoral nerve is positioned directly __________ to the femoral artery.

The median nerve and tendons of the FDS and FDP muscles all pass directly__________ to the transverse carpal ligament.
Superficial
Deep
Superior
Inferior
Deep
The median nerve and tendons of the FDS and FDP muscles all pass directly__________ to the transverse carpal ligament.

As they exit the greater sciatic foramen, the superior gluteal nerve, artery and vein arepositioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.
A. superior B. inferior C. medial D. lateral
Superior
As they exit the greater sciatic foramen, the superior gluteal nerve, artery and vein arepositioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.

The obturator internus tendon passes directly __________ to the neck of the femur.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Posterior
The obturator internus tendon passes directly __________ to the neck of the femur.

The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle passes directly __________ to thesustentaculum tali of the calcaneus.
A. anterior B. posterior C. superior D. inferior
Inferior
The tendon of the flexor hallucis longus muscle passes directly __________ to thesustentaculum tali of the calcaneus.

The tibial nerve passes directly __________ to the medial malleolus.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Posterior
The tibial nerve passes directly __________ to the medial malleolus.

The sural nerve passes __________ to the lateral malleolus.
A. anterior-superior
B. anterior-inferior
C. posterior-superior
D. posterior-inferior
posterior-inferior
The sural nerve passes __________ to the lateral malleolus.

The tibial attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament is positioned __________ to the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Anterior
The tibial attachment of the anterior cruciate ligament is positioned __________ to the tibial attachment of the posterior cruciate ligament.
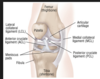
The plantar calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament is positioned ______ to the head ofthe talus.
A. medial B. lateral C. superior D. inferior
Inferior
The plantar calcaneonavicular (spring) ligament is positioned ______ to the head ofthe talus.

As it exits the greater sciatic foramen, the sciatic nerve is positioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.
A. superior B. inferior C. medial D. lateral
Inferior
As it exits the greater sciatic foramen, the sciatic nerve is positioned __________ to the piriformis muscle.

The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes __________ to the long plantar ligament.
A. superior B. inferior C. medial D. lateral
Superior
The tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes __________ to the long plantar ligament.
The radial artery passes __________ to the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle prior to piercing the 1st dorsal interosseous muscle.
A. anterior B. posterior C. medial D. lateral
Anterior
The radial artery passes __________ to the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle prior to piercing the 1st dorsal interosseous muscle.

Which of the following procedure is most likely to produce radiation that can lead toa skin burn?
A. 3-View X-ray of the hand
B. 60 minute US exam of the pelvis
C. 60 slice CT scan of the chest
D. Angiographic pulmonary procedure
Angiographic pulmonary procedure
The DICOM standard has proven useful in medical imaging b/c images
can be routinely reivewed by multiple caregivers
Fertilization normally takes place within the:
Ampulla of the Fallopian (uterine) duct
The conceptus on its way through the uterine tube absorbs fluids to the extent a fluid-filled cavity is formed. At this point the conceptus is referred to as a:
Blastula
The individual cells that form as the result of cleavage following fertilization are called:
Blastomeres
The portion of the blastocyst that makes first contact w/the maternal tissue is the:
Trophoblast
What is the ideal site for implantation of the conceptus?
Endometrium
What occurs during the 2nd week of embryonic development
- extraembryonic ectoderm forms
- lacunar stage
What derives from hypoblasts
Yolk sac
Which of the following structures of the 2nd week conceptus gives rise to all embryonic tissues?
Epiblasts
Intraembryonic coelom forms in…
the lateral mesoderm
What is the result of embryonic folding
cardiogenic area is positioned caudal to oropharyngeal membrane
Which layer of the embryonic disc undergoes neurulation?
Ectoderm
What is derived from neural Canal
- central canal of spinal cord
- ventricles of the brain
The ventral body cavities of adults arise from which of teh following embryonic structures
Intraembryonic coelom
Which of the following strucures is responsible for teh formation of 3 germ layers during the 3rd week of development?
Primitive streak
What would you find on a developing limb bud?
- motor nerve (axons)
- myotome
- neural crest
Which of the following is innervated by the dorsal rami of the spinal nerve?
A. Erector spinae
B. Intercostal muscles
C. Quadratus lumborum
D. Rectus abdominis
E. Strap (anterior) muscles of the neck
Erector spinae
Which of the following is true for the development of the musculoskeletal system?
A. C8 spinal nerve is located cranial to C8 vertebra
B. T1 spinal nerve is located caudal to the T1 vertebra
C. All muscles of the limbs arise from the epimere
D. Cranial 1/3 of the C7 somite is permanently lost during resegmentation
E. None of the above
T1 spinal nerve is located caudal to the T1 vertebra
Dermatomes represent
a segmental sensory innervation of teh body
The _______ of the brachial plexus is formed by the union of roots C5 and C6
Upper trunk
The _______ of the brachial plexus is formed by the union of roots C5 and C6

The upper trunk of the brachial plexus is formed by the union of roots ___ and ___
C5 and C6
The upper trunk of the brachial plexus is formed by the union of roots ___ and ___

The posterior wall of the axilla is bounded by the teres major, latissimus dorsi, and _____ muscles
subscapularis
The posterior wall of the axilla is bounded by the teres major, latissimus dorsi, and _____ muscles

The posterior wall of the axilla is bounded by the _____, _________, and ________ muscles
teres major, latissimus dorsi, and subscapularis muscles
The posterior wall of the axilla is bounded by the ____, ___, ____ muscles

The pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis and short head of teh biceps brachii all attach in part to the _____ and are innervated by branches of the _____ cord of the brachial plexus
Coracoid process; lateral
The pectoralis minor, coracobrachialis and short head of teh biceps brachii all attach in part to the _____ and are innervated by branches of the _____ cord of the brachial plexus
An infection associated with the hypothenar eminance would typically first spread to the ______ lymph nodes of the upper extremity
Supratrochlear
An infection associated with the hypothenar eminance would typically first spread to the ______ lymph nodes of the upper extremity
Supertrochlear lymph nodes:
- Superior to medial epicondyl of humerus.
- Drains the middle, ring, and little fingers, medial potion of hand, & superficial forearm
The rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder include the supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and ________
Infraspinatus
The rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder include the supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and ________
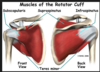
The rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder include the _____, ________, __________, and ________
The rotator cuff muscles of the shoulder include the supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and infraspinatus

The ________ muscles of the shoulder include the supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and infraspinatus
Rotator cuff muscles
The ________ muscles of the shoulder include the supraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis, and infraspinatus
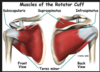
The ______ muscle attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus and is innervated by a branch of axillary nerve
Teres Minor
The ______ muscle attaches to the greater tubercle of the humerus and is innervated by a branch of axillary nerve
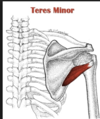
The teres minor muscle attaches to the ________ of the humerus and is innervated by a branch of axillary nerve
Greater tubercle
The teres minor muscle attaches to the ________ of the humerus and is innervated by a branch of axillary nerve
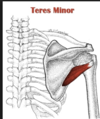
The superior and middle bands of the glenohumeral ligament attach to the ______ of the humerus
Lesser tubercle
The superior and middle bands of the glenohumeral ligament attach to the ______ of the humerus

The superior and middle bands of the ___________ attach to the lesser tubercle of the humerus
glenohumeral ligament
The superior and middle bands of the ___________ attach to the lesser tubercle of the humerus

The ulnar nerve passes between 2 heads of the _________ muscle as it enters the forearm
Flexor carpi ulnaris
The ulnar nerve passes between 2 heads of the _________ muscle as it enters the forearm

The _______ nerve passes between 2 heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris as it enters the forearm
Ulnar nerve
The _______ nerve passes between 2 heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris as it enters the forearm

The radial recurrent artery typically anastomoses with the __________ artery
radial collateral
The radial recurrent artery typically anastomoses with the __________ artery
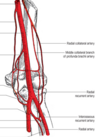
The radial collateral artery typically anastomoses with the __________ artery
radial recurrent artery
The radial collateral artery typically anastomoses with the __________ artery

The ______ and ____ muscles have only a single primary function: flexion of the forearm
brachialis and brachioradialis
The ______ and ____ muscles have only a single primary function: flexion of the forearm
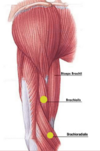
The brachialis and brachioradialis muscles have only a single primary function: __________
Flexion of the forearm
The brachialis and brachioradialis muscles have only a single primary function: __________

The carpal tunnel is bounded anteriorly by the __________
transverse carpal ligament
The carpal tunnel is bounded anteriorly by the __________

A loss of cutaneous innervation of the lateral aspect of the thenar eminence is consistent with a lesion of the ________ branch of the radial nerve
Superficial
A loss of cutaneous innervation of the lateral aspect of the thenar eminence is consistent with a lesion of the ________ branch of the radial nerve
Thenar eminence: group of muscles, palm of the hand, base of the thumb
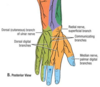
The ulnar side of the dorsal venous network of the hand is typically drained by the ______ vein
Basilic
The ulnar side of the dorsal venous network of the hand is typically drained by the ______ vein

The _______ side of the dorsal venous network of the hand is typically drained by the basilic vein
ulnar side
The _______ side of the dorsal venous network of the hand is typically drained by the basilic vein
The _____ branch of the radial artery typically crosses the flexor pollicis brevis muscle as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar arch
Superficial palmar
The _____ branch of the radial artery typically crosses the flexor pollicis brevis muscle as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar arch
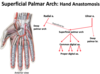
The superficial palmar branch of the radial artery typically crosses the ______ muscle as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar arch
flexor pollicis brevis muscle
The superficial palmar branch of the radial artery typically crosses the ______ muscle as it anastomoses with the superficial palmar arch
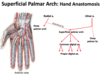
The ____ muscle attaches in part to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and functions in flexion of the proximal IP joint of digits 2-5
Flexor digitorum superficialis
The ____ muscle attaches in part to the medial epicondyle of the humerus and functions in flexion of the proximal IP joint of digits 2-5

The radiocarpal joint is innervated by branches of the _____, ______, and ______ nerves
Ulnar, median, radial nerves
The radiocarpal joint is innervated by branches of the _____, ______, and ______ nerves

The spinal nerves and radicular vessels exit the vertebral canal by transversing the ________
Intervertebral foramina
The spinal nerves and radicular vessels exit the vertebral canal by transversing the ________
The _____ and _____ exit the vertebral canal by transversing the intervertebral foramina
spinal nerves and radicular vessels
The _____ and _____ exit the vertebral canal by transversing the intervertebral foramina
The _____ muscle (subdivision of erector spinae) attaches in part to the costal angles of the ribs
Iliocostalis
The _____ muscle (subdivision of erector spinae) attaches in part to the costal angles of the ribs
The iliocostalis muscle (subdivision of erector spinae) attaches in part to the _____ of the ribs
costal angles
The iliocostalis muscle (subdivision of erector spinae) attaches in part to the _____ of the ribs
The CSF is located in the ______ space surrounding the spinal cord
Subarachnoid space
The CSF is located in the ______ space surrounding the spinal cord
The _____ is located in the subarachnoid space surrounding the spinal cord
CSF
The _____ is located in the subarachnoid space surrounding the spinal cord
The medial edge of the ______ muscle forms the lateral border of the femoral triangle
Sartorius
The medial edge of the ______ muscle forms the lateral border of the femoral triangle

The medial edge of the sartorius muscle forms the lateral border of the ________
Fermoral triangle
The medial edge of the sartorius muscle forms the lateral border of the ________
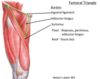
The femoral triangle is made up of the :
lateral border: medial edge of the _______
Medial border: medial border of______
Superiorly by ___________
The femoral triangle is made up of the :
lateral border: medial edge of the sartorius muscle
Medial border: medial border of adductor longus
Superiorly by inguinal ligament

The perforating branches of the _____ artery are the primary blood supply to the posterior compartment of the thigh
profunda femoral
The perforating branches of the _____ artery are the primary blood supply to the posterior compartment of the thigh
The perforating branches of the profunda femoral artery are the primary blood supply to the ____________
Posterior compartment of the thigh
The perforating branches of the profunda femoral artery are the primary blood supply to the ____________
The _____ muscle attaches in part adjacent to the anterior superior iliac spine and is innervated by a branch of the superior gluteal nerve
Tensor fasciae latae
The _____ muscle attaches in part adjacent to the anterior superior iliac spine and is innervated by a branch of the superior gluteal nerve
The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches in part adjacent to the _________ and is innervated by a branch of the superior gluteal nerve
anterior superior iliac spine
The tensor fasciae latae muscle attaches in part adjacent to the _________ and is innervated by a branch of the superior gluteal nerve
The ______ muscle attaches in part to the adductor tubercle of the femur and is innervated by the ______ and _____ nerves
Adductor magnus; obturator and sciatic nerves
The ______ muscle attaches in part to the adductor tubercle of the femur and is innervated by the ______ and _____ nerves

The ligament of the femoral head attaches in part to the ________ of the inominate
acetabular notch
The ligament of the femoral head attaches in part to the ________ of the inominate

Swelling within the anterior compartment of the leg may cause compression of the _____ nerve
Deep Peroneal
Swelling within the anterior compartment of the leg may cause compression of the _____ nerve
At the distal end of the tibia, the tibial nerve is positioned betwen the tendons of the _____ and _____ muscles
flexor hallucis longus & flexor digitorum longus
At the distal end of the tibia, the tibial nerve is positioned betwen the tendons of the _____ and _____ muscles
At the distal end of the tibia, the ______ nerve is positioned betwen the tendons of the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus muscles
tibial nerve
At the distal end of the tibia, the ______ nerve is positioned betwen the tendons of the flexor hallucis longus and flexor digitorum longus
muscles
A “______” (loss or weakness of wrist extension) is typically associated with a lesion of the radial nerve
“wrist drop”
A “______” (loss or weakness of wrist extension) is typically associated with a lesion of the radial nerve
A “wrist drop” (loss or weakness of wrist extension) is typically associated with a lesion of the _____nerve
radial nerve
A “wrist drop” (loss or weakness of wrist extension) is typically associated with a lesion of the _____nerve
A _____ syndrome is typically associated w/ a compression of the median nerve at the wrist
Carpal tunnel
A _____ syndrome is typically associated w/ a compression of the median nerve at the wrist
A carpal tunnel syndrome is typically associated w/ a compression of the ____ nerve at the wrist
Median nerve
A carpal tunnel syndrome is typically associated w/ a compression of the ____ nerve at the wrist
A _____ gait, characterized by a tilting of the pelvis towards the uninvolved side, may be due to a lesion of the superior gluteal nerve
gluteal
A _____ gait, characterized by a tilting of the pelvis towards the uninvolved side, may be due to a lesion of the superior gluteal nerve
A gluteal gait, characterized by a tilting of the pelvis towards the uninvolved side, may be due to a lesion of the ________ nerve
superior gluteal nerve
A gluteal gait, characterized by a tilting of the pelvis towards the uninvolved side, may be due to a lesion of the ________ nerve
The common peroneal nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the lower extremity due to its close association with the neck of the _______
fibula
The common peroneal nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the lower extremity due to its close association with the neck of the _______
The _______nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the lower extremity due to its close association with the neck of the fibula
common peroneal nerve
The _______nerve is the most commonly injured nerve in the lower extremity due to its close association with the neck of the fibula
Intramuscular injections should be restricted to the superior lateral quadrant of the _____ region of the lower extremity due to the absence of neurovascular structures
Gluteal
Intramuscular injections should be restricted to the superior lateral quadrant of the _____ region of the lower extremity due to the absence of neurovascular structures
A depressed _____ tendon reflex is consistent with a compression of either the S1 or S2 spinal roots
Calcaneal
A depressed _____ tendon reflex is consistent with a compression of either the S1 or S2 spinal roots
A depressed calcaneal tendon reflex is consistent with a compression of either the ___ or ___ spinal roots
S1 or S2
A depressed calcaneal tendon reflex is consistent with a compression of either the ___ or ___ spinal roots
The popliteus muscle functions to “unlock” the knee joint during ______ of the leg
Flexion
The popliteus muscle functions to “unlock” the knee joint during ______ of the leg
(popliteus muscle initiates knee flexion)
The _____ muscle functions to “unlock” the knee joint during flexion of the leg
popliteus muscle
The _____ muscle functions to “unlock” the knee joint during flexion of the leg
The _____ artery and axillary nerve typically traverse the quadrangular space, an anatomical region bounded inferiorly by the teres major muscle
Posterior circumflex humeral
The _____ artery and axillary nerve typically traverse the quadrangular space, an anatomical region bounded inferiorly by the teres major muscle

The quadrangular space is bounded by:
Superior: teres minor, subscapularis
inferiorly: teres major
medially: triceps brachii
laterally: surgical neck of the humerus
Important bc: the axillary nerve and posterior circumflex humeral artery can be compressed or damaged due to space-occupying lesions or disruption in the anatomy due to trauma

The pronator teres muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the ____ fossa
Cubital
The pronator teres muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the ____ fossa
The _____ muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the cubital fossa
Pronator teres muscle
The _____ muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the cubital fossa
cubital fossa: elbow pit (anterior)
the ______ muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the cubital fossa
pronator teres
the ______ muscle is the (infero-) medial border of the cubital fossa
The ____ and ____ nerves are the two nerves most at risk for injury during the surgical excision of the axillary lymph nodes
Thoracodorsal & long thoracic nerves
The ____ and ____ nerves are the two nerves most at risk for injury during the surgical excision of the axillary lymph nodes

The thoracodorsal and long thoracic nerves are the two nerves most at risk for injury during the surgical excision of the _____ lymph nodes
Axillary lymph nodes
The thoracodorsal and long thoracic nerves are the two nerves most at risk for injury during the surgical excision of the _____ lymph nodes

“Jogger’s foot” (aching, burning, numbness and tingling on the medial side of the foot’s sole) may be due to compression of the _____ nerve where this nerve passes deep to the abductor hallucis muscle
Medial plantar
“Jogger’s foot” (aching, burning, numbness and tingling on the medial side of the foot’s sole) may be due to compression of the _____ nerve where this nerve passes deep to the abductor hallucis muscle
“Jogger’s foot” (aching, burning, numbness and tingling on the medial side of the foot’s sole) may be due to compression of the medial plantar nerve where this nerve passes deep to the _______ muscle
Abductor hallucis muscle
“Jogger’s foot” (aching, burning, numbness and tingling on the medial side of the foot’s sole) may be due to compression of the medial plantar nerve where this nerve passes deep to the _______ muscle
The doralis pedis artery is the distal continuation of the ______ artery
Anterior tibial
The doralis pedis artery is the distal continuation of the ______ artery
The deltoid ligament attaches to the tiba, talus, navicular and calcaneus, and resists forced ______ (movement) of the foot
Eversion
The deltoid ligament attaches to the tiba, talus, navicular and calcaneus, and resists forced ______ (movement) of the foot
Eversion: process of turning inside out
The _____ ligament attaches to the tiba, talus, navicular and calcaneus, and resists forced eversion (movement) of the foot
Deltoid ligament
The _____ ligament attaches to the tiba, talus, navicular and calcaneus, and resists forced eversion (movement) of the foot
The deltoid ligament attaches to the ___, _____, ____, and _____, and resists forced eversion (movement) of the foot
tibia, talus, navicular, and calcaneus
The deltoid ligament attaches to the ___, _____, ____, and _____, and resists forced eversion (movement) of the foot
The iliofemoral ligament helps to maintain the body in an erect posture by preventing overextension of the _______ joint
Hip
The iliofemoral ligament helps to maintain the body in an erect posture by preventing overextension of the _______ joint
The ______ ligament helps to maintain the body in an erect posture by preventing overextension of the hip joint
iliofemoral ligament
The ______ ligament helps to maintain the body in an erect posture by preventing overextension of the hip joint
The ____ muscle attaches in part to the adductor tubercle and ischial tuberosity
Adductor magnus
The ______ ligament helps to maintain the body in an erect posture by preventing overextension of the hip joint

The adductor magnus muscle attaches in part to the ________ and _______
Adductor tubercle and ischial tuberosity
The adductor magnus muscle attaches in part to the ________ and _______

The obturator internus and obturator externus muscles both attach in part to the ______ of the femur
Trochanteric fossa
The obturator internus and obturator externus muscles both attach in part to the ______ of the femur
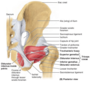
The subscapularis muscle attaches in part to the _____ of the humerus
Lesser tubercle
The subscapularis muscle attaches in part to the _____ of the humerus

The long head of the triceps brachii muscle attaches in part to the ____ of the scapula
Infraglenoid tubercle
The long head of the triceps brachii muscle attaches in part to the ____ of the scapula

The _____ muscle attaches in part to the dorsal aspect of the base of the 3rd metacarpal
Extensor carpi radialis brevis
The _____ muscle attaches in part to the dorsal aspect of the base of the 3rd metacarpal
The extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle attaches in part to the ____ aspect of the base of the ____ metacarpal
Dorsal aspect; 3rd
The extensor carpi radialis brevis muscle attaches in part to the ____ aspect of the base of the ____ metacarpal
The ___ muscle attaches in part to the palmar base of the distal phalanx of the thumb
flexor pollicis longus
The ___ muscle attaches in part to the palmar base of the distal phalanx of the thumb

What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Root C6
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
general sensory
taste
Dorsal Root C6
General sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Root T1
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Dorsal Root T1
General sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Root L2
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Dorsal Root L2
General Sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Root C7
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Ventral Root C7
Motor (skeletal muscle)
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Root T2
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Ventral Root T2
Motor
Preganglionic symp.
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Root T12
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Ventral Root T12
Motor (skeletal)
Preganlionic symp.
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Root L1
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Ventral Root L1
Motor (skeletal)
Preganglionic symp
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Root S1
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Ventral Root S1
Motor (skeletal)
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Ramus C8
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Dorsal Ramus C8
Motor (skeletal)
Postganglionic symp
General sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Ramus T1
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Dorsal Ramus T1
Motor (skeletal)
postganglionic symp
Gen. sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Dorsal Ramus L3
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
Gen. sensory
taste
Dorsal Ramus L3
motor
postganglionic symp
gen. sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Ramus C5(distal to Gray ramus)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
Ventral ramus C5 (distal to gray ramus)
motor
post ganglionic symp
gen. sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Ramus T1(distal to Gray ramus)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
VEntral ramus T1 (distal to gray ramus)
motor
post ganglionic symp
gen sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Ramus L1 (distal to Gray ramus)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
Ventral Ramus L1 (distal to gray ramus)
motor
post ganglionic symp
gen sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Ventral Ramus S2 (distal to Gray ramus)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
Ventral Ramus S2 (distal to gray ramus)
motor
post ganglionic symp
(Preganglionic para)
gen sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Suprascapular Nerve (at its origin)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
Suprascapular nerve
motor
post ganglionic symp
gen. sensory
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
musculocutaneous nerve (at its origin)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
musculocutaneous nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Median nerve (at origin)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
median nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen. sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
ulnar nerve (origin)
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
Ulnar nerve
motor
post gan symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
obturator nerve
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
obturator nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
inferior gluteal nerve
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
inferior gluteal nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
sciatic nerve
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
sciatic nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Tibial nerve
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
tibial nerve
motor
post gang symp
gen sensation
What is the fxn of the axons present in the following roots, rami, or peripheral nerves?
Sural nerve
Motor (skeletal muscle)
Preganglionic symp.
Post ganglionic symp.
preganglionic para.
post ganglionic para.
gen. sensory
taste
sural nerve
post gang symp
gen sensation


