Practice Questions Flashcards
(21 cards)
_________ is a part of the brain that helps coordinate motor activity and is affected in Parkinson’s disease?
a. Substantia nigra
b. Cerebral Cortex
c. Subthalamic nucleus
d. Caudate Nucleus
a. Substantia nigra

Dysregulation of the neurotransmitter ___________ may contribute to the development of panic attacks
- Serotonin
- Epinephrine
- Norepinephrine
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)

Which of the following is an underlying mechanism of secondary hypothyroidism?
a. Decreased thyroid-releasing hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone
b. Increased thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroid-releasing-hormone
c. Decreased thyroid-releasing hormone and increased thyroid-stimulating hormone
d. Increased thyroid hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone
a. Decreased thyroid-releasing hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone

Mr. Thompson has a 26 pack year smoking history with diagnosis of cardiovascular disease. Which of the following is a contributing factor from smoking?
- Reduction of catecholamines
- Peripheral vasodilation
- Decreases high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
- Glycation of vascular proteins
Decreases high-density lipoprotein (HDL)

Sarah has a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD). Which of the following results would you expect to see on laboratory data?
a. High C-reactive protein
b. Decreased Troponin
c. Low homocysteine
d. Increased adiponectin
a. High C-reactive protein

A patient arrives to the ED with severe chest pain unrelieved by rest involving a transmural infarct of the endocardium through the epicardium. Which of the following would be the correct diagnosis?
- Non-STEMI myocardial infarction
- STEMI myocardial infarction
- Unstable angina
- Acute pericarditis
STEMI myocardial infarction

Which of the following is an underlying pathophysiologic process of pulmonary edema?
a. Impaired diffusion of oxygen across the alveocapillary membrane
b. Decreased pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure
c. Occludes the airway creating increased intrathoracic positive pressure
d. Capillary injury that decreases capillary permeability
a. Impaired diffusion of oxygen across the alveocapillary membrane
During an asthmatic attack, histamine, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes result in which of the following actions? Select all that apply.
a. Increased mucus secretion
b. Enhanced fibroblast secretion
c. Vascular permeability
d. Bronchoconstriction
a. Increased mucus secretion
c. Vascular permeability
d. Bronchoconstriction
During and after an asthmatic attack, ____________ causes bronchial smooth muscle contraction and mucus secretion.
a. acetylcholine
b. histamine
c. interleukin 4 (IL-4)
d. immunoglobulin E (IgE
a. acetylcholine

Which of the following contributes to the development of emphysema?
- Bronchial edema
- Reduced endogenous antiproteases
- Bacterial colonization of airways
- Hypersecretion of mucus
Reduced endogenous antiproteases
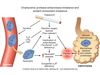
Why does hyperkalemia develop in diabetic ketoacidosis?
a. Because sodium is low and that stimulates aldosterone to retain sodium and potassium
b. Because hydrogen shifts into the cell in exchange for potassium to compensate for metabolic acidosis
c. Because phosphorus shifts into the cell in exchange for potassium due to the lack of insulin
d. Because the blood is concentrated due to the loss of water from polyuria
b. Because hydrogen shifts into the cell in exchange for potassium to compensate for metabolic acidosis
DKA causes K+ to shift from intracellular to extracellular compartments due to insulin deficiency, hyperglycemia, extracellular hyperosmolarity, acidosis and increased catabolism and breakdown of cellular protein. This is reflected as hyperkalemia on lab values.
As the metabolic acidosis is corrected with the lowering of the blood glucose (insulin pushes K+ into the cell), the potassium will shift back into the cells
Atherogenesis plays a primary role in the development of coronary artery disease. What is the primary mechanism of atherogenesis?
a. The release of the inflammatory cytokines tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α).\
b. The release of the growth factor granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF)
c. The release of free radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL)
d. The release of interleukin 6 (Il-6) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
c. The release of free radicals that oxidize low-density lipoproteins (LDL)

How can angiotensin II increase the workload of the heart?
a. By increasing the peripheral vascular resistance
b. By causing dysrhythmias as a result of hyperkalemia
c. By causing dysrhythmias as a result of hyperkalemia
d. By stimulating the sympathetic nervous system
a. By increasing the peripheral vascular resistance

- Which of the following disrupt impulse transmission in dementia of Alzheimer type?
a. Hypophosphorylation
b. Lewy bodies
c. Neurofibrillary tangles
d. Cholinesterase
c. Neurofibrillary tangles

- Which of the following underlying mechanisms can produce depression? Select all that apply
a. Deficiency of monoamine neurotransmitters
b. Excessive glucocorticoid secretion
c. Increase in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels
d. Blocking serotonin reuptake in the synapse
a. Deficiency of monoamine neurotransmitters
b. Excessive glucocorticoid secretion
- A high ventilation-perfusion ratio (high V/Q) results from which of the following?
a. Asthma
b. Atelectasis
c. Pneumonia
d. Pulmonary embolus
d. Pulmonary embolus

Which of the following is TRUE regarding insulin resistance?
a. Increased cytokines from obesity is a contributing factor
b. Initially leads to hypoinsulinemia due to glucagon dysfunction
c. Contains low amounts of insulin antagonists
d. All of the above
a. Increased cytokines from obesity is a contributing factor

Which neurotransmitters are NOT involved in the pathophysiology of migraine headaches? (Select all that apply)
a. Norepinephrine
b. Epinephrine
c. Dopamine
d. Serotonin
a. Norepinephrine
b. Epinephrine
c. Dopamine
Which anatomic structure secretes follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)?
a. Hypothalamus
b. Ovaries
c. Anterior pituitary
d. Adrenal cortex
c.Anterior pituitary

Which hormone stimulates gonads to produce both male and female hormones?
a. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
b. Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
c. Luteinizing hormone (LH)
d. Estrogen
c.Luteinizing hormone (LH)

it is LH that stimulates the ovaries to secrete estrogen in women and the leydig cells to produce testosterone in men. While, FSH stimulates the ovaries to produce inhibin in women and the sertoli cells to produce androgen bind globulin (ABG) as well as inhibin in men.
- Estrogen has many biological effects on the female body including:
(Select all that apply.)
a. Maturation of reproductive organs
b. Differentiating female physical characteristics
c. Postpuberty closure of short bones
d. Regulation of the menstrual cycle
e. Endometrial regeneration after menstruation
a. Maturation of reproductive organs
b. Differentiating female physical characteristics
d. Regulation of the menstrual cycle
e. Endometrial regeneration after menstruation


