Practical Exam Flashcards
(43 cards)
During slaughter, an animal presents with a pronounced odour. What disposition would you provide?
Carcase and all carcase parts condemned. May be recovered for animal food.
If the odour was only slight it could be retained for further disposition after chilling.
An animal presents for slaughter looking like this among a mob of healthy cattle, what disposition would you provide?

Condemed - cachexic. Possibly has a chronic condition.
An animal presents for slaughter in a moribund state with subnormal temperature, weak pulse and disturbed senses. What disposition would you provide?
Animal Condemned
An animal presents for slaughter in a state of exhaustion but with no signs of acute disease. What disposition would you provide?
Animal should be witheld from slaughter and ante-mortem repeated after adequate rest
An animal presents for slaughter with a fever. What disposition would you provide?
Animal condemned.
OR withhold the animal until it has recovered provided there is no risk of spread of disease, no undue suffering and recovery is considered likley.
What are the ante-mortem dispositions?
- Passed for unconditional slaughter
- Restricted sluaghter - passed for slaughter subject to conditions specified by the vet/inspector (a ‘suspect’ animal)
- Withheld from slaughter
- Passed for emergency slaughter
- Condemned - rejected for slaughter
What are the post-mortem dispositions?
- Passed for human consumption
- Retained for final disposition
- Unfit for human consumption and may be recovered for animal food
- Unfit for human consumption and may be recovered for pharmaceutical material
- Condemned
What descriptors can be used when assessing post-mortem lesions?
- Number / percentage
- Distribution
- Colour
- Shape
- Content (granular, caseous, etc)
- Duration / time (chronic, acute)
- Location / tissue type
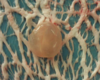
Describe this lesion:
Would it need to be condemned?

Focal, well-demarcated, yellow caseous mass contained within adipose tissue.
Caseous necrosis of fat.
No need to condemn - just trim.
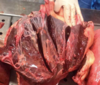
Describe these lesions and what disposition you would provide:

Multifocal to coalescing, subacute (red), moderate, raised, fibrinous lesion on the pleura - pleurisy.
If diffuse carcase condemned.
Describe these lesions. What disposition would you apply?
Many nephroliths - condemn kidenys and if an evidence of uraemia carcase is condemned.
Why must you condemn an animal with evidence of uraemia and what signs can you look for to indicate uraemia?
Uraemia = toxaemia
Signs:
- kidney damage
- GI ulcers
- tar tar build up
- underweight
Describe these lesions. What disposition would you apply?

Multiple, pale, randomly distributed, 2-5mm, non-raised, chronic (as they are pale non-raised) infarcts - nephritis
Reject the kidneys - check for evidence of uraemia, oedema or abnormal smelling urine
Describe this lesion. What action should be taken?

Acute, gangrenous mastitis
Condemn carcase - toxaemic
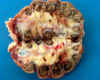
Describe this lesion and what action should be taken:

Multiple small abscesses on one quarter of the udder - chronic mastitis
Trim
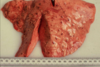
How would you describe these lesions?
What are they likely to be caused by?

Four to five dark red focal, chronic, hepatised, well-demarcated, depressed foci mainly in the caudal lobes - atelectasis and consolidation
Dictylocaulus Viviparous (lung worm) – pre patent larval stage

What are the 2 main species of lung worm found in sheep in Australia?
Dictilocaulus filaria and Muellerius capillaris
What is this? What action should be taken?

Taenia hydatidgena cyst
Reject all affected carcase parts
Which parasite causes this appearance in the liver of pigs?
What action should be taken for this liver?

Ascaris suum
Partial or total condemnation of the liver - depending on extent (purely for aesthetics)
What do you see here? What does it indicate and what action should be taken?
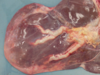
Cholefibrosis
Indicates liver fluke - condemn liver
What might have caused this in a liver?
What action should be taken?

Echinococcus granulosa
Condemn any affected organs
What is occurring in this kidney?

Amyloidosis - associated with severe inflammation
Condemn carcase
What test is this?

Methylene blue test for milk
- If viable bacteria are present the milk will become white again
- Faster change occurs, the more bacteria that are present
How can alkaline phosphatase be used to asses milk?
Alkaline phosphatase is present in raw milk
- if present in ‘pasteurised milk, the milk was NOT sufficiently pasteurised
- OR high number of bacteria in milk