Powertrain Flashcards
(40 cards)
What is the approximate thermal efficiency of IC engines?
The worst 30%. The best 50% In the real world, around 40%
What is the air fuel mixture in diesel engines like?
Very lean. 30:1 is common
How does power, torque and fuel consumption vary with RPM with petrol and diesel engines?
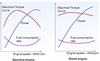
Why is engine efficiency lower at lower speeds?
1) poorer mixing 2) poorer combustion; 3) relatively higher losses
What are the relative ignition tempertatures of petrol and diesel?
450 for petrol
350 for diesel.
What is IMEP?
Indicated mean effective pressure
Fictional consant pressure that would provide the same power if it acted on the pisston all the way down. It is independent of engine speed and volume
A good measure of effectiveness of the design of the engine.
Also known as net mean effective pressure
Roughly between 0.9 and 1.3 MPa
How is conrod length defined?
λ=r/I
Ratio of crank and control length
Normally around 1/3
How do you find BMEP?
BMEP=IMEP-FMEP
BMEP=2πTn / Vd
T=torque
n=number of revs per power stroke(normally 2)
Vd=engine displacement
Which pressures corespond to the different areas?

A=gross mean effective pressure
B=pumping mean effective pressure
IMEP=A-B
What bore/stroke ratios are used for which applications?

What are the relative merrits of two-stoke and four stroke engines?

What is volatility?
How readily a fluid becomes vapour
What is the relative volatility, flash point and ignition temperature of petrol and diesel?
Petrol is more volatile and has the lower flash point. Diesel has the lower autoignition temperature.
What is the equation for the distance between shafts of a gearbox?

What is Rg?
Ratio of the top gear ratio to the bottom gear ratio
What are the typical largest smallest gear ratios in different types of vehicles?
Top gear ratio= 0.7-1
Bottom gear ratio= 3-4.5 for passenger vehicles
5-8 for commercial vehicles
What is the equation relating the distance between gear shafts and the number of teeth on engaging gears?
Z1+Z2=2A*cos(β)*(1/M)
M is the module
Z is the number of teeth
A is the distance between the shafts
β is the helix angle of the gears.
What equation gives the ratio of first gear from the number of gear teeth?
ratio=(driven/drive)*(driven/driver)

What equation gives the power of an engine from the torque?
2πTn/Vd
T is the torque
n is the number of revolutions per power stroke (2 for 4 stroke engine)
Vd is the total volume of the engine
What is the mean piston speed?
stroke of engine*RPM / 30
What is the effect of increasing the number of cyclinders and the bore of the engine?
When n increases for given other design conditions total engine mass and size decrease but length increases
Increasing D is commonly used to upgrade an engine design for higher power
What are the typical engine compresstion ratios?
10 to 12 for gasoline
14 to 18 for diesel
Draw the diagram that explains how the force acting on the piston becomes torque

What is the valve timing clock for the best engine performance?