porphyrin metab Flashcards
1
Q
describe the synthesis of heme
A
- Aminolevulinic acid synthase synthesizes ALA from succinyl-CoA and glycine
- 2 Molecules of ALA are joined to form porphobilinogen (PBG)
- Four molecules of PBG are joined to form Uroporphyrinogen
- Modifactions of side-chains generate coporphyrinogen and protoporphyrinogen
- Ferrochelatase INSERTES a Fe2+ into the molecule to yield heme

2
Q
describe the regulation points of HEME synethesis
A
- Low HEME concentration ACTIVATES ALA synthase
- Increased demand for heme Increases, ALA synthase restocks the heme
- negative feedback loop
- Increased demand for heme Increases, ALA synthase restocks the heme
- Synthesis of Heme-containing cytochrome p450 enzymes consumes Heme
- induction of p450 enzymes (EtOH, Barbituates) induces HEME SYNTHESIS

3
Q
describe Lead affect on Heme production
A
inhibits heme at 2 sites
- Lead inhibits PBG synthase (ALA dehydratase)
- leads to accumulation of Aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
- leads inhibits Ferrochelatase
- leads to build up protoprophyrinogen IX in the mitochondrion
- SYMPTOMS are similary to porphyrias (mental symptoms, light sensitivity, abdominal pain etc)
4
Q
Acute intermittent porphyria (AIP)
A
- Caused by ALPHA deficiency in porphobilinogen deaminase (PBGD)
- ALA and PBG Accumulate in the circualtion and in URINE, giving the urine a DARK RED COLOR
- AIP can be life-threatening and causes episodes of confusion and sharp abdominal pain
- drinking alcohol can trigger this disorder
5
Q
Porphyria cutanea tarda (PCT)
A
- Results from a deficiency of UROPORPHYRINOGEN DECARBOXYLASE
- leads to a buildup of porphyrins (can be detected in the urine)
- Porphyrins are able to absorb visible and UV light
- (LIGHT SENSITIVITY)
- blistering of the skin
- urine held under UV light will glow pink
6
Q
describe Bilirubin formation and conjugation
A
- Heme –Heme oxgenase–> Biliverdin
- Biliverdin –biliverdin reductase–> bilirubin (electron acceptor, can protect from oxidative stress)
- Bilirubin –conjugated in liver by UGT–> bilirubin diglucuronide which is excreted in bile
- also called direct bilirubin
- direct bilirubin is conjugated and more water soluble

7
Q
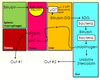
overview of bilirubin metabolism
A
- Bilirubin in splenic macrophages –> blood where it binds to albumin and transported to liver
- Bilirubin becomes conjugated to glucuronic acid to form bilirubin-DG
- transported into gut where it is broken down by bacteria to bilirubin and urobilinogen
- can be reabsorbed into the liver where it goes to blood ad through kidneys
- OR it can continue into the gut and excreted through feces
BILIRUBIN IN THE URINE is ABNORMAL
8
Q
Jaundice
A
- yellow pigment accumlation in the skin (bilirubin)
- defect in the process of bilirubin metabolism and excretion
- 3 types
- pre-hepatic jaundic
- hepatic jaundice
- post-hepatic jaundice
9
Q
Prehepatic Jaundice
A
- TOO MUCH UNCONJUGATED BILIRUBIN PRODUCED
- often caused by hemolysis–> newborn jaundice
- So much it NO LONGER BINDS TO ALBUMIN therefore unconjugated bilirubin starts to accumulate in other tissues and BRAIN
- liver is still conjugated bilirubin and functioning normally
- urine and feces appear normal (normal levels)
10
Q
Hepatic jaundice
A
- Liver does not produce enough conjugated bilirubin
- lots of unconjugated bilirubin in body (found in tissues, including brain)
- bilirubin conc in serum is normal or slightly elevated (high in membranes)
- Since liver doesn’t produce conjugated bilirubin
- Pale urine and Pale feces (no pigment –> no bilirubin)
- occurs in acetaminophen poisoning, hepatitis impair bilirubin conjugation/excretion
11
Q
POST-hepatic jaundice
A
- Occluded digestive tract leads to lots of conjugated bilirubin going through the kidneys –> DEEP ORANGE color of urine and PALE FECES
- Unconjugated bilirubin and conjugated bilirubin found in other tissues including brain
- occurs in gallstones, cancer, cirrhosis close gall duct
12
Q
describe the lab values associated with prehepatic jaundice
A
- bilirubin usually only slightly elevated
- no bilirubin in urine
- blood anaylsis shows hemolysis
- hemoglobin is low
13
Q
describe lab values of hepatic juanidce
A
- elevated bilirbuin
- bilirubin in urine (indicative of cholestasis)
- markers of liver disease up (ALT and AST)
14
Q
lab alues of post-hepatic jaundice
A
- bilirubin may be highly elevated (MOSTLY CONJUGATED)
- bilirubin in urine (conjugated)
- markers of cholestasis are up (alkaline phosphatase)


