PMHNP Flashcards
(145 cards)
BET
What disorders have ELEVATED rates of OCD?
BIPOLAR, eating disorders, and Tourette’s.

Location of 5-HT in brain
Raphe Nuclei (Brain Stem)

The most common type of delusions (i.e., belief that one is going to be harmed, harassed, and so forth by an individual, organization, or other group)
Persecutory

An over-importance of thoughts and need to control thoughts are characteristics of
OCD

OCD beliefs can include an inflated sense of responsibility an overestimate of
threat

OCD patients strive for perfection and are intolerant of
uncertainty

In individuals with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, the prevalence of OCD is approximately
12%.

Name 5 body systems involved in panic disorder

ANS, Cognition (brain),
Cardiorespiratory (heart/lung),
GI (stomach), and Otoneurologic (ear)

True or False. Lipid solubility increase the absorption of drug into blood.

True
Ionization of a molecule determine its solubility. T/F

True
These bind to receptors with selectivity
Ligands

Large proteins on membrane or within cells that is the initial site of action

Receptors
Pavlov Classical Conditioning Experiment involved
Dog, bell, food

Type of learned behavior that reinforces/discourages acts
Operant Conditioning

Drugs are usually weak acid/bases and not readily

lipid soluable
Drugs can become ionized when dissolved in water depending on
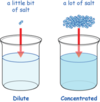
The pH of solution and property of molecule.
The pKa is the solution a drug becomes
50/50 ionized/non-ionized in
acid need alkaline environments and vice versa

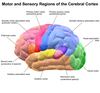
Grey Matter communicates _____ information

Sensorimotor
White Matter (Corpus Callosm)
Myelinated (Communicate between hemispheres)

Limbic System integrate emotions and regulate motivated

learning and behavior
Hippocampus is involved in these type of memories

New & long term
Nucleui Accumbens (Limibic System)

Reinforces Reward (VTA/Mesolimbic pathways)
Amygdala (Temporal Lobe)
Coordinate
Emotional Response and Memories

Dopamine is found in the
Substania Nigra and VTA