Pictures Flashcards
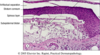
Which layers of skin are shown here? Top–>Bottom

Top:
stratum corneum
stratum granulosum (darker color)
stratum spinosum (pretty big)
stratum basale
Bottom
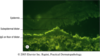
What is shown here? Where is this structure found in the body?

apocrine gland
found in axilla & groin
nonfcnl
What is shown here? What is its fcn?

these are secretory glands–eccrine sweat glands
secrete sweat & fcn in thermoregulation of skin
Where is this type of skin found?

on the soles of feet & palms of hands
note the thick keratin & absence of adnexal structures in the dermis
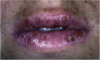
What is macroscopic lesion?

this is a hypopigmented patch
What type of macroscopic lesion does this picture show?

hyperpigmented patch
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

pinpoint macules of hypopigmentation
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

a papule
it is dome shaped, well circumscribed
less than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

a papule
it is dome shaped, well circumscribed
less than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

a papule
it is dome shaped, well circumscribed
less than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

nodule
papule’s larger body, greater than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

a nodule
the larger buddy of a papule, greater than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown in this picture?

a nodule
larger buddy of the papule
greater than 5 mm
Which type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

plaque
elevated flat top lesions that are greater than 5 mm
Which types of macroscopic lesions are shown here?

plaques
flat topped lesions that are greater than 5 mm
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

pustule
raised lesions that are pus filled
like abscesses or acne
what type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

vesicle
less than 5 mm
fluid-filled blister
the little sibling of the bulla
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

bulla
greater than 5 mm
fluid-filled blisters
larger sibling of the vesicle
What type of macroscopic lesion is shown here?

wheal
itchy transient elevated lesions
some blistering & dermal edema
What is shown here?

wheal
What type of microscopic lesion is shown here?

hyperkeratosis
What type of microscopic lesion is shown here?

parakeratosis
the nuclei will be in the top layer
What type of microscopic lesion is shown here?

acanthosis
epidermis is thickened
What type of microscopic lesion is shown here?

papillomatosis
thickened epidermis + distinct papillary fragments