Picture/Symbol Cards Flashcards
Describe the resolution of vectors
- Formula for resolving vectors
- Two formulas for reconstructing resolved vectors

Identify the two important trigonometric identities that link sine and cosine

What is the pythagorean theorem?
r2 = x2 + y2
This only works on right angle triangles
It is important to memorize certain common values of trigonometric functions. List the sinθ, cosθ and tanθ values for the following angles (θ):
0°
30°
45°
60°
90°
180°

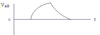
Recall the graph representing instantaneous velocity

What is the formula used to determine average acceleration between two points in time?
Where v’ is final velocity and v is initial velocity.

What is a uniformly accelerated motion and how can you measure total displacement of it?
Of the magnitude of forces acting on an object are constant, the magnitude of acceleration will be constant (resulting in unformly accelerated motion). The initial displacement, velocity and acceleration at any given time contribute to the overall displacement of the system.
displacement: x = x0- xf (due to initial displacement)
x = v0t (displacement due to inital velocity at t)
x = ½at2(displacement due to acceleration at t)
Total displacement: x = x0+ v0t + ½at2
The translational motion is the motion of the centre of gravity of a system (ie object) through space, illustrated by the above equation
List the three most important equations of kinematics (objects in motion with respect to space and time).
These must be memorized!
x = x0 + v0t + ½at2
v = vo+ at
v2 = vo2 + 2ax
What is the law of gravitation? Provide the formula expressing this
The law of gravitation states that there is a force of attraction existing between any two bodies of masses m1 and m2, the force is proportional to the product of the masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distances between them.
F = KG(m1m2)/(r2)
r: distance between the bodies, KG is the universal constant of gravitation (value depends on units)
What is the equation for uniformly gravitationally accelerated motion?
Average velocity of free fall?
x = xo + vot + ½gt2
v = gt
How is the vertical component of a projectile motion calculated for:
initial speed
displacement at time t
Speed at any time t
Initial speed: Voy = Vosinα
displacement at t: y = Voy + ½gt2
speed at t: Vy = Voy + gt
How is the horizontal component of a projectile motion calculated for:
intiial speed?
displacement at any time t?
speed at any time t?
initial speed: Vox = Vocosα
displacement at t: x = voxt
speed at time t: Vx = Vox (speed is constant due to negligable air friction)
After calculation (or presentation) of the vertical and horizontal components of a projectile motion, how do you calculate:
magnitude of inital velocity?
Direction of motion?

How can you calculate the horizontal distance from the origin of a projectile motion?

Give the formula for the maximal frictional force
fmax = μN
Where μ is the coefficient of friction and N is the normal force to the surface on which the object rests (always perpendicular to surface).
What is static friction and what is the formula which allows the coefficient of static friction (μs) to be calculated?
What is the coefficient of kinetic friction (μk)?
μs = tanα
where α is the angle at which the object first begins to move on an inclined plane as the angle is increased from 0 degrees to α degrees.
μk <μs
μkexists when surfaces are always in motion.
Display the forces and motions acting on/resulting from an object on a sloped surface. Contrast this to an object on a level surface.

Describe uniform circular motion and the formulas that can calculate acceleration and force.
(This applies to things like balls on strings, cars banking on turns and wall of an amusement park rotor)
Magnitude of velocity is constant, but direction is constantly changing (and therefore the velocity vector is continuously changing).
- The velocity is always tangent to the circle, creating an acceleration directed radially inward, called the centripetal acceleration ac
ac = v2/r (where r is radius of circle)
Centripetal force (Fc) = mac = mv2/r

Give the formulas for:
circumference of a circle
area of a circle
circumference of a circle: 2πr
area of a circle: πr2
For pully systems, give the formulas for:
acceleration of the objects (a)
tension on the string (T)
Note: T is always between the weight of mass m1 and m2

What are two kinds of collisions that objects can have?
Give a formula for calculating the motion before and after a collision
- Elastic (objets rebound off each other, conservation of kinetic energy and momentum)
- Inelastic (Objects stick together, there is conservation of momentum, but not kinetic energy, which is lost as heat or sound)
m1v1i + m2v2i = m1v1f + m2v2f
If directions are not the same, then the each momentum must be resolved into x and y components as necessary.
What is kinetic energy? How can it be calculated?
Kinetic energy (Ek) is the energy of motion which can produce work. It is proportional to the mass of the object and its velocity
Ek = ½(mv2)
What is potential energy? How is it calculated?
Potential energy (Ep) is accumulated by the system that contained it. It varies with the configuration of the system (ie distances varying = interactions between particles vary).
The variation of the potential energy is equal to the work performed by the interior forces caused by the interaction between the particles of the system.
Give formulas for the following examples of potential energy (Ep)
- Electric potential
- Universal attraction Ep
- Gravitational force Ep
- Elastic force Ep
Electrical potential: Ep = kq1q2/r
(q = point charge, r = distance between each)
**Universal attraction: **Ep = Gm1m2/r
**Gravitational force: **Ep = mgh
(h = height)
**Elastic force: **Ep = kx2/2
(k = spring constant, x = displacement)