Physiology of Hearing & balance Flashcards
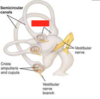
Identify the parts of the ear


What is the purpose of the middle ear?
Transforms acoustic energy from the medium of air to the medium of fluid
To do this - it acts as an amplifier
How does the middle ear amplify noise?
1) Area effect of the tympanic membrane (eardrum):
- ratio of TM to stapes footplate is 17:1
2) Lever action of ossicular chain (auditory bones):
- ratio of pressure on stapes footplate to pressure on malleus is 1.3:1
What is OME?
What type of hearing loss does it cause?
Otitis media with Effusion - (aka “Glue ear”)
- Conductive hearing loss
Described as non-infectious fluid in the middle ear for more than three months
- However it is caused by (respiratory tract) infection
Identify the problem shown.
What is the effect on hearing?

Small perforation of TM
Effect on hearing is variable
Main indication for repair is if the patient has recurrent ear infections
What is shown here and what is the effect on hearing?

Sub-total perforation
Massive loss of hearing:
- If sensorineural hearing is maintained then maximum hearing loss in order of 60 dB
What is otosclerosis?
Deposition of new bone where footplate of stapes fits into oval window
Reduces the movement of stapes footplate causing conductive hearing loss

Identify the parts of the diagram of the inner ear


What is the cochlea?
a hollow, spiral-shaped bone found in the inner ear that participates in the process of auditory transduction
Identify the parts of the cochlea in the diagram and cross-section
The ones in green are the main bits so care more about that

In the diagram, the Helictotrema is not shown. This is where the Scala Vestibuli and Scala Tympani meet. Its basically the centre of the cochlea spiral

Describe how acoustic energy moves through the cochlea
Pressure wave flows up the scala vestibuli from the piston action of the stapes
Wave continues through the helictotrema at the apex and down the scala tympani
The pressure differential deflects the basilar membrane of the scala media (the one between the SV & ST)
What is the organ of Corti?
Receptor organ for hearing in the Cochlea
This highly varied strip of epithelial cells allows for transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses’ action potential
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cChx6oZGJpk (good shit)

Travelling pressure waves move up the SV and down the ST - as we know
Describe the steps in the hearing mechanism of the cochlea
The wave causes movement of the basilar membrane and movement of the inner and outer hair cells in the Organ of Corti in relation to the tectorial membrane
The cilia of the hair cells are deflected and ion channels open
Cations (K+) flow from the endolymph into the hair cells
Depolarisation takes place and an impulse is sent up the cochlear nerve
Inner hair cells activate the afferent nerves
Outer hair cells modify the response of the inner hair cells
What is meant by the ‘Tonotopic arrangement’?
Wordy answer coming up
The basilar membrane contains hair cells that run along it. As you go up it, the hair cells become most sensitive to lower and lower frequencies
This means that for every frequency of audible sound, there is a specific point along the basilar membrane where the hair cells are most specific to that frequency
This tonotopic arrangement continues up to the acoustic area of the temporal lobe.
What ways can hearing be assessed?
Clinical testing
Tuning fork tests:
- Weber - lateralisation
- Rinne - air conduction vs. bone conduction
Audiometry:
- Pure tone, Visual reinforcement, Play, Tympanometry
Objective testing
What is pure tone audiometry?
Pure-tone air conduction hearing test determines the faintest tones a person can hear at selected pitches (frequencies), from low to high.
Earphones are worn so that information can be obtained for each ear.
What is shown here?

Healthy Cochlear cilia
Identify the type of hearing loss shown in this audiogram
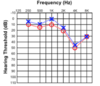
Noise-induced hearing loss
This is loss of hearing of a specific frequency, usually due to prolonged exposure to noise of that frequency.
If you imagine a factory worker being surrounded by loud machines, they will lose hearing of the frequency of those machines.