Physics Test Tuesday March 20th Flashcards
Electrotherapy

the use of electric currents passed through the body to stimulate nerves and muscles, chiefly in the treatment of various forms of paralysis. (Google)
is a branch of the physical treatment, in which direct current and pulsed currents of low and medium frequencies are used for medicinal purposes. (slides)
Electrotherapy Tests
- (TENS) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
- (HVPC) High Voltage Pulsed Current
- Diadynamic Currents
- Interference Current
- (NMES) Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
- Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Muscle

(TENS) Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
- Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is the use of electric current produced by a device to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. (Google)
- The application of electrical stimulation to the skin via surface electrodes to stimulate nerve fibers primarily for pain relief. (slides)
Types of TENS
- conventional TENS
- acupuncture like TENS
- burst train TENS
- brief-intense TENS
Conventional TENS
(High Frequency, Low Intensity)
- most commonly used mode of electrostimulation
- combination of parameters stimulates A beta afferents

Convetional TENS Effects
- When A Beta fibers are stimulated, the conventional TENS mode achieves analgesia, primarily by spinal segmental mechanisms
-
Analgesia tends to be relatively short, lasting up to a few hours post-treatment
- Analgesia is the inability to feel pain.
-
Analgesia tends to be relatively short, lasting up to a few hours post-treatment
Conventional TENS Modes
- low intensity
- high frequency, over 100 Hz
- pulse duration is usually short, (50-80µs)

Acupuncture like TENS
(Low Frequency, High Intensity)
- Primarily stimulates A delta and C nociceptive fibers and small motor fibers
- Electrodes should be positioned to produce visible muscle contrations, over a myotome related to the painful area
Acupuncture Like TENS Modes
- Low frequency, (1-4 Hz)
- High Intensity, (enough to produce visible muscle contractions)
- long pulse duration, (200µs)

Acupuncture like TENS Effects
- patient will experience paraesthesia and muscle contrations with this mode
- the analgesia lasts longer than with conventional TENS
- <em>paraesthesia is an abnormal sensation, typically tingling or pricking (‘pins and needles’), caused chiefly by pressure on or damage to peripheral nerves.</em>
Burst Train TENS
(High Frequency trains of pulses delivered at Low Frequency)
- this is a mixture of conventional and acupuncture like TENS, and comprises a baseline low frequency current together with high frequency trains
- Patients must tolerate the stimulus intensity required to produce the desired strong muscle twitches, which are much better than single impulses
- <em>This type was developed by Eriksson and Sjolund in 1976 as a result of their experiences with chinese electroacupuncture</em>
Burst Train TENS Modes
- Low frequency of trains, (1-4 Hz)
- High Internal Frequency of Trains, (100 Hz)
- pulse duration, (100-200 µs)
Brief-Intense TENS
(High Frequency, Long Pulse Duration)
- this mode can be used for painful procedures such as skin debridement, suture removal, etc.
Brief-Intense TENS Modes
- High Frequency, (100-150 Hz)
- Long duration pulse, (150-250 µs)
(Not important)
Postions of Electrode Placement

TENS Indications
TENS is useful for:
TENS is useful for:
- Pain relief after amputation
- Nerve pain after shingles
- phantom pain
- peripheral neuropathies caused by metabolic disorders
- pain-related cause of CNS damage
(HVPC) High Voltage Pulsed Current
Parameters
- very short phase durations, (5-6 µs)
- very high peak, current amplitude (2000-2500 mA)
- a high-driving voltage, (up to 500V)
- The total current delivered to tissue does not exceed (1.2-1.5 mA)
(HVPC) High Voltage Pulsed Current
Graph

(HVPC) High Voltage Pulsed Current
Indications and Advantages
HVPC is particularly useful for:
- soft tissue wounds, (bedsores, ulcers, burns)
- Edema
- Pain conditions, (Ex. Muscle pain, etc.)
Advantages
- Deeper penetration of tissue
- risk of pain during application is minimal
- risk of skin damage is minor
Diadynamic Currents
(Dia-through)
(Dynamis-Force)
- Six types of current in which we can distinguish two components: direct current and alternating sinusoidal current
- first described and used in clinical practice in 1950 by Bernard
Diadynamic Currents
How are they delivered?
- These currents are delivered through anode and cathode as:
-
monophasic
- half-wave pulses
- full-wave pulses
-
monophasic
- rectified from 50 Hz alternating current
- Individual pulses have duration of 10 ms
Diadynamic Currents
Forms
- MF current
- DF current
- CP current
- LP current
- RS current
- MM current
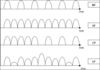
Diadynamic Currents
(DF) Diphase Fixe
- DF is the preferred current for pain modulation
- DF produces a vibrating, prickling sensation which subsides gradually as sensory accomodation occurs in response to the constant amplitude stimulation
- DF is especially recommended for pain conditions of sympathetic origin

Diadynamic Currents
(MF) Monophase Fixe
- MF produces a strong vibratory sensation and much slower sensory accomodation occurs because of the 10 ms delay between successive pulses
- More suitable to elicit muscle contraction and generally not used for isolated pain conditions

Diadynamic Currents
(CP) Courtes Periods
- CP combimes MF and DF currents, so that each one alternates at intervals of 1 second to prevent sensory accomodation
- CP is usually recommended for the treatment of pain that is associated with sprains, strains, and contustions

Diadynamics Currents
(LP) Longues Periods
- LP also combines the MF and DF current modes such that during 5 second periods, MF and DF occur together but out of phase, with DF being amplitude modulated. This is followed by 10 seconds of MF current.
- LP is recommended for providing longer-lasting pain relief in acute pain conditions
Diadynamic Currents
(RS) *Russian Stimulation* -not sure
(MM) -<em>not sure</em>
- RS and MM are generally used for muscle stimulation application

Diadynamic Currents
Graphs Extra

Diadynamic Currents
Effects/Influence of human body
- effect of analgesic: (DC, LP, CP)
- effect of congestion: (LP, CP, MF)
- muscle relaxation: (DF, LP, CP)
- muscle tension: (MF)
DF-LP-CP-MF
Trabert Current - Effects
(Ultra Reiz)
This current has:
- an analgesic effect
- a congestive effect
- Trabert Current causes muscle tremors

Trabert Current - Parameters & Application
(Ultra Reiz)
Parameters
- Pulse duration: 2ms
- Pulse interval: 5ms
- Frequency: 143 Hz
Application
- This current is commonly applied in the treatment of spine pain syndromes.
Kotz’ Current
Uses
Kotz’ current is used in:
- muscle atrophy following immobilization
- for muscle training
- for muscle stimulation
- to support strength training or muscle endurance training
- in order to improve metabolism and reduce muscle tension
Kotz’ Current
Effect and Application
- this gives the possibilty to set higher amplitude and achieve complete muscle contraction
- Medium frequency currents penetrate deeper into the tissue due to its partially capacitative nature.
- Continuous current with an average frequency causes constant muscle contraction. Constant contraction leads to impaired blood circulation and muscle pain. In order to achieve a therapeudic effect, there is need to apply modulation
Kotz’ Current
Parameters and Waveform
- Kotz’ Currents are based on a sin wave wth a frequency of 2.5kHz
- It is a bipolar current. Carrier frequency is modulated by a rectangular wave with a frequency adjustable in the range from 5Hz to 100Hz
- Rectangular wave form modulation indicates that the slopes of “packages” are as quick as the filling sin wave
(NMES) Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Definition and Goal of Treatment

- It is the application of electrical current to elicit a muscle contraction:
- two waveforms used, asymmetrical biphasic rectangular**, and **symmetrical biphasic rectangular waveforms
- Goal of treatment is to elicit a strong muscle contraction through stimulation of the alpha motor nerve
(NMES) Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Graph Description
- The rectangular wave
- fast-rising leading edge of the pulse
- flat plateau at peak rapid return to zero at the end

(NMES) Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Treatment
Neuromuscular electrostimulation is applied for treatment of:
- disuse athrophy
- muscle re-education and facilitation
- spasticity management
- orthotic substitution
- and to increase and maintain range of motion
(NMES) Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation
Waveforms

Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Muscle
How it works:
- the electrode configuration is usually monopolar with the active or treatment electrode positioned over the part of the denervated muscle that is the most excitable
- the inactive electrode is placed over a distant body part.

Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Muscle
Description of Electrodes
- size of inactive electrode is very large
- size of active electrode is very small (1-2 cm2)
- the usually used parameters are suggested by Gillert
Electrical Stimulation of Denervated Muscle
How is Effectiveness determined?
The effectiveness of the electrical stimulation of denervated muscle depends upon many factors:
- type of current
- duration of stimulus
- current amplitude
- type of contractions
- length and frequency of therapy sessions
Interference Current
Definition
- this is the current of medium frequency
- it arises as a result of interference of two alternating sinusoidal currents of medium frequency in the tissues, whose frequencies differ a little from each other
- Currents whose frequency is about 4000Hz is used: for example 3900Hz and 4000Hz or 4000Hz and 4100Hz
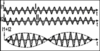
Interference Current
Effect on Tissues
Effect of Modulated Frequency on the Tissues:
- 0-10 Hz - induces muscle contractions
- 25-50 Hz - stimulates the muscle to spasm and improves peripheral circulation
- 50-100 Hz - produces analgesic effect and improves the nutritive processes of tissues
- 90-100 Hz - causes analgesia and reduces tension of the sympathetic nervous system
- 0-100 Hz - causes all these effects
>>> Interference is achieved by using 2 independent circuits, using two pairs of electrodes which are placed in such a way that interference occurs deep in the tissues in the area where the disease is located <<<
Interference Current
Adavantages
- weaker effects on the sensory receptors of the skin
- limited electrochemical effects on the tissues
- better penetration of this current into the tissues


