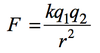Physics Formulas Flashcards
(61 cards)
Velocity Equation

Position Equation

No Time Equation

Net Force Equation

Centripetal Acceleration Equation

Torque Equation

Momentum Equation

Impulse Equation
J = Impulse

Kinetic Energy Equation

Potential Energy Equation
Ug = Gravitational Potential Energy

Work Equation
r = Radius or Distance

Power Equation (Mechanics)

Acceleration Equation
a = change in velocity / t = (vf - v0) / t
No Acceleration Equation
x = ½ (vf + v0)t
What is given during the horizontal motion of a projectile?
ax = 0
Constant Velocity
vfx = xx / t
What is given during the vertical motion of a projectile?
ay (g) = 10 m/s2
vfy = v0y + gt
xy = v0yt + ½gt2
Coeficient of static and kinetic friction Equation

The speed of an object moving in a circle
v = circumference/period
What is period?
Time it takes to make one revolution (T)
What is frequency?
Units?
The number of revolutions per unit time measured in hertz
What is the relationship between period and frequency?
T = 1 / f
Angular momentum formula
L = mvr
L = angular momentum
What is the lowest point in the swing of a pendulum called?
Equilibrium Position
Hooke’s Law
Finding the force of a spring
x = Stretched length of spring
k = Spring constant