Phospholipids and Membrane Proteins Flashcards
In the plasma membrane, lipid-protein interactions are:
non-covalent
proteins and lipids can often move in bilayer
The four major classes of phospholipids:
- Phosphoglycerides
- Sphingolipids
- Glycolipids
- Sterols
Phosphoglycerides:
- derived from 3-carbon glycerol backbone
- 2 fatty acid chains attached to backbone
- three major types
Sphingolipids:
- derived from sphingosine backbone
- sphingomyelin is major one
Glycolipids:
- often sphingosine backbone
- carbohydrate always on external face
Sterols:
- primarily cholesterol
What leads to the ability of lipids to assemble into a bilayer?
- the amphipathic structure of lipids
- polar head groups
- non-polar fatty acid chains
Function of lipid-bilayer:
- insulates the cell from the environment and organelles from the cytoplasm and from each other.
Amphipathic membrane lipids assemble spontaneously into:
- lipid bilayers and then into liposomes
- energetically favorable = maximizes hydrophobic interactions
Basic structure of phosphoglycerides:
- Two fatty acid chains attached to two of the three carbons of glycerol backbone.
- One fatty acid chain non-saturated, leads to kink that opposes dense packing and increases membrane fluidity.

What are the three common phosphoglycerides of the cell membrane:
- phosphatidyl-ethanolamine
- phosphatidyl-serine
- phosphatidyl-choline
What phosphoglyceride carries a net negative charge?
- phosphatidyl-serine
Basic structure and function of cholesterol in plasma membrane:
- Polar molecule with a rigid ring structure.
- Stiffens regions of membrane in its vicinity.
- Aliphatic regions keep phospholipid chains apart.

Glycolipids structure:
- Derived from sphingosine with sugars added rather than phosphate.
- Asymmetric – sugar on external face of plasma membrane only.
GM1 ganglioside used for entry of:
cholera toxin

Sphingosine structure:
- one fatty acid chain
- contains an amide

Cholesterol and sphingomyelin (SM) are primarily found in what types of membranes?
- plasma membranes
- very minimal content in internal membranes of organelles
Intracellular membranes (organelles) are primarily composed of what types of phospholipids?
- PT-ethanolamine and PT-choline
Glycolipids are primarily found in what types of membranes?
- plasma membrane and myelin
- little content in internal membranes
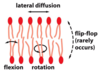
Is lipid positioning in the plasma membrane constant?
- No, they are very mobile.
- diffuse laterally
- flexion
- rotate
- occassionally flip-flop
Are plasma membrane lipids are symmetrically distributed between the internal and external faces?
- No.
The inner leaflet of the plasma membrane primarily consists of what two phospholipids?
- PT-serine
- PT-ethanolamine
The outer leaflet of the plasma membrane primarily consists of what three phospholipids?
- sphingolipids
- glycolipids
- PT-choline
Cholesterol distribution in the plasma membrane:
- roughly equal between leaflets





