Pharmacokinetics Flashcards
What is Euler’s number?
e = 2.718
This is a constant which describes exponential processes.
The variable increases or decreases at a rate that is proportional to it’s own magnitude.
What can Euler’s number be used to describe?
- compound interest
- probability theory
- radioactive decay
- redistribution and metabolism of drugs
- properties of biological APs
- charging and discharging of a capacitor
- bacterial growth
What is a tear-away function?
A variable increase in magnitude of a quantity
What is an asymptote?
WHen the curve gets ever closer to the axis but never meets it (eg radioactive decay or elimination of drug from the body).
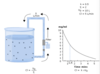
What is the shape of the end tidal N2 concentration against time during pre-oxygenation?
It is an exponential function.
To make the graphical representation easier, a natural logarithmic transformation applied to the variable that is plotted against time gives a straight line by compressing the concentration axis.
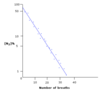
What are natural logarithms to the base of?
To base 2.718, or base e, because they deal with naturally occuring processes.
What happens if you plot N2% to the base e against time?
You get a straight line.
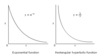
How can you tell the difference between an exponential graph and rectangular hyperbola?
- both asymptote the x-axis
- exponential curve meets the y-axis
- hyperbolic curve asymptotes the y-axis
- rectangular hyperbola is a section of a cone
- exponential function models naturally occurring processes
What does the graph of current vs time look like when charging a capacitor?
It looks like a drug elimination curve, because as charging proceeds less electrons are required to attempt to complete the charge and the current therefore falls
The charge vs time and the voltage vs time graphs would resemble wash-in curves.
What do natural exponential processes need to produce straight line graphs?
They need natural logarithmic transforms
What are the 3 constants that an exponential function can be described by?
- rate constant, k
- time constant τ (tau)
- half-life (t1/2)
What does the rate constant, k, describe in a decreasing exponential function?
The relationship between the rate of decrease and the magnitude of the variable.
In effect, mathematically, k is the ratio of the slope of the graph to it’s height.
You can work out the slope at any point and will find that the relationship of the slope to the height is constant.
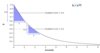
What are the units of the rate constant, k?
They’re the units of slope/units of height
ie m.sec-1/m or sec-1
In exponential processes that occur over time, the units of k are always sec-1.
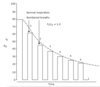
What is tau (τ), the time constant?
Can be described 4 ways:
- the time it would have taken for a negative exponential process to complete, were the initial rate of change to be maintained
- the time taken for the value of an exponential to fall to 37% of it’s previous value
- the time taken for the value of an exponential function change by a factor e1
- the reciprocal of the rate constant
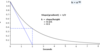
How many time constants will an exponential process be complete after?
3 (94.9% complete at this point)
What is the half-life?
The time required for the magnitude of the variable to fall to one half of it’s original value.
It must always be shorter time than that required to fall to 37% (the half life is always less than the τ )
What is the relationship between the constants in a decreasing exponential function (pharmacokinetics)?
τ = 1/k
k = 1/τ
t½ = τ x 0.693
What are the units of the rate constant?
Units of rate (eg per second)
What is drug clearance?
The volume of plasma that is cleared of drug in unit time
What are the units of drug clearance?
ml/kg/min and litres/min
How is drug clearance related to τ?
It is volume of distribution divided by τ
What is the volume of distribution?
A mathematical concept where a drug is evenly distributed through a hypothetical compartment.
When a drug does is delivered to a patient it results in a concentraion of that drug within the body. If it’s evenly distributed you get a virtual volume for that compartment (Vd) and a drug concentration in this volume.

How are the different rate constant for the passage of drugs into the outside (ie eliminated) labelled?
o is outside and the numbers refer to the compartment
eg k1o refers to the rate constant for passage of the drug from compartment 1 to the outside, ie elimination
If you gave a theoretical patient 100mg of propofol, and their initial Vd was 10L, what would the concentration of each ml be?
It would be 10mg/L or 10mcg/ml