Petechiae, Purpura and Vasculitis Flashcards
What are the main types of purpura?
1) Macular/non-palpable purpura (generally non-inflammatory)
2) palpable purpura (sign of vasculitis)
These are NON blanchable
What kind of purpura is this?

Petechiae (not blanchable)- small (less than 3mm) usually found in the ‘dependent’ areas of the body (legs when standing, back/butt when lying down in a hospital bed)
generally painless
What are the main causes of petechiae?
1) platelet related (low platelets or dysfunction)
2) non-platelet related (things that increase capillary fragility or allow them to leak)- sun damage can do this!!
*Petechiae are usually a sign of platelet dysfunction, and not a coagulation defect*
What are ecchymoses?
large (5+mm) non-palpable purpura that may or may not be painful or tender
While most petechiae are platelet related, ecchymoses are more likely to reflect what?
abnormalities in coagulation, rather than platelet defects (can result from hypercoag- OR hypocaguable states)

What are some causes of purpura?
-thrombocytopenia or abnormal platelet function + infection/inflammation/trauma
poor dermal support + trauma (actinic damage, amyloid, Ehler’s Danlos, scurvy)
Anticoagulant stage + trauma (DIC, vitamin K deficiency)
What is this?

Solar purpura- chronic sun damage can cause bleeding
What is happening here?

thrombocytopenia + trauma (linear purpura (=vibex))
What are the main causes of petechiae?
ABNORMAL PLATELET FUNCTION
- DIC and infection
- low platlets due to idiopathic, drug-induced, or autoimmune reasons
- inflammatory skin diseases
What are the main causes of ecchymoses?
COAGULATION DEFECTS
- DIC and infection
- trauma
- weak skin
- Waldenstrome hypergammaglobinemia
What is happening here?

Hypergammaglobulinemic Purpura of Waldenstrom
What is this?

Henoch-Schonlein purpura (these are palpable- remember, unlike bland petechiae/ecchymosis, palpable purpura is assoicated with inflammation in blood vessels
due to IgA deposition in vascular walls

How are vasculites categorized?
Primarily based on the size of the blood vessel involved
What are some diseases associated with small vessel vasculitis?
- Henoch Schonleion purpura (IgA vasculitis)
- Infections, drug reactions, maligancies and autoimmune disease

What is this?

Small vessel vasculitis
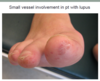
What is this?

Meningococcemia (acute)
What is this?

Leukocytoclastic vasculitis


What are some mixed size (small and medium vessel) vasculites?
ANCA assoicated vasculites (Churg-Strauss, Microscopic polyangiitis, Wegener’s granulomatosis)
-Cyroglobulinemic vasculitis
What is this?

Churg-Strauss vasculitis
What is a common medium vessel vasculitis?
Polyarteritis nodosa
What are some common large vessel vasculites?
- giant cell arteritis
- Takayasu arteritis
- Behcet’s
Skin lesions depend on the size of the blood vessel involved. How do small vessel vasculities present?
These present as palpable purpura or blisters and rarely hives









