pelvis A Flashcards
What are the 4 portals for portal hyerptension
Left/right gastric vv , superior mesenteric v, inferior mesenteric v, paraumbilical v

Where does the left/right gastric vv drain back to? and what organ does it effect if there is portal hypertension? (verices)
Esophageal v, to the Azygos to the SVC. Esophagus
Where does the superior mesenteric v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension (verices)
Colic vv, tp the ascending lumbar v to the SVC. colon
Where does the inferior mesenteric v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension? (verices)
Superior rectal v, middle/inferior rectal vv, IVC. rectum
Where does the paraumbilical v drain back to? and what organ does it effect in portal hypertension? (verices)
periumbilical vv, inferior epigastric v, IVC. umbilicus
Differences in male and female pelvis. MALE
Heavy bones, heart shaped pelvic inlet conical pelvic cavity ant/post oval pelvic outlet narrow (90 degrees) infrapubic angle narrow and deep iliac fossa
Differences in male and female pelvis. FEMALE
Light bones oval pelvic inlet cylindrical pelvic cavity circular pelvic outlet wide (120 degrees) indrapubic angle wide and shallow iliac fossa
what is Levator Ani muscle
puborectalis, m puboococcygeus m iliococcygeus m. floor of the pelvis with pelvic diaphram. same in both sexes except females with have another hiatus for vagina

what is pelvic diaphragm?
levator ani mm + coccygeus m. floor of the pelvis.

what is the pelvic outlet? what perineum triangles are in the pelvic outlet
the inferior hole of the pelvis. urogenital triangle and anal triangle

what is in the urogenital, and anal triangle? which one is more superior?
Perineum. urogenital is more superior.

what makes up the anal triangle?
sacrotuberous ligaments, sacrum, and imaginary line between the two triangles

what makes up the urogenital triangle?
ischiopubic rami and imaginary line

which anal sphincter is voluntary?
external

which anal schinter is controled by autonomics?
Internal anal sphincter

which autonomics is the internal anal sphincter innervated by?
pelvic and sacral sphlanchnic
what nerve is the external anal sphincter innervated by?
pudendal nerves. somatic
how many transverse folds do we have in the rectum? what do they do?
2 on the left 1 on the right
gives rise to the curvature of the pelvis
ischioanal fossa is filled with what?
it is a fat filled space

what muscle is the internal pudendal vasculature and pudendal nerve closely associated with?
obturator internus muscle

what is the round ligament anaolgous to in males?
inferior scrotal ligament. a remnant of the gubernaculum. it is a content of the inguinal canal in females but is usally obliterated.

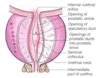
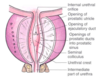
bladder, uterine and rectum… which ones are anterior middle and posterior?
anterior: bladder
posterior: rectum
middle: uterus
Deep pouch is surounded by?
superior UG fascia. and inferior UG fascia aka perineal membrane.

what is the superfical pouch surounded by?
a fascia of perineum and the perineum membrane
what is the the crus of the clitoris or the penis covered by? point out the crus of the clitoris in the picture
ischiocavernosus muscle

what is the bulb of the clitoris covered by? and point out bulb of clitoris in the picture.
bulbospongius muscle

is the rectum intra, secondarily retro, or retro peritoneal?
retroperitoneal?
which side of the uterus are the eggs dispersed or emmineated
lateral side out towards the fimbrae

what is the path of a sperm trying to get to an egg?
up the uterine tube towards the ampulaie

what is the path of an egg trying to get fertilized?
ampulae isthmus and then the body of the uterus

usually the female pelvis is… retroverted or anteverted, anteflexed or retroflexed?
anteverted and anteflexed. anterior trajectory covering up the bladder

if someone tries a coathanger abortion what is one of the worst things that can happen?
puncture of the posterior fornix, because of the pouch of douglas,(the piercing of the peritenal cavity.
what does the ovarian ligament do?
teathers the internal pole of the ovary to the uterus

what does the suspensory ligament do?
teathers the external pole of the uterus to the pelvis. really helps suport the uterus superior to the vagina.

what makes up the broad ligament?
Mesosalpinx + Mesovarium + Mesometrium

what does the suspensory ligament carry with it?
the ovarian artery and vein
where do the ovarian arteries emerge from the aorta?
L2
what part of the broad ligament is in closest association to the ovary?
mesovarium

what part of the broad ligament is just inferior to the uterine tube?
mesosalpinx

what is the part of the broad ligament that is not in closes association to the ovary or the uterine tube but every thing else?
mesometrium

what is the majority of the broad ligament made up of?
mesometrium

what is in the superficial pouch in males?
crus of penis and bulb of penis

what is the crus of the penis directly adhered to?
ischiopubic rami

what is the bulb of the penis associated with?
the urethrea

what is the crus of the penis covered by?
ischiocavernosis muscle
what is the bulb of the penis covered by?
bulbospongiosis muscle
what is the supericial layer of the pelvis called in males?
Colle’s fascia important in extravigation of urine
what weeks in the womb are sexes undifferential?
4-7. can see the genital tubercle and urogenital folds
what weeks in the womb are sexes can be distinguishable
9th week
what week in the womb is there complete differentiation?
week 12
what is the sequence of name changes the pudendal nerve has once it re enters the lesser sciatic foramen? point them out on the picture
inferior rectal nerve, perineal nerve, posterior labial/scrotal nerve, and dorsal clitoral/penial nerve

the pudendal nerve exits the _______ and re enters the ______
exits greater sciatic foramen
re enters the lesser sciatic foramen

what vertebrae does the pudendal nerve get contribution from?
S2-S4
label the arteries and veins.
Pudendal nerve
internal pudendal A/V
inferior rectal VAN
Perineal VAN
Posterior Labial/scrotal VAN
Dorsal Clitoral/penial VAN

answers on pelvis A slide 25

label corpus spongiosum and corpus cavernosium

what was corpus cavernosum dervived from? and what was corpus spongiosum dervied from?
corpus cavernosum- crus of the penis/clitoris
corpus spongiosum- bulb of the penis/clitoris
what is the spongy part of the urethra covered by?
corpus spongiosum and then tunica albuginea of corpus spongiosum

deep penile fascia is also known as what?
Bucks fascia
label this diagram

label it

what does the ejaculatory duct receive secretions from?
seminal vesicle (its own fluid) and ampulla of ductus deferens (sperm)